|
|
LUNA CUARTO MENGUANTE=LETRA D = DIANA = DENARIO = DAN = LINAJE DE A-DAN = DINERO = DAN BROWN = DA VINCI -NEXO 11 DE SEPTIEMBRE DEL 2001 = DIA DEL JUICIO = LEVITICO 23:31 (9 DE TISHRI/ 10 DE TISHRI)
En el contexto al VERDADERO CALENDARIO LUNI-SOLAR HEBREO, el 11 de SEPTIEMBRE DEL 2001, EVIDENCIA LA RELACION CON LA MUERTE DE LADY DY (PRINCESA DIANA) EL 31 DE AGOSTO DE 1997. TODO ES UNA REFERENCIA AL NEXO CON LA LUNA CUARTO MENGUANTE QUE TIENE LA FORMA DE LA LETRA D. EN EL VERDADERO CALENDARIO LUNI-SOLAR HEBREO, EL VERDADERO REPOSO BIBLICO ES EN EL MARCO A LAS FASES DE LA LUNA. CON MESES DE 29 DIAS LOS MISMOS CAEN EN EL DIA 8, 15,22 Y 29 Y CON MESES DE 30 DIAS CAEN EN EL DIA 9,16,23 Y 30. EN ESTE MARCO EL ULTIMO DIA DEL MES LUNAR SIEMPRE ES REPOSO. LA VARIACION DE LOS DIAS DEPENDE DE LO QUE DEMORE LA LUNA LLENA EN SALIR. EN ESTE MARCO EL 9 DE TISHRI, EN EL MARCO A LEVITICO 23:32 A LA PUESTA DEL SOL, COMIENZA EL DIA DEL JUICIO Y FINALIZA EL 10 DE TISHRI O SEPTIMO MES HEBREO. OSEA QUE EN EL MARCO A SEPTIEMBRE DEL 2001, DICHO DIA COMENZO EN EL DIA 10 DE SEPTIEMBRE Y FINALIZO EN EL 11 DEL MISMO.
Considerando LA LUNA LLENA EL 2 DE SEPTIEMBRE el 11 del mismo mes CAE EXACTAMENTE EN EL DIA DE LA EXPIACION O YOM KIPUR, fiesta hebrea con FUERTE RELACION CON EL LUGAR SANTISIMO Y LA SHEKINAH.
LEVITICO 23
f) El día de la expiación (YOM KIPUR)
23:26 Habló Yahveh a Moisés, diciendo:
23:27 Además el día décimo de este séptimo mes será el día de la Expiación,  en el cual tendréis reunión sagrada; ayunaréis y ofreceréis manjares abrasados a Yahveh. en el cual tendréis reunión sagrada; ayunaréis y ofreceréis manjares abrasados a Yahveh.
23:28 No haréis en ese mismo día ningún trabajo, pues es el día de Expiación, en el que se ha de hacer la expiación por vosotros   delante de Yahveh, vuestro Dios. delante de Yahveh, vuestro Dios.
23:29 El que no ayune ese día será exterminado de entre su pueblo.
23:30 Al que haga en tal día un trabajo cualquiera, yo lo haré perecer de en medio de su pueblo.
23:31 No haréis, pues, trabajo alguno. Es decreto perpetuo, de generación en generación, dondequiera que habitéis.
23:32 Será para vosotros día de descanso completo y ayunaréis; el día nueve del mes, por la tarde, de tarde a tarde, guardaréis descanso.
23:33 Habló Yahveh a Moisés, diciendo:
Fases Lunares para el mes de Septiembre del año 2001
En el calendario lunar se calculan los años según los ciclos de la luna en lugar de los del sol como se hace en el calendario occidental. En dicho calendario lunar, cada mes lunar corresponde a una lunación, que comprende el período entre dos momentos en que la luna se halla exactamente en la misma fase lunar. Cada mes lunar comprende 29.53 días solares.
Aunque cada día del mes lunar correspondería a una fase lunar, las fases de la luna a las que se conoce con un nombre concreto son la Luna Nueva, Cuarto Creciente, Luna Llena y Cuarto Menguante. Estas fases lunares se asocian a diferentes porcentajes de iluminación o ángulos de fase que van del 0% en la luna nueva, 50% en los cuartos y 100% en la luna llena.
| Día | Fase lunar | Porcentaje iluminado |
| 17 |
Luna Nueva |
En la fase lunar de Luna Nueva la visibilidad es del 0% |
| 25 |
Cuarto Creciente |
En la fase lunar de Cuarto Creciente la visibilidad es del 50% |
| 3 |
Luna Llena |
En la fase lunar de Luna Llena la visibilidad es del 100% |
| 10 |
Cuarto Menguante |
En la fase lunar de Cuarto Menguante la visibilidad es del 50% |
|
|
|
|
|
ISLA SAN GIORGIO (VENECIA)=GEORGE LEMAITRE
GEMATRIA EN INGLES DE SEED=33
GEMATRIA EN INGLES DE GATE=33
SARA (CE-SAREA DE FILIPO)=PARALELO 33
 the Apple
| milky way in Simple Gematria Equals: 119 |
( |
m 13 |
i9 |
l 12 |
k 11 |
y 25 |
0 |
w 23 |
a1 |
y 25 |
) |
| queen mary in Simple Gematria Equals: 119 |
( |
q 17 |
u 21 |
e5 |
e5 |
n 14 |
0 |
m 13 |
a1 |
r 18 |
y 25 |
|
| hebrew calendar in Simple Gematria Equals: 119 |
( |
h8 |
e5 |
b2 |
r 18 |
e5 |
w 23 |
0 |
c3 |
a1 |
l 12 |
e5 |
n 14 |
d4 |
a1 |
r 18 |
| mary magdalene in Simple Gematria Equals: 119 |
( |
m 13 |
a1 |
r 18 |
y 25 |
0 |
m 13 |
a1 |
g7 |
d4 |
a1 |
l 12 |
e5 |
n 14 |
e5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| De: Rolmen |
Enviado: 18/05/2019 02:55 |
|
|
|
|
|

salt lake city=alchemy (salt)=dollar=$= LOT S WIFE (SODOMA AND GOMORRA)
Cathedral of the Madeleine
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Cathedral of the Madeleine is a Roman Catholic church in Salt Lake City, Utah, United States. It was completed in 1909 and currently serves as the cathedral, or mother church, of the Diocese of Salt Lake City. It is the only cathedral in the U.S. under the patronage of St. Mary Magdalene.
Description[edit]
The cathedral was built under the direction of Lawrence Scanlan, the first bishop of Salt Lake City, who dedicated it to St. Mary Magdalene.[2] It was designed by architects Carl M. Neuhausen and Bernard O. Mecklenburg. The exterior is predominantly a Neo-Romanesque design, while the inside displays more Neo-Gothic details. Construction began in 1900 and was completed in 1909. It was dedicated by James Cardinal Gibbons, Archbishop of Baltimore.
It is theorized that Bishop Scanlan chose Mary Magdalene as the patron saint of the Diocese of Salt Lake because her feast day is on July 22, two days before Pioneer Day, a celebration commemorating the arrival of the Mormon pioneers in Salt Lake Valley, so that Catholics would have something to celebrate alongside the region's dominant faith.[3]
The interior of the cathedral was created under the direction of Joseph S. Glass, the second bishop of Salt Lake. Bishop Glass enlisted John Theodore Comes, one of the preeminent architects in the country, to decorate the interior of the cathedral. His plans for the interior were largely based upon the Spanish Gothic style. The colorful murals and polychrome were added at this time, as were the ornate shrines. In 1916, Bishop Glass also changed the name of the cathedral to the French spelling after visiting her purported tomb.[2]
In the 1970s, the exterior of the building was restored, and between 1991 and 1993, the interior of the cathedral was renovated and restored under Bishop William K. Weigand. This included not only the removal of dust and dirt and restoration of the interior but also changes to the liturgical elements of the cathedral to bring them into conformity with certain widespread changes in liturgical practice that developed after the Second Vatican Council.
This included constructing a new altar, moving the cathedra, creating a separate chapel for the Blessed Sacrament, and adding an ample baptismal font. The Blessed Sacrament Chapel also contains the tomb of Bishop Scanlan.[4] Resting atop the tomb is a case containing a small relic of Saint Mary Magdalene. The cathedral in Salt Lake City and the Basilica of Saint-Maximin-la-Sainte-Baume in France are the only cathedrals in the world holding first-class relics of the saint and are named in her honor.[5] The major restoration of the interior of the cathedral was accomplished through the vision of Monsignor M. Francis Mannion.[6]
The cathedral is home to the only co-educational Catholic Choir School in the United States. The Madeleine Choir School, established in 1996, now serves over 400 students in Pre-Kindergarten through Grade Eight.[7] The Cathedral Choir has recorded several CDs and routinely tours both nationally and internationally. In addition to singing daily services at the Cathedral of the Madeleine, choristers have sung at St. Peter's Basilica (Vatican City), Notre Dame de Paris (France), and in churches across the United States of America, Spain, Italy, France, Belgium, and Germany, among other places.[8]
Composer Amédée Tremblay notably served as the church's organist from 1920 to 1925.[9]
-
-
Cathedral of the Madeleine, looking east
-
Interior of the cathedral
-
   |
|
|
|
|

Jordan River (Utah)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Jordan River, in the state of Utah, United States, is a river about 51 miles (82 km) long. Regulated by pumps at its headwaters at Utah Lake, it flows northward through the Salt Lake Valley and empties into the Great Salt Lake. Four of Utah's six largest cities border the river: Salt Lake City, West Valley City, West Jordan, and Sandy. More than a million people live in the Jordan Subbasin, part of the Jordan River watershed that lies within Salt Lake and Utah counties. During the Pleistocene, the area was part of Lake Bonneville.
Members of the Desert Archaic Culture were the earliest known inhabitants of the region; an archaeological site found along the river dates back 3,000 years. Mormon pioneers led by Brigham Young were the first European American settlers, arriving in July 1847 and establishing farms and settlements along the river and its tributaries. The growing population, needing water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use in an arid climate, dug ditches and canals, built dams, and installed pumps to create a highly regulated river.
Although the Jordan was originally a cold-water fishery with 13 native species, including Bonneville cutthroat trout, it has become a warm-water fishery where the common carp is most abundant. It was heavily polluted for many years by raw sewage, agricultural runoff, and mining wastes. In the 1960s, sewage treatment removed many pollutants. In the 21st century, pollution is further limited by the Clean Water Act, and, in some cases, the Superfund program. Once the home of bighorn sheep and beaver, the contemporary river is frequented by raccoons, red foxes, and domestic pets. It is an important avian resource, as are the Great Salt Lake and Utah Lake, visited by more than 200 bird species.
Big Cottonwood, Little Cottonwood, Red Butte, Mill, Parley's, and City creeks, as well as smaller streams like Willow Creek at Draper, Utah, flow through the sub-basin. The Jordan River Parkway along the river includes natural areas, botanical gardens, golf courses, and a 40-mile (64 km) bicycle and pedestrian trail, completed in 2017.[6]
The Jordan River is Utah Lake's only outflow. It originates at the northern end of the lake between the cities of Lehi and Saratoga Springs. It then meanders north through the north end of Utah Valley for approximately 8 miles (13 km) until it passes through a gorge in the Traverse Mountains, known as the Jordan Narrows. The Utah National Guard base at Camp Williams lies on the western side of the river through much of the Jordan Narrows.[7][8] The Turner Dam, located 41.8 miles (67.3 km) from the river's mouth (or at river mile 41.8) and within the boundaries of the Jordan Narrows, is the first of two dams of the Jordan River. Turner Dam diverts the water to the right or easterly into the East Jordan Canal and to the left or westerly toward the Utah and Salt Lake Canal. Two pumping stations situated next to Turner Dam divert water to the west into the Provo Reservoir Canal, Utah Lake Distribution Canal, and Jacob-Welby Canal. The Provo Reservoir Canal runs north through Salt Lake County, Jacob-Welby runs south through Utah County. The Utah Lake Distribution Canal runs both north and south, eventually leading back into Utah Lake.[9] Outside the narrows, the river reaches the second dam, known as Joint Dam, which is 39.9 miles (64.2 km) from the river's mouth. Joint Dam diverts water to the east for the Jordan and Salt Lake City Canal and to the west for the South Jordan Canal.[10][11][12]
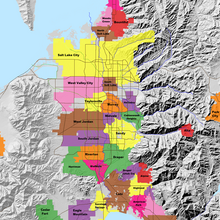
Map of the Salt Lake Valley
The river then flows through the middle of the Salt Lake Valley, initially moving through the city of Bluffdale and then forming the border between the cities of Riverton and Draper.[7] The river then enters the city of South Jordan where it merges with Midas Creek from the west. Upon leaving South Jordan, the river forms the border between the cities of West Jordan on the west and Sandy and Midvale on the east. From the west, Bingham Creek enters West Jordan. Dry Creek, an eastern tributary, combines with the main river in Sandy. The river then forms the border between the cities of Taylorsville and West Valley City on the west and Murray and South Salt Lake on the east. The river flows underneath Interstate 215 in Murray. Little and Big Cottonwood Creeks enter from the east in Murray, 21.7 miles (34.9 km) and 20.6 miles (33.2 km) from the mouth respectively. Mill Creek enters on the east in South Salt Lake, 17.3 miles (27.8 km) from the mouth. The river runs through the middle of Salt Lake City, where the river travels underneath Interstate 80 a mile west of downtown Salt Lake City and again underneath Interstate 215 in the northern portion of Salt Lake City. Interstate 15 parallels the river's eastern flank throughout Salt Lake County. At 16 miles (26 km) from the mouth, the river enters the Surplus Canal channel. The Jordan River physically diverts from the Surplus Canal through four gates and heads north with the Surplus Canal heading northwest. Parley's, Emigration, and Red Butte Creeks converge from the east through an underground pipe, 14.2 miles (22.9 km) from the mouth.[7] City Creek also enters via an underground pipe, 11.5 miles (18.5 km) from the river's mouth. The length of the river and the elevation of its mouth varies year to year depending on the fluctuations of the Great Salt Lake caused by weather conditions. The lake has an average elevation of 4,200 feet (1,300 m) which can deviate by 10 feet (3.0 m).[3] The Jordan River then continues for 9 to 12 miles (14 to 19 km) with Salt Lake County on the west and North Salt Lake and Davis County on the east until it empties into the Great Salt Lake.[7][8][11]
Discharge[edit]
The United States Geological Survey maintains a stream gauge in Salt Lake City that shows annual runoff from the period 1980–2003 is just over 150,000 acre-feet (190,000,000 m3) per year or 100 percent of the total 800,000 acre-feet (990,000,000 m3) of water entering the Jordan River from all sources. The Surplus Canal carries almost 60 percent of the water into the Great Salt Lake, with various irrigation canals responsible for the rest. The amount of water entering the Jordan River from Utah Lake is just over 400,000 acre-feet (490,000,000 m3) per year. Inflow from the 11 largest streams feeding the Jordan River, sewage treatment plants, and groundwater each account for approximately 15 percent of water entering the river.[13]
Watershed[edit]
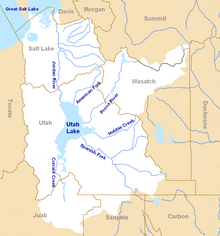
Map of the entire Jordan River Basin
|
|
|
|
|
Jordan River (Utah)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Jordan River, in the state of Utah, United States, is a river about 51 miles (82 km) long. Regulated by pumps at its headwaters at Utah Lake, it flows northward through the Salt Lake Valley and empties into the Great Salt Lake. Four of Utah's six largest cities border the river: Salt Lake City, West Valley City, West Jordan, and Sandy. More than a million people live in the Jordan Subbasin, part of the Jordan River watershed that lies within Salt Lake and Utah counties. During the Pleistocene, the area was part of Lake Bonneville.
Members of the Desert Archaic Culture were the earliest known inhabitants of the region; an archaeological site found along the river dates back 3,000 years. Mormon pioneers led by Brigham Young were the first European American settlers, arriving in July 1847 and establishing farms and settlements along the river and its tributaries. The growing population, needing water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use in an arid climate, dug ditches and canals, built dams, and installed pumps to create a highly regulated river.
Although the Jordan was originally a cold-water fishery with 13 native species, including Bonneville cutthroat trout, it has become a warm-water fishery where the common carp is most abundant. It was heavily polluted for many years by raw sewage, agricultural runoff, and mining wastes. In the 1960s, sewage treatment removed many pollutants. In the 21st century, pollution is further limited by the Clean Water Act, and, in some cases, the Superfund program. Once the home of bighorn sheep and beaver, the contemporary river is frequented by raccoons, red foxes, and domestic pets. It is an important avian resource, as are the Great Salt Lake and Utah Lake, visited by more than 200 bird species.
Big Cottonwood, Little Cottonwood, Red Butte, Mill, Parley's, and City creeks, as well as smaller streams like Willow Creek at Draper, Utah, flow through the sub-basin. The Jordan River Parkway along the river includes natural areas, botanical gardens, golf courses, and a 40-mile (64 km) bicycle and pedestrian trail, completed in 2017.[6]
The Jordan River is Utah Lake's only outflow. It originates at the northern end of the lake between the cities of Lehi and Saratoga Springs. It then meanders north through the north end of Utah Valley for approximately 8 miles (13 km) until it passes through a gorge in the Traverse Mountains, known as the Jordan Narrows. The Utah National Guard base at Camp Williams lies on the western side of the river through much of the Jordan Narrows.[7][8] The Turner Dam, located 41.8 miles (67.3 km) from the river's mouth (or at river mile 41.8) and within the boundaries of the Jordan Narrows, is the first of two dams of the Jordan River. Turner Dam diverts the water to the right or easterly into the East Jordan Canal and to the left or westerly toward the Utah and Salt Lake Canal. Two pumping stations situated next to Turner Dam divert water to the west into the Provo Reservoir Canal, Utah Lake Distribution Canal, and Jacob-Welby Canal. The Provo Reservoir Canal runs north through Salt Lake County, Jacob-Welby runs south through Utah County. The Utah Lake Distribution Canal runs both north and south, eventually leading back into Utah Lake.[9] Outside the narrows, the river reaches the second dam, known as Joint Dam, which is 39.9 miles (64.2 km) from the river's mouth. Joint Dam diverts water to the east for the Jordan and Salt Lake City Canal and to the west for the South Jordan Canal.[10][11][12]

Map of the Salt Lake Valley
The river then flows through the middle of the Salt Lake Valley, initially moving through the city of Bluffdale and then forming the border between the cities of Riverton and Draper.[7] The river then enters the city of South Jordan where it merges with Midas Creek from the west. Upon leaving South Jordan, the river forms the border between the cities of West Jordan on the west and Sandy and Midvale on the east. From the west, Bingham Creek enters West Jordan. Dry Creek, an eastern tributary, combines with the main river in Sandy. The river then forms the border between the cities of Taylorsville and West Valley City on the west and Murray and South Salt Lake on the east. The river flows underneath Interstate 215 in Murray. Little and Big Cottonwood Creeks enter from the east in Murray, 21.7 miles (34.9 km) and 20.6 miles (33.2 km) from the mouth respectively. Mill Creek enters on the east in South Salt Lake, 17.3 miles (27.8 km) from the mouth. The river runs through the middle of Salt Lake City, where the river travels underneath Interstate 80 a mile west of downtown Salt Lake City and again underneath Interstate 215 in the northern portion of Salt Lake City. Interstate 15 parallels the river's eastern flank throughout Salt Lake County. At 16 miles (26 km) from the mouth, the river enters the Surplus Canal channel. The Jordan River physically diverts from the Surplus Canal through four gates and heads north with the Surplus Canal heading northwest. Parley's, Emigration, and Red Butte Creeks converge from the east through an underground pipe, 14.2 miles (22.9 km) from the mouth.[7] City Creek also enters via an underground pipe, 11.5 miles (18.5 km) from the river's mouth. The length of the river and the elevation of its mouth varies year to year depending on the fluctuations of the Great Salt Lake caused by weather conditions. The lake has an average elevation of 4,200 feet (1,300 m) which can deviate by 10 feet (3.0 m).[3] The Jordan River then continues for 9 to 12 miles (14 to 19 km) with Salt Lake County on the west and North Salt Lake and Davis County on the east until it empties into the Great Salt Lake.[7][8][11]
Discharge[edit]
The United States Geological Survey maintains a stream gauge in Salt Lake City that shows annual runoff from the period 1980–2003 is just over 150,000 acre-feet (190,000,000 m3) per year or 100 percent of the total 800,000 acre-feet (990,000,000 m3) of water entering the Jordan River from all sources. The Surplus Canal carries almost 60 percent of the water into the Great Salt Lake, with various irrigation canals responsible for the rest. The amount of water entering the Jordan River from Utah Lake is just over 400,000 acre-feet (490,000,000 m3) per year. Inflow from the 11 largest streams feeding the Jordan River, sewage treatment plants, and groundwater each account for approximately 15 percent of water entering the river.[13]
Watershed[edit]

Map of the entire Jordan River Basin
|
|
|
|
|
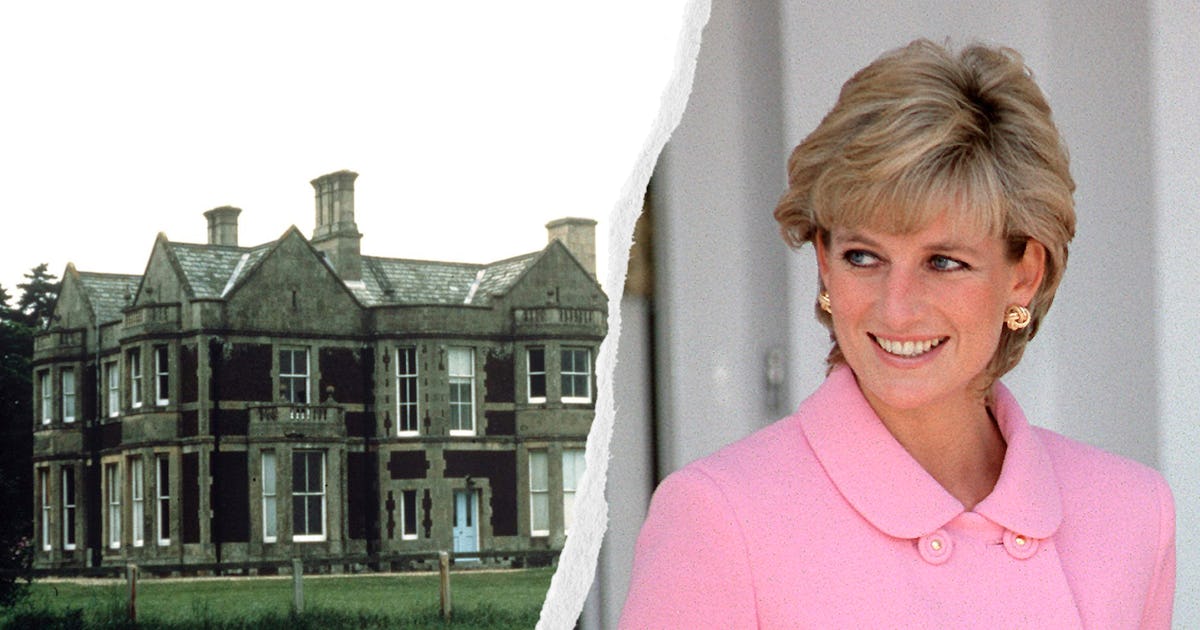
   
St Mary Magdalene Church is a church in Sandringham, Norfolk, England, located just to the southwest of Sandringham House. Members of the British Royal Family attend services when in residence at Sandringham, which normally includes Christmas.[1] The church is dedicated to Mary Magdalene, a disciple of Jesus. The rector is the Reverend Canon Paul Williams.[2]
History[edit]
 The chancel
The Grade II* listed[3] church is dedicated to Mary Magdalene[4] and is described as a small building in the Perpendicular style, "nobly lying on raised ground".[5][6] The current building dates to the 16th century and was restored by S. S. Teulon in 1855 and Arthur Blomfield in 1890. It is considered to be a noteworthy example of a carrstone building.[7][8] It is located in the park and is approached from Sandringham House through the garden by "an avenue of fine old Scotch firs".[6]
Much of the decoration and the church's stained glass in the east window was created by Charles Eamer Kempe whom King Edward VII had also commissioned in 1903 to create a stained glass window for Buckingham Palace of his eldest son, Prince Albert, Duke of Clarence.[9][10] The church's silver altar and reredos, created by the silversmiths Barkentin & Krall, were presented to Queen Alexandra by the American department store owner Rodman Wanamaker as a tribute to Edward VII. He also presented her with the silver pulpit and a silver 17th-century Spanish processional cross. Of note also is a Florentine marble font and a Greek font dating to the 9th-century.[7][11]
Burials[edit]
There are memorials to many members and relations of the Royal Family in the church and churchyard. Prince John (12 July 1905 – 18 January 1919) is buried here. After his death in February 1952, the body of King George VI was placed in the church for two days prior to its lying in state in Westminster Hall.[12]
Baptisms[edit]
The church has been the site of many royal baptisms. These baptisms include:[13][14]
|
|
|
|
|
Mary Magdalene is considered to be a saint by the Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, and Lutheran denominations. In 2016, Pope Francis raised the level of liturgical memory on July 22 from memorial to feast, and for her to be referred to as the "Apostle of the apostles".
|
|
|
|
|

Jordan River (Utah)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Jordan River, in the state of Utah, United States, is a river about 51 miles (82 km) long. Regulated by pumps at its headwaters at Utah Lake, it flows northward through the Salt Lake Valley and empties into the Great Salt Lake. Four of Utah's six largest cities border the river: Salt Lake City, West Valley City, West Jordan, and Sandy. More than a million people live in the Jordan Subbasin, part of the Jordan River watershed that lies within Salt Lake and Utah counties. During the Pleistocene, the area was part of Lake Bonneville.
Members of the Desert Archaic Culture were the earliest known inhabitants of the region; an archaeological site found along the river dates back 3,000 years. Mormon pioneers led by Brigham Young were the first European American settlers, arriving in July 1847 and establishing farms and settlements along the river and its tributaries. The growing population, needing water for drinking, irrigation, and industrial use in an arid climate, dug ditches and canals, built dams, and installed pumps to create a highly regulated river.
Although the Jordan was originally a cold-water fishery with 13 native species, including Bonneville cutthroat trout, it has become a warm-water fishery where the common carp is most abundant. It was heavily polluted for many years by raw sewage, agricultural runoff, and mining wastes. In the 1960s, sewage treatment removed many pollutants. In the 21st century, pollution is further limited by the Clean Water Act, and, in some cases, the Superfund program. Once the home of bighorn sheep and beaver, the contemporary river is frequented by raccoons, red foxes, and domestic pets. It is an important avian resource, as are the Great Salt Lake and Utah Lake, visited by more than 200 bird species.
Big Cottonwood, Little Cottonwood, Red Butte, Mill, Parley's, and City creeks, as well as smaller streams like Willow Creek at Draper, Utah, flow through the sub-basin. The Jordan River Parkway along the river includes natural areas, botanical gardens, golf courses, and a 40-mile (64 km) bicycle and pedestrian trail, completed in 2017.[6]
The Jordan River is Utah Lake's only outflow. It originates at the northern end of the lake between the cities of Lehi and Saratoga Springs. It then meanders north through the north end of Utah Valley for approximately 8 miles (13 km) until it passes through a gorge in the Traverse Mountains, known as the Jordan Narrows. The Utah National Guard base at Camp Williams lies on the western side of the river through much of the Jordan Narrows.[7][8] The Turner Dam, located 41.8 miles (67.3 km) from the river's mouth (or at river mile 41.8) and within the boundaries of the Jordan Narrows, is the first of two dams of the Jordan River. Turner Dam diverts the water to the right or easterly into the East Jordan Canal and to the left or westerly toward the Utah and Salt Lake Canal. Two pumping stations situated next to Turner Dam divert water to the west into the Provo Reservoir Canal, Utah Lake Distribution Canal, and Jacob-Welby Canal. The Provo Reservoir Canal runs north through Salt Lake County, Jacob-Welby runs south through Utah County. The Utah Lake Distribution Canal runs both north and south, eventually leading back into Utah Lake.[9] Outside the narrows, the river reaches the second dam, known as Joint Dam, which is 39.9 miles (64.2 km) from the river's mouth. Joint Dam diverts water to the east for the Jordan and Salt Lake City Canal and to the west for the South Jordan Canal.[10][11][12]

Map of the Salt Lake Valley
The river then flows through the middle of the Salt Lake Valley, initially moving through the city of Bluffdale and then forming the border between the cities of Riverton and Draper.[7] The river then enters the city of South Jordan where it merges with Midas Creek from the west. Upon leaving South Jordan, the river forms the border between the cities of West Jordan on the west and Sandy and Midvale on the east. From the west, Bingham Creek enters West Jordan. Dry Creek, an eastern tributary, combines with the main river in Sandy. The river then forms the border between the cities of Taylorsville and West Valley City on the west and Murray and South Salt Lake on the east. The river flows underneath Interstate 215 in Murray. Little and Big Cottonwood Creeks enter from the east in Murray, 21.7 miles (34.9 km) and 20.6 miles (33.2 km) from the mouth respectively. Mill Creek enters on the east in South Salt Lake, 17.3 miles (27.8 km) from the mouth. The river runs through the middle of Salt Lake City, where the river travels underneath Interstate 80 a mile west of downtown Salt Lake City and again underneath Interstate 215 in the northern portion of Salt Lake City. Interstate 15 parallels the river's eastern flank throughout Salt Lake County. At 16 miles (26 km) from the mouth, the river enters the Surplus Canal channel. The Jordan River physically diverts from the Surplus Canal through four gates and heads north with the Surplus Canal heading northwest. Parley's, Emigration, and Red Butte Creeks converge from the east through an underground pipe, 14.2 miles (22.9 km) from the mouth.[7] City Creek also enters via an underground pipe, 11.5 miles (18.5 km) from the river's mouth. The length of the river and the elevation of its mouth varies year to year depending on the fluctuations of the Great Salt Lake caused by weather conditions. The lake has an average elevation of 4,200 feet (1,300 m) which can deviate by 10 feet (3.0 m).[3] The Jordan River then continues for 9 to 12 miles (14 to 19 km) with Salt Lake County on the west and North Salt Lake and Davis County on the east until it empties into the Great Salt Lake.[7][8][11]
Discharge[edit]
The United States Geological Survey maintains a stream gauge in Salt Lake City that shows annual runoff from the period 1980–2003 is just over 150,000 acre-feet (190,000,000 m3) per year or 100 percent of the total 800,000 acre-feet (990,000,000 m3) of water entering the Jordan River from all sources. The Surplus Canal carries almost 60 percent of the water into the Great Salt Lake, with various irrigation canals responsible for the rest. The amount of water entering the Jordan River from Utah Lake is just over 400,000 acre-feet (490,000,000 m3) per year. Inflow from the 11 largest streams feeding the Jordan River, sewage treatment plants, and groundwater each account for approximately 15 percent of water entering the river.[13]
Watershed[edit]

Map of the entire Jordan River Basin
|
|
|
 Primer Primer
 Anterior
17 a 31 de 31
Siguiente Anterior
17 a 31 de 31
Siguiente
 Último
Último

|

