|
جواب |
رسائل 1 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
El mismo dia de JUDAS TADEO, Y EL MISMO DIA DEL EXPERIMENTO FILADELFIA
Statue of Liberty
The height of the Statue of Liberty is 111′-1″ from bottom of foot to top of head. The 7 rays on the crown and the 11 points of the base star echo the proportions of the Great Pyramid’s 7:11 height to base proportion. The superb book Talisman by Graham Hancock and Robert Bauval convincingly shows this goddess is actually the Egyptian Isis.

Image courtesy Elcobbola under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.
http://www.viewzone.com/onstott66.html
Experimento Filadelfia
De Wikipedia, la enciclopedia libre
El Experimento Filadelfia, también llamado Proyecto Arcoíris, es el nombre que recibió un supuesto experimento secreto llevado a cabo por la marina estadounidense en los astilleros navales de Filadelfia, en el estado de Pensilvania, durante o antes del 28 de octubre de 1943. En el cual el destructor escolta de la Armada USS Eldridge al parecer fue invisibilizado (o "encubierto") electrónicamente contra los dispositivos enemigos. La marina de Estados Unidos comenta que ha buscado archivos que se refieran a este hecho y no los ha encontrado, ni ha encontrado evidencia de que se intentara.[cita requerida]
El incidente fue reportado repetidamente como una farsa.[1] [2] [3]
A finales de los años 30, el ingeniero eléctrico Nikola Tesla, afirmó[cita requerida] haber completado una teoría dinámica de la gravedad, que básicamente explica la gravedad como una mezcla de ondas electromagnéticas longitudinales y transversales. Estos razonamientos calaron hondo en un grupo de trabajo que experimentaba con los campos electromagnéticos en la Universidad de Chicago[cita requerida], donde se estaban iniciando las investigaciones sobre la posibilidad de la invisibilidad a través del uso de campos eléctricos y magnéticos. Este proyecto se habría trasladado en 1939 al Instituto de Estudios Avanzados de la Universidad de Princeton[cita requerida].
En un momento determinado, se afirmó haber conseguido la invisibilidad de pequeños objetos, con lo que se presentó al gobierno de los Estados Unidos.[cita requerida] Por lo que en el plano militar vieron el potencial de esta nueva tecnología y decidieron sufragar el curso de las investigaciones a fin de direccionarlas en el sentido que les convenía: su aplicación a la industria bélica. El USS Eldridge, es modificado para transportar toneladas de equipamiento electrónico, entre el que se incluirían dos enormes generadores de 75 kV cada uno, montados en el lugar que debería ocupar la torreta de cañones de proa, y que distribuían su potencia a través de cuatro bobinas montadas en cubierta. Tres transmisores RF de 2 megavatios cada uno, 3.000 tubos amplificadores 6L6 (empleados para canalizar los campos de las bobinas de los dos generadores), circuitos de sincronización y modulación... fueron empleados para generar campos electromagnéticos masivos que, correctamente configurados, serían capaces de curvar las ondas de luz y de radios alrededor del buque, haciéndolo invisible.
Las pruebas habrían empezado el verano de 1943, y hasta cierto punto tuvieron éxito al principio. Una prueba, el 22 de julio de 1943, volvió al USS Eldridge (DE-173) casi totalmente invisible, con algunos testigos reportando una "niebla verdosa" —sin embargo, algunos miembros de la tripulación se quejaron de náuseas posteriormente. En ese momento, el experimento fue alterado a petición de la Marina, con el objetivo de hacer al navío invisible a los radares únicamente.[cita requerida]
El equipo fue recalibrado y el experimento se llevó a cabo el 28 de octubre. Esta vez, el Eldridge no sólo se volvió totalmente invisible a la vista, sino que de hecho desapareció del área en un relámpago azul. Al mismo tiempo, la base naval estadounidense en Norfolk, Virginia, a 600 km de distancia, un tripulante en sus costas declaró haber visto al Eldridge durante 15 minutos, al final de los cuales desapareció, para volver a aparecer en Filadelfia, en sus coordenadas originales —supuestamente un caso accidental de teletransportación.[cita requerida]
Según el relato de Carlos Allende[cita requerida], los efectos fisiológicos en la tripulación fueron profundos. Mareos muy violentos, personal que desapareció por completo, otros que simplemente se volvieron locos o padecieron esquizofrenia severa, y lo más terrorífico fue el hallazgo de cinco miembros de la tripulación fundidos completamente con la estructura de metal de la proa del buque y otros tantos sufrieron desmaterializaciones de algunas partes de sus cuerpos. Supuestamente, los oficiales navales horrorizados cancelaron el experimento inmediatamente. Los supervivientes nunca fueron los mismos, y permanecieron en una suerte de amnesia total.[cita requerida]
Publicación de la historia[editar]
Los detalles de este experimento fueron revelados indirectamente.
Carl Allen/Carlos Allende[editar]
En 1955, K. Jessup, un astrónomo amateur, antes investigador postuniversitario, publicó The Case for the UFO, un examen del fenómeno del OVNI (UFO en inglés) en el que teorizaba los medios de propulsión que un platillo volador del estilo de un OVNI podría utilizar. Jessup especuló que la anti-gravedad o el electromagnetismo pueden ser responsables del comportamiento de vuelo observado en los OVNIs, y lamentó, tanto en el libro como en la publicidad del tour que siguió, que la investigación de los vuelos espaciales se concentrara en el área de los cohetes, y que se pusiera poca atención a otros medios teóricos de vuelo, que él consideraba rendirían más frutos al final.
El 13 de enero de 1956, Jessup recibió una carta de un hombre que se identificaba como "Carlos Miguel Allende". En ella, Allende informaba a Jessup del Experimento Filadelfia, aludiendo a artículos periodísticos de la época de fuentes dudosas como "prueba". Allende también decía haber sido testigo de la desaparición y reaparición del Eldridge mientras trabajaba en un barco mercante que se encontraba cerca, el SS Andrew Furuseth. Incluso mencionó los nombres de otros tripulantes del Andrew Furuseth, y decía saber del destino de algunos miembros de la tripulación del Eldridge tras el experimento, incluyendo uno que dice haber visto "desaparecer" durante una pelea en un bar. Jessup le respondió a Allende con una postal, pidiendo más evidencia y corroboración de la historia, tales como fechas y detalles específicos de la misma. La respuesta llegó varios meses más tarde; sin embargo, esta vez el hombre se identificaba como "Carl M. Allen". Allen dijo que no podría proveer los detalles pedidos por Jessup, pero insinuaba que podrían ser obtenidos a través de la hipnosis. Jessup decidió cortar la correspondencia.
EXPERIMENTO FILADELFIA=22 DE JULIO=DIA DE MARIA LA MAGDALENA
EXPERIMENTO FILADELFIA=22 DE JULIO=DIA DE MARIA LA MAGDALENA
EXPERIMENTO FILADELFIA=22 DE JULIO=DIA DE MARIA LA MAGDALENA
|
|
|
|
GENESIS
3:14 Y Jehová Dios dijo a la serpiente: Por cuanto esto hiciste, maldita serás entre todas las bestias y entre todos los animales del campo; sobre tu pecho andarás, y polvo comerás todos los días de tu vida.
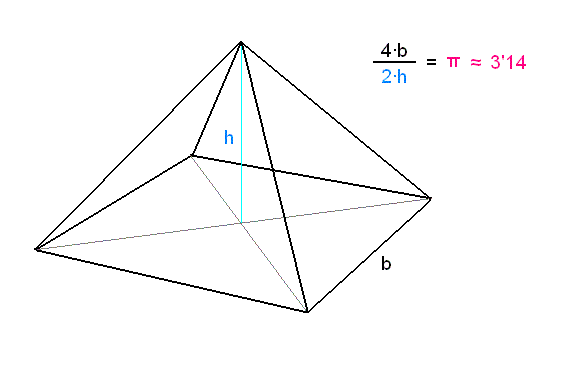 3:15 Y pondré enemistad entre ti y la mujer, y entre tu simiente y la simiente suya; ésta te herirá en la cabeza, y tú le herirás en el calcañar. 3:16 A la mujer dijo: Multiplicaré en gran manera los dolores en tus preñeces; con dolor darás a luz los hijos; y tu deseo será para tu marido, y él se enseñoreará de ti. 3:17 Y al hombre dijo: Por cuanto obedeciste a la voz de tu mujer, y comiste del árbol de que te mandé diciendo: No comerás de él; maldita será la tierra por tu causa; con dolor comerás de ella todos los días de tu vida. 3:18 Espinos y cardos te producirá, y comerás plantas del campo. 3:19 Con el sudor de tu rostro comerás el pan hasta que vuelvas a la tierra, porque de ella fuiste tomado; pues polvo eres, y al polvo volverás. 3:20 Y llamó Adán el nombre de su mujer, Eva, por cuanto ella era madre de todos los vivientes. 3:21 Y Jehová Dios hizo al hombre y a su mujer túnicas de pieles, y los vistió. 3:22 Y dijo Jehová Dios: He aquí el hombre es como uno de nosotros, sabiendo el bien y el mal; ahora, pues, que no alargue su mano, y tome también del árbol de la vida, y coma, y viva para siempre. 3:23 Y lo sacó Jehová del huerto del Edén, para que labrase la tierra de que fue tomado. 3:24 Echó, pues, fuera al hombre, y puso al oriente del huerto de Edén querubines, y una espada encendida que se revolvía por todos lados, para guardar el camino del árbol de la vida. 3:15 Y pondré enemistad entre ti y la mujer, y entre tu simiente y la simiente suya; ésta te herirá en la cabeza, y tú le herirás en el calcañar. 3:16 A la mujer dijo: Multiplicaré en gran manera los dolores en tus preñeces; con dolor darás a luz los hijos; y tu deseo será para tu marido, y él se enseñoreará de ti. 3:17 Y al hombre dijo: Por cuanto obedeciste a la voz de tu mujer, y comiste del árbol de que te mandé diciendo: No comerás de él; maldita será la tierra por tu causa; con dolor comerás de ella todos los días de tu vida. 3:18 Espinos y cardos te producirá, y comerás plantas del campo. 3:19 Con el sudor de tu rostro comerás el pan hasta que vuelvas a la tierra, porque de ella fuiste tomado; pues polvo eres, y al polvo volverás. 3:20 Y llamó Adán el nombre de su mujer, Eva, por cuanto ella era madre de todos los vivientes. 3:21 Y Jehová Dios hizo al hombre y a su mujer túnicas de pieles, y los vistió. 3:22 Y dijo Jehová Dios: He aquí el hombre es como uno de nosotros, sabiendo el bien y el mal; ahora, pues, que no alargue su mano, y tome también del árbol de la vida, y coma, y viva para siempre. 3:23 Y lo sacó Jehová del huerto del Edén, para que labrase la tierra de que fue tomado. 3:24 Echó, pues, fuera al hombre, y puso al oriente del huerto de Edén querubines, y una espada encendida que se revolvía por todos lados, para guardar el camino del árbol de la vida.JUAN 20
Juan 20
1. El primer día de la semana, María Magdalena fue de mañana, siendo aún oscuro, al sepulcro; y vio quitada la piedra del sepulcro.
2. Entonces corrió, y fue a Simón Pedro y al otro discípulo, aquel al que amaba Jesús, y les dijo: Se han llevado del sepulcro al Señor, y no sabemos dónde le han puesto.
3. Y salieron Pedro y el otro discípulo, y fueron al sepulcro.
4. Corrían los dos juntos; pero el otro discípulo corrió más aprisa que Pedro, y llegó primero al sepulcro.
5. Y bajándose a mirar, vio los lienzos puestos allí, pero no entró.
6. Luego llegó Simón Pedro tras él, y entró en el sepulcro, y vio los lienzos puestos allí,
7. y el sudario, que había estado sobre la cabeza de Jesús, no puesto con los lienzos, sino enrollado en un lugar aparte.
8. Entonces entró también el otro discípulo, que había venido primero al sepulcro; y vio, y creyó.
9. Porque aún no habían entendido la Escritura, que era necesario que él resucitase de los muertos.
10. Y volvieron los discípulos a los suyos.
11. Pero María estaba fuera llorando junto al sepulcro; y mientras lloraba, se inclinó para mirar dentro del sepulcro;
12. y vio a dos ángeles con vestiduras blancas, que estaban sentados el uno a la cabecera, y el otro a los pies, donde el cuerpo de Jesús había sido puesto. (LOS MISMOS ANGELES DE GENESIS 3:24 QUE CUSTODIABAN EL INGRESO AL ARBOL DE LA VIDA)
13. Y le dijeron: Mujer, ¿por qué lloras? Les dijo: Porque se han llevado a mi Señor, y no sé dónde le han puesto.
14. Cuando había dicho esto, se volvió, y vio a Jesús que estaba allí; mas no sabía que era Jesús.
15. Jesús le dijo: Mujer, ¿por qué lloras? ¿A quién buscas? Ella, pensando que era el hortelano, le dijo: Señor, si tú lo has llevado, dime dónde lo has puesto, y yo lo llevaré.
16. Jesús le dijo: ¡María! Volviéndose ella, le dijo: ¡Raboni! (que quiere decir, Maestro).
17. Jesús le dijo: No me toques, porque aún no he subido a mi Padre; mas ve a mis hermanos, y diles: Subo a mi Padre y a vuestro Padre, a mi Dios y a vuestro Dios.
18. Fue entonces María Magdalena para dar a los discípulos las nuevas de que había visto al Señor, y que él le había dicho estas cosas.
|
|
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 70 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 71 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 72 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
 the Apple
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 73 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 74 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 75 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 76 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 77 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 78 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 79 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 80 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 81 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
ISLA SAN GIORGIO (VENECIA)=GEORGE LEMAITRE
GEMATRIA EN INGLES DE SEED=33
GEMATRIA EN INGLES DE GATE=33
SARA (CE-SAREA DE FILIPO)=PARALELO 33
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 82 من 84 في الفقرة |
|

Jordan River (Utah)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Jordan River, in the state of Utah, United States, is a river about 51 miles (82 km) long. Regulated by pumps at its headwaters at Utah Lake, it flows northward through the Salt Lake Valley and empties into the Great Salt Lake. Four of Utah's six largest cities border the river: Salt Lake City, West Valley City, West Jordan, and Sandy. More than a million people live in the Jordan Subbasin, part of the Jordan River watershed that lies within Salt Lake and Utah counties. During the Pleistocene, the area was part of Lake Bonneville.
Members of the Desert Archaic Culture were the earliest known inhabitants of the region; an archaeological site found along the river dates back 3,000 years. Mormon pioneers led by Brigham Young were the first European American settlers, arriving in July 1847 and establishing farms and settlements along the river and its tributaries. The growing population, needing water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use in an arid climate, dug ditches and canals, built dams, and installed pumps to create a highly regulated river.
Although the Jordan was originally a cold-water fishery with 13 native species, including Bonneville cutthroat trout, it has become a warm-water fishery where the common carp is most abundant. It was heavily polluted for many years by raw sewage, agricultural runoff, and mining wastes. In the 1960s, sewage treatment removed many pollutants. In the 21st century, pollution is further limited by the Clean Water Act, and, in some cases, the Superfund program. Once the home of bighorn sheep and beaver, the contemporary river is frequented by raccoons, red foxes, and domestic pets. It is an important avian resource, as are the Great Salt Lake and Utah Lake, visited by more than 200 bird species.
Big Cottonwood, Little Cottonwood, Red Butte, Mill, Parley's, and City creeks, as well as smaller streams like Willow Creek at Draper, Utah, flow through the sub-basin. The Jordan River Parkway along the river includes natural areas, botanical gardens, golf courses, and a 40-mile (64 km) bicycle and pedestrian trail, completed in 2017.[6]
The Jordan River is Utah Lake's only outflow. It originates at the northern end of the lake between the cities of Lehi and Saratoga Springs. It then meanders north through the north end of Utah Valley for approximately 8 miles (13 km) until it passes through a gorge in the Traverse Mountains, known as the Jordan Narrows. The Utah National Guard base at Camp Williams lies on the western side of the river through much of the Jordan Narrows.[7][8] The Turner Dam, located 41.8 miles (67.3 km) from the river's mouth (or at river mile 41.8) and within the boundaries of the Jordan Narrows, is the first of two dams of the Jordan River. Turner Dam diverts the water to the right or easterly into the East Jordan Canal and to the left or westerly toward the Utah and Salt Lake Canal. Two pumping stations situated next to Turner Dam divert water to the west into the Provo Reservoir Canal, Utah Lake Distribution Canal, and Jacob-Welby Canal. The Provo Reservoir Canal runs north through Salt Lake County, Jacob-Welby runs south through Utah County. The Utah Lake Distribution Canal runs both north and south, eventually leading back into Utah Lake.[9] Outside the narrows, the river reaches the second dam, known as Joint Dam, which is 39.9 miles (64.2 km) from the river's mouth. Joint Dam diverts water to the east for the Jordan and Salt Lake City Canal and to the west for the South Jordan Canal.[10][11][12]
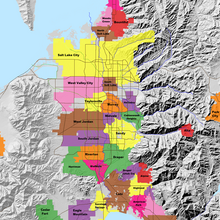
Map of the Salt Lake Valley
The river then flows through the middle of the Salt Lake Valley, initially moving through the city of Bluffdale and then forming the border between the cities of Riverton and Draper.[7] The river then enters the city of South Jordan where it merges with Midas Creek from the west. Upon leaving South Jordan, the river forms the border between the cities of West Jordan on the west and Sandy and Midvale on the east. From the west, Bingham Creek enters West Jordan. Dry Creek, an eastern tributary, combines with the main river in Sandy. The river then forms the border between the cities of Taylorsville and West Valley City on the west and Murray and South Salt Lake on the east. The river flows underneath Interstate 215 in Murray. Little and Big Cottonwood Creeks enter from the east in Murray, 21.7 miles (34.9 km) and 20.6 miles (33.2 km) from the mouth respectively. Mill Creek enters on the east in South Salt Lake, 17.3 miles (27.8 km) from the mouth. The river runs through the middle of Salt Lake City, where the river travels underneath Interstate 80 a mile west of downtown Salt Lake City and again underneath Interstate 215 in the northern portion of Salt Lake City. Interstate 15 parallels the river's eastern flank throughout Salt Lake County. At 16 miles (26 km) from the mouth, the river enters the Surplus Canal channel. The Jordan River physically diverts from the Surplus Canal through four gates and heads north with the Surplus Canal heading northwest. Parley's, Emigration, and Red Butte Creeks converge from the east through an underground pipe, 14.2 miles (22.9 km) from the mouth.[7] City Creek also enters via an underground pipe, 11.5 miles (18.5 km) from the river's mouth. The length of the river and the elevation of its mouth varies year to year depending on the fluctuations of the Great Salt Lake caused by weather conditions. The lake has an average elevation of 4,200 feet (1,300 m) which can deviate by 10 feet (3.0 m).[3] The Jordan River then continues for 9 to 12 miles (14 to 19 km) with Salt Lake County on the west and North Salt Lake and Davis County on the east until it empties into the Great Salt Lake.[7][8][11]
Discharge[edit]
The United States Geological Survey maintains a stream gauge in Salt Lake City that shows annual runoff from the period 1980–2003 is just over 150,000 acre-feet (190,000,000 m3) per year or 100 percent of the total 800,000 acre-feet (990,000,000 m3) of water entering the Jordan River from all sources. The Surplus Canal carries almost 60 percent of the water into the Great Salt Lake, with various irrigation canals responsible for the rest. The amount of water entering the Jordan River from Utah Lake is just over 400,000 acre-feet (490,000,000 m3) per year. Inflow from the 11 largest streams feeding the Jordan River, sewage treatment plants, and groundwater each account for approximately 15 percent of water entering the river.[13]
Watershed[edit]
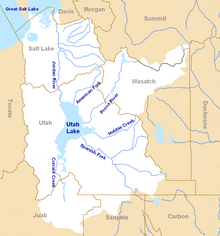
Map of the entire Jordan River Basin
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 83 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
|
جواب |
رسائل 84 من 84 في الفقرة |
|
|
|
 أول أول
 سابق
70 a 84 de 84
لاحق سابق
70 a 84 de 84
لاحق
 آخر
آخر

|

