|
|
General: FUTURO CALENDARIO EN CHILE EN FUNCION AL 25 DE JULIO, DIA DE SANTIAGO?
Elegir otro panel de mensajes |
|
|
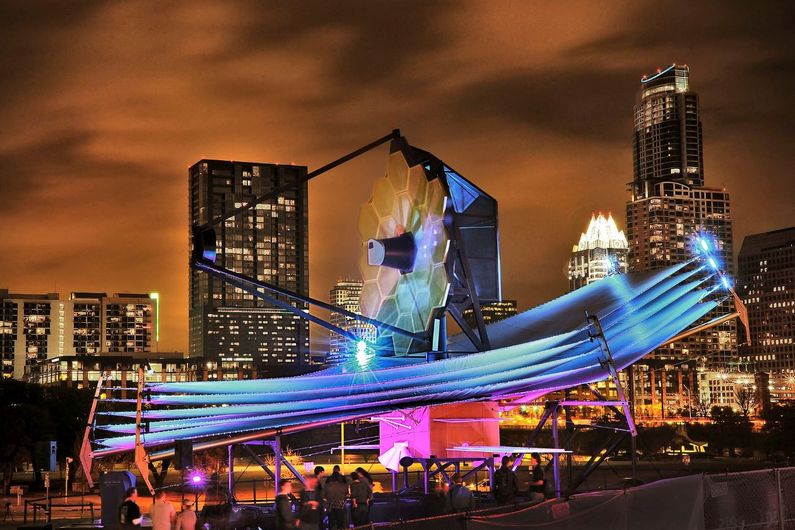
The James Webb telescope: part alien life detector, part time machine
In the lead-up to the launch of the James Webb telescope, we look at the scientific objectives of the most powerful space observatory ever sent into orbit.
Are we alone in the universe? What did the first galaxies formed after the Big Bang look like? How did the planets in our solar system emerge? The James Webb telescope hopes to find answers to these existential questions.
Set to launch on December 22, the James Webb is the product of the combined scientific prowess of NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) – and by extension, Université de Montréal (UdeM). The CSA contributed a scientific instrument and a guidance sensor to the massive observatory and René Doyon, Director of UdeM’s Institute for Research on Exoplanets (iREx) and a professor in the Physics Department, is the principal investigator on the Canadian scientific team.
Together, the components supplied by the CSA, NASA and the ESA form the most complex, accurate and powerful space observatory ever built, one that promises revolutionary discoveries in astronomy.
The unparalleled power of the observatory will help scientists throughout the world scrutinize the distant reaches of the universe to learn more about the composition and inhabitability of exoplanets and study the life cycle of stars.
Exploring new worlds in search of life
The James Webb Telescope is the successor to the Hubble space telescope but is more precise and efficient because of the size of its mirror, the range of light it can detect and its location.
These attributes will enable the Webb to study the planets in our solar system and other planetary systems in unprecedented detail. Moreover, the scientific instrument developed by Doyon’s team is designed to analyze many types of celestial bodies, including the atmospheric composition of distant exoplanets.
“What we’re looking for, our holy grail, are ‘biosignatures,’ that is, signs of extraterrestrial life,” explained iREx coordinator Nathalie Ouellette, an astrophysicist who does communications for the James Webb.
She hastened to add that we shouldn’t imagine these signs of life the way they are depicted in science fiction films: “We’re talking about finding signs of biological activity or the signature of certain molecules that we have identified as essential to life, such as oxygen, water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane and ozone. Based on the presence of such molecules, particularly in certain combinations, we may be able to determine that conditions are conducive to the development of life when we explore an exoplanet using the telescope.”
Casting light on the dawn of the universe
Telescopes are also time machines of a sort. “Looking into space is like looking into the past,” said Ouellette. “Light waves travel so fast that, to the naked eye, they seem to flash instantly from one point to another. In space, however, the distances are so vast that the time it takes light to travel is perceptible.”
That makes the Webb a marvellous time machine. It will be able to see back in time to 200 million years after the Big Bang, something that has never been done before. “With the Hubble, we could go to 500 million years after the Big Bang, so now we’re going 300 million years further,” noted Ouellette. “That’s remarkable, considering that the beginning of the universe was a tumultuous period. Galaxies were colliding and stars were forming at a rapid pace.”
“Tell me where you come from and I’ll tell you who you are”
The Webb will thus improve our understanding of the development of the first luminous objects (galaxies) over time. Ouellette believes the telescope will also provide insight into the creation of our own solar system.
“We still have many questions about the origins of life in our solar system. We don’t know exactly how we came to be on Earth and how the planets were formed,” Ouellette pointed out. “By studying other systems, stars and planets at various stages of development, we hope to be able to trace our own history and understand ourselves better.”
That is the ultimate goal of the James Webb: to revolutionize our understanding of the universe and, above all, to place the Earth, in all its fragility and uniqueness, in a broader context.
https://nouvelles.umontreal.ca/en/article/2021/12/09/the-james-webb-telescope-part-alien-life-detector-part-time-machine/ |
|
|
|
|
MONDAY JULY 16TH ALAMOGORDO
SUNDAY JULY 22TH=MARY MAGDALENE S DAY
|
|
|
|
|
Arthur James Balfour, I conde de Balfour, KG, OM, PC (25 de julio de 1848-19 de marzo de 1930) fue un político, aristócrata y estadista británico que se convirtió en el trigésimo tercer primer ministro de ese país.
|
|
|
|
|
Año Nuevo Maya
Año Nuevo Maya
Si amas la cultura, la tradición, las aventuras extremas y planeas pasar unas vacaciones inolvidables, te invitamos a celebrar el Año Nuevo Maya en la Riviera. Pero, si piensas que tendrás que esperar a que finalice el año, tenemos buenas noticias para ti: esta celebración milenaria ocurre en julio y no tendrás que esperar tanto, al contrario de la celebración mundial de Finde Año. A continuación, te contaremos la historia y orígenes de esta tradición y por qué no puedes dejar de vivirla. ¿Estás listo?
¿Año nuevo en Julio?
Es bien conocido que la cultura maya era ávida conocedora de la astronomía y de manera muy disciplinada seguían el movimiento de los astros para calendarizar y tipificar la importancia de los eventos que ocurrían en la tierra, en total sincronía con lo que ocurría en el cielo.
De acuerdo con el calendario maya “Haab” que sigue puntualmente el ciclo de la tierra en relación al sol, los astrónomos mayas determinaron que para ellos, el ciclo del año no iniciaba en enero, a diferencia del calendario gregoriano que rige nuestros ciclos y que heredamos de la cultura romana; los mayas medían el tiempo calculando hasta 18 ciclos vinculados por los movimientos de las principales luminarias de nuestro sistema (Luna y Sol), así como por los tránsitos planetarios de Venus y la ubicación de constelaciones como las Pléyades.
De acuerdo a este cálculo, el 26 de julio de cada año, daba inicio a un nuevo ciclo y a una nueva personalidad que caracterizaba al nuevo año y que era identificado con su propio glifo.
Pero, aunque el 26 es un día súper especial para esta ancestral cultura, el día 25 (El Día Fuera Del Tiempo) era incluso más importante porque en esta fecha los mayas acostumbraban a dar las gracias y tomarse un tiempo para reflexionar sobre las ganancias, logros y sobre todo, las lecciones que se aprendieron a los largo del ciclo anterior.
|
|
|
|
|
Parroquia Santa María Magdalena
|
|
|
|
|
 Pirámide Chichén Itzá Pirámide Chichén Itzá
El 26 de julio en el calendario Gregoriano coincide con la celebración del Año Nuevo Maya, que se extiende hasta el día 24 de julio del siguiente año. Pero, ¿qué sucede con el 25 de julio? Éste es el llamado "Día fuera del Tiempo".
Para ellos, el tiempo de la tierra está en sintonía con las frecuencias del universo. Por eso, un año dura lo que para nosotros serían 13 meses de 28 días; exactamente el tiempo que tarda la tierra en dar un giro completo al sol, de acuerdo a los ciclos lunares (por eso un año en el calendario maya equivale a 13 lunas completas). Pero, si cuentas bien verás que 13 meses de 28 días dan un resultado de 364, dejando uno como "el día perdido".
Ese día, el sol se sincroniza con la estrella más brillante del cielo (Sirio) y empieza una revolución solar de la tierra. Sirio representa la intuición, el sol secreto; por eso, ese día todas las energías del año se reúnen. Para los mayas esto era muy especial, y por eso lo consideraban un momento óptimo para preparar el alma, purificar el espíritu, reflexionar y meditar antes de comenzar un nuevo ciclo. Justamente por los rituales de limpieza y sanación con la Madre Tierra, el Día Fuera del Tiempo también se conoce como "día verde".
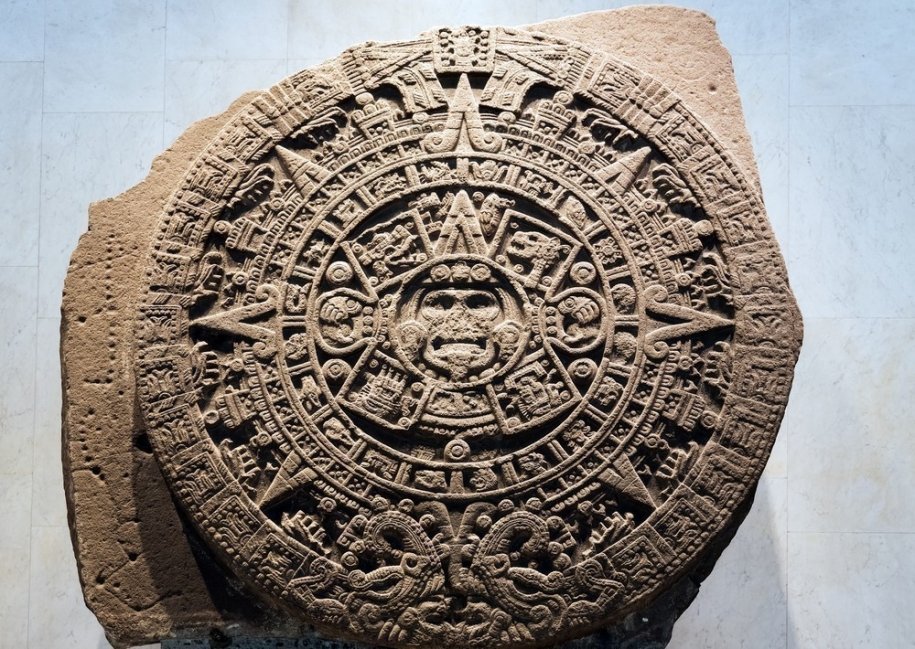 Calendario Maya Calendario Maya
Tres círculos que representan el arte, la ciencia y la espiritualidad dentro de otro más grande que simboliza a la cultura, conforman el emblema de este día, que es la bandera de la paz. Especialmente, en este día, además, se hace la Plegaria a las siete direcciones en sentido contrario a las manecillas del reloj.
- ESTE. Desde la Casa Este de la Luz, que la sabiduría se abra en aurora sobre nosotros para que veamos las cosas con claridad.
- NORTE. Desde la Casa Norte de la Noche, que la sabiduría madure entre nosotros para que conozcamos todo desde adentro.
- OESTE. Desde la Casa Oeste de la Transformación, que la sabiduría se transforme en acción correcta para que hagamos lo que haya que hacerse.
- SUR. Desde la Casa Sur del Sol Eterno, que la acción correcta nos de la cosecha para que disfrutemos los frutos del ser planetario.
- CIELO. Desde la Casa Superior del Paraíso, donde se reúne la gente de las estrellas y los antepasados, que sus bendiciones lleguen hasta nosotros ahora.
- TIERRA. Desde la Casa Inferior de la Tierra, que el latido del corazón cristal del planeta, nos bendiga con sus armonías para que acabemos con las guerras.
- CORAZÓN. Desde la Fuente Central de la Galaxia, que está en todas partes y al mismo tiempo, que todo se reconozca como luz de amor mutuo.
Hay muchos que sostienen que el calendario Gregoriano, que usamos por imposición del Papa Gregorio XIII, no está en sincronía con el tiempo del Universo, ya que contamos que la Tierra da la vuelta al sol por 365 días, y cada cuatro años sumamos un día más. Eso da lugar a un desajuste que incide, según algunos creen, en nuestra percepción del entorno y la realidad en sí. Si tomáramos un calendario como el maya, posiblemente podríamos empezar a percibir las sincronicidades que nos suceden con mayor claridad.
Hoy, ese día es un momento para celebrar la vida, el amor, la paz, el perdón, el arte (de hecho su filosofía es "El Tiempo es Arte"), y para recordar que todo en el Universo está perfectamente conectado, y que aún estamos a tiempo de tomar un rumbo diferente en nuestra forma de vida.
Fuente: La Bioguia - Observatorio de Medios del Centro de Saberes Africanos, Americanos y Caribeños.
https://www.saberesafricanos.net/noticias/cultura/3622-que-es-el-dia-fuera-del-tiempo-y-por-que-podria-cambiar-tu-vida.html |
|
|
|
|
July 25th — A Day Out Of Time In The Mayan Calander
Image @ig_fama
Secrets Of The Mayan Calander
OnJuly 25th, Sirius (the dog star) rises with the sun. This day is free of time in the 13 Moon Calendar. It is a day of reverence and cultural appreciation for the concept ‘Time is Art.
The Day Out of Time is not specific to the Mayan calendar alone. It is associated with the 13-month lunar-solar calendar known as the “Dreamspell” calendar, inspired by the Mayan system. The Dreamspell calendar was developed by Jose Arguelles, who sought to bring attention to the importance of time and its influence on human consciousness.
“Day Out of Time” is a fascinating aspect of the Mayan calendar. The Mayan calendar is a complex and ancient system that the Maya civilization used to track time and various cycles. One of the essential components of this calendar is the “Day Out of Time,” also known as “Weyeb.”
Typically falls on July 25th of the Gregorian calendar. It is a day of celebration and reflection, representing a pause in the regular 13-moon, 28-day calendar cycle. Today, people are encouraged to disconnect from their usual routines, take a break from their daily responsibilities, and connect with nature and their inner selves.
The Day Out of Time is considered a day of unity, forgiveness, and global peace. It allows individuals to reset, meditate, and focus on timelessness. People come together to participate in ceremonies, creative expressions, and communal events to promote harmony and understanding.
For those following the Dreamspell calendar or other systems inspired by the Mayan tradition, the Day Out of Time is a special occasion to celebrate the cycle of time and connect with the universe on a deeper level.
Please note that the concept of the Day Out of Time may be viewed differently by various communities or individuals who incorporate elements of the Mayan calendar into their spiritual practices. As always essential to respect and understand different cultural perspectives and interpretations.
Onanother note though. Is Cosmic consciousness is resonating within you?
Galactic ‘vs’ Cosmic — What’s the difference? Cosmic = Macrocosm and Galactic = Macrocosm. Galactic Activation is a spiritual technology that works with DNA / Blueprints of the human consciousness beings to re-awaken this original spiritual consciousness while alive in a physical body.
“Shapeshifting requires the ability to transcend your attachments, particularly your ego attachments to identity and who you are. You can be virtually anybody if you can get over your attachment to labelling yourself and cherishing your identity. You can slip in and out of different shells, even different animal forms or deity forms.” ― Zeena Schreck
https://tribalalchemy.medium.com/july-25th-a-day-out-of-time-in-the-mayan-calander-26b5627dd127 |
|
|
|
|
New Year's Prophecy
Intertemporal Perspective via 2016 Tower & Star Rituals
By Goro Adachi
December 30, 2016

Century II - 41
The great star will burn for seven days,
The cloud will make two suns appear:
The large mastiff will howl all night
When the great pontiff changed territory.
- Nostradamus
Not all New Year's Days are created equal and this one coming up happens to be a special one. The previous one was special as well, both being attached to the year 2016, the point of no return. And if the pattern holds, we are in for a whole new set of inter-temporal "clues" which, if decoded properly, should be quite prophetic in nature. Decoding these things happens to be my specialty, or obsession...
It's telling that The Economist's annual, end of the year crystal ball edition features a cover with tarot cards. Obviously they were inspired by the irresistible combination of "Trump" (cards) and the idea of divination (predicting the future). Not too surprising there. (What is surprising though is how most people trying to "decode" it can't even crack the first step: The only two tilted cards, "Judgment" and "The Star", are card #20 and card #17 per tradition, spelling out "20-17" or "2017".)
The Economist is actually a bit late to the party as there was a whole lot of foreshadowing going on last year through the tarot symbolism on New Year's Eve/Day (2015/2016). It came in the form of Dubai's tower inferno evoking the Tower card numbered 16 (as in 20 16)...
...in effect foreshadowing the earthshaking rise of "Trump" who famously lives in Trump Tower (= Tower trump card).
Extending the pattern forward in time would have the new year 2017 correspond to tarot card #17 - " The Star".

It would most certainly be Sirius on New Year's Eve/Day as a magical celestial moment arrives every year when the brightest star in the night sky "culminates" due south reaching its highest point right around midnight on New Year's Eve/Day.
But as I said, it's extra special around 2016. I'm quite aware of this, and it seems so was Nostradamus. Let me introduce you to quatrain II-41, or as I like to call it the "Sirius quatrain":
Century II - 41
La grand' estoille par sept jours bruslera,
Nuee fera deux soleils apparoir:
Le gros mastin toute nuit hurlera,
Quand grand pontife changera de terroir.
The great star will burn for seven days,
The cloud will make two suns appear:
The large mastiff will howl all night
When the great pontiff changed territory.
- Nostradamus
Right now it is highly relevant and timely as shown below:
Line 1: The great star will burn for seven days
Being the brightest star in the night sky, Sirius certainly qualifies as a "great star". It "burns" in the sense that the name "Sirius" means "scorcher" plus the phrase "Dog Days of summer" derives from Sirius's nickname "Dog Star". Even the "seven days" (sept jours) part relates to Sirius in that ancient Egyptians called the star Spd, Spdt, or Sept, resonating with the French sept meaning "seven. ("Seven days" can also allude to the 7-day festival Saturnalia, Dec 17-23.)
Line 2: The cloud will make two suns appear
In esoteric tradition Sirius has been considered the "second sun".
Line 3: The large mastiff will howl all night
Sirius is the "Dog Star" ("mastiff") and it "howls all night" on New Year's Eve/Day by being visible all night long. (Culminating around midnight implies being visible from dusk to dawn.)
Line 4: When the great pontiff changed territory
The last time there was a change in the papacy was back in 2013 when Pope Benedict XVI stepped down and Pope Francis took over. Unbeknownst to most, it managed to multicontextually encode an arrow pointing ahead to the year 2016:
- Pope Benedict XVI is "16" (XVI), numerically resonating with 2016 and the Tower card (XVI)
 
- Pope Francis's first foreign trip ("changing territory") as head of the Catholic Church was to Rio de Janeiro, Brazil in July 2013, where the Summer Olympics would take place in 2016
 Aug 05, 2016 Rio Olympic Games begin
- A geo-alignment pinpointing Rio was implied via Pope Benedict XVI's resignation announcement taking place concurrently with a major meteor impact event in Russia
Feb 11, 2013: Pope Benedict XVI announces resignation Feb 15, 2013: Major meteor impact in Chelyabinsk, Russia  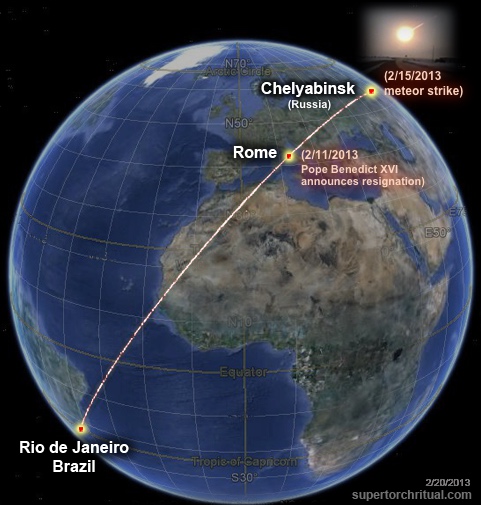 In the context of the "Sirius quatrain" II-41, it makes a lot of sense for Rio to be highlighted in this manner. It has to do with the real, hidden reason behind the name "Rio de Janeiro" or " River of January" which I'm revealing here for the first time anywhere (aside from STRUG/members section which is always ahead)... Firstly, the term " January" (Janeiro) derives from Janus the god of beginnings, endings, time, and doorways. Basically a perfect set of descriptions for New Year's Eve/Day (= beginning of January).

And it just so happens it's right around New Year's Day, when Sirius "howls all night", that Rio and the Sun are aligned in terms of latitude & declination. In other words, the Sun is directly overhead at noon in Rio right around New Year's Day. Rio in this way indeed is a "city of Janus/January"!

As above, so below... Sirius is the " New Year's star" above, Rio de Janeiro is the " New Year's city" below. Having established this and 2016 being the year of the Rio Olympics, we can then quite easily infer that the beginning and ending of 2016 are of special, "ritualistic" significance. We already saw this in action at the beginning of 2016 (Dubai tower fire), and we are now about to witness something at the end of 2016. The straightforward expectation would be that it would reflect " The Star" card - #17 representing "2017" - just as the Dubai tower inferno was a simulation of the "Tower" tarot card, #16. This would mean it would likely involve Sirius on New Year's Eve/Day. (I may actually already know the ritual taking place, but I'll save it for another article, perhaps early next year.) There is another approach here to discerning the nature of the end of 2016 "ritual(s)". It has to do with the fact that Rio and the Sun are also aligned on ~December 10th (equidistant from the solstice).
That "preview" window precisely coincided with a major geopolitical flareup stemming from the apparent Russian cyber attacks against the US during the 2016 presidential election.
 It's an ongoing situation, happening in real time as I write this and it wouldn't be surprising if we hear more about the US retaliation against Russia around the New Year's Eve/Day weekend, such as actual US cyber attacks against Russia.
(I've consistently pointed to the significance of the Russian cyberwar situation since the very beginning. See: Jul 26 tweet, Jul 27 tweet, Jul 30 tweet, Aug 30 update. Here we are, it's like the Cold War has returned.) Saturnalia (Dec 17-23) was another important window we were watching very closely... (Saturnalia starts on Pope Francis's birthday, by the way.) My tweet from Nov 24:
And it was intense indeed...
Notable as it connects right back to the 2015-2016 New Year's Eve/Day "ritual". The name "Dubai" means "market". And the fire there took place right next to the Dubai's spectacular New Year's fireworks.
Makes us wonder if these constitute an omen foreshadowing a major market/financial event coming in the New Year.

I'm going to end this article here, but really we've just scratched the surface. Just the tip of the iceberg for what's unfolding... because 2016 was a tipping point, the point of no return. We didn't even touch on the earth changes and the sixth mass extinction already being discussed on STRUG...
https://www.goroadachi.com/etemenanki/newyears-prophecy.html |
|
|
 Primer Primer
 Anterior
49 a 63 de 63
Siguiente Anterior
49 a 63 de 63
Siguiente
 Último
Último

|
|
| |
|
|
©2026 - Gabitos - Todos los derechos reservados | |
|
|
 Nombre:Parroquia Santa María Magdalena
Nombre:Parroquia Santa María Magdalena Teléfono:+56228500245 / 56975407026
Teléfono:+56228500245 / 56975407026 E-mail:parroquia.smmagdalena@gmail.com
E-mail:parroquia.smmagdalena@gmail.com Sitio Web:Sin información
Sitio Web:Sin información Dirección:Sargento Menadier 221
Dirección:Sargento Menadier 221 Comuna:Puente Alto
Comuna:Puente Alto Región:Sin información
Región:Sin información Facebook:@psantamariamagdalena
Facebook:@psantamariamagdalena YouTube:@ParroquiaMaríaMagdalena
YouTube:@ParroquiaMaríaMagdalena Instagram:@p_santamariamagdalena
Instagram:@p_santamariamagdalena Twitter:Sin información
Twitter:Sin información WhatsApp:+56975407026
WhatsApp:+56975407026 Zona:Maipo
Zona:Maipo Vicario Episcopal:Pbro. Rodrigo MAGAÑA VENEGAS
Vicario Episcopal:Pbro. Rodrigo MAGAÑA VENEGAS Decanato:Sin información
Decanato:Sin información