July 25th has witnessed a series of pivotal events that have shaped the course of history across various fields.
From groundbreaking achievements in aviation and medical science to significant political shifts and cultural moments, this day encapsulates a diverse array of historical milestones.
Join us as we explore some of the most notable occurrences on this date, delving into their impacts and legacies that continue to resonate today.
July 25th – On this Day in History
306 – Constantine I proclaimed Roman Emperor
On July 25, 306, Constantine the Great was declared Roman Emperor by his troops after the death of his father, Constantius Chlorus, in Eboracum (modern-day York, England).
This proclamation marked the beginning of Constantine’s reign, during which he would play a crucial role in shaping the future of the Roman Empire.
Also Read: July 24 Events in History
His subsequent policies and reforms, including the Edict of Milan in 313, which granted religious tolerance to Christians, had a lasting impact on both the empire and the Christian religion. Constantine’s rule laid the foundation for the Byzantine Empire and the spread of Christianity throughout Europe.
315 – Arch of Constantine inaugurated in Rome
The Arch of Constantine, one of Rome’s most famous monuments, was inaugurated on July 25, 315. Erected to commemorate Constantine I’s victory over Maxentius at the Battle of the Milvian Bridge in 312, the arch stands near the Colosseum.
It is a triumphal arch adorned with sculptures and reliefs that celebrate Constantine’s victory and his consolidation of power.
The arch not only served as a political symbol of Constantine’s authority but also showcased the artistic and architectural styles of the time, incorporating elements from earlier monuments to glorify the emperor’s achievements.
1261 – Constantinople recaptured by Nicaean forces, ending the Latin Empire
On July 25, 1261, forces from the Empire of Nicaea recaptured Constantinople, ending the Latin Empire established by the Fourth Crusade in 1204. This event marked the restoration of the Byzantine Empire under Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos.
Also Read: July 26th – On this Day in History
The recapture of the city was a significant turning point, as it restored Byzantine control over its historic capital. However, the empire never fully recovered its former power and prestige, struggling against internal strife and external threats until its eventual fall to the Ottoman Turks in 1453.
1593 – Henry IV of France converted from Protestantism to Catholicism
On July 25, 1593, Henry IV of France converted from Protestantism to Catholicism, famously stating, “Paris is well worth a mass.” This pragmatic decision was made to secure his position as king and bring peace to a country torn apart by religious wars.
His conversion helped to end the French Wars of Religion, a series of conflicts between Catholics and Huguenots (French Protestants), and paved the way for the Edict of Nantes in 1598, which granted religious tolerance to Protestants.
Henry IV’s reign brought stability and prosperity to France and earned him the nickname “Good King Henry.”
1759 – French defeated at the Battle of Ticonderoga in the Seven Years’ War
On July 25, 1759, during the Seven Years’ War, British forces under General Jeffrey Amherst captured the French stronghold of Fort Carillon (later renamed Fort Ticonderoga) in present-day New York. This victory was part of a larger campaign to gain control over the strategic waterways of North America.
The fall of Ticonderoga marked a turning point in the war in favor of the British, who sought to expand their colonial territories at the expense of the French. The victory opened the way for further British advances into Canada and played a significant role in shaping the future of North America.
1797 – Horatio Nelson lost more than 300 men and his right arm during the failed conquest of Tenerife
On July 25, 1797, British Admiral Horatio Nelson led an attack on Santa Cruz de Tenerife in the Canary Islands during the French Revolutionary Wars. The expedition aimed to capture the strategic port, but it ended in failure.
During the battle, Nelson sustained a severe wound, resulting in the amputation of his right arm. Despite this setback, he displayed remarkable resilience and continued his naval career, eventually becoming one of Britain’s greatest naval heroes. This event highlighted his determination and contributed to his legendary status.
1814 – War of 1812: Battle of Lundy’s Lane, one of the bloodiest battles of the war, takes place
The Battle of Lundy’s Lane, one of the bloodiest battles of the War of 1812, took place on July 25, 1814, near Niagara Falls. American and British forces clashed in a fierce and indecisive engagement that lasted well into the night.
Despite high casualties on both sides, neither could claim a decisive victory. The battle demonstrated the intensity of the conflict along the Canadian-American border and underscored the strategic stalemate that characterized much of the war. It also highlighted the valor and resilience of both American and British troops.
1837 – First commercial use of an electric telegraph
On July 25, 1837, the first commercial use of an electric telegraph took place, marking a significant advancement in communication technology.
Developed by William Fothergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone in England, the telegraph revolutionized long-distance communication by transmitting messages through electrical signals over wires.
This innovation laid the groundwork for the global telecommunications industry, transforming how information was shared and playing a crucial role in commerce, journalism, and personal communication.
1861 – Congress passed the Crittenden-Johnson Resolution, stating the Civil War was fought to preserve the Union, not to end slavery
On July 25, 1861, the United States Congress passed the Crittenden-Johnson Resolution, asserting that the ongoing Civil War was being fought to preserve the Union, not to interfere with slavery. This resolution aimed to maintain the loyalty of the border states and reassure Northerners who were concerned about the war’s purpose.
However, as the war progressed, the focus shifted increasingly towards the abolition of slavery, especially after the issuance of the Emancipation Proclamation in 1863. The resolution reflects the complex and evolving motivations behind the Union’s war effort.
1866 – Ulysses S. Grant became the first General of the Army
On July 25, 1866, Ulysses S. Grant was appointed as the first General of the Army, a newly created rank in the United States military.
This appointment recognized Grant’s leadership and success as a Union general during the Civil War, particularly his role in key victories at battles such as Vicksburg and Appomattox.
As General of the Army, Grant oversaw the post-war military and played a significant role in Reconstruction efforts. His leadership and strategic acumen contributed to his later election as the 18th President of the United States.
1898 – United States invades Puerto Rico during the Spanish-American War
On July 25, 1898, during the Spanish-American War, American forces led by General Nelson A. Miles invaded Puerto Rico. This military action was part of a larger campaign against Spanish colonial rule in the Caribbean and the Pacific. The invasion was relatively swift, facing limited resistance from Spanish troops.
The conflict resulted in the Treaty of Paris, which ceded Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines to the United States, significantly expanding American influence and marking a turning point in U.S. imperialism.
1909 – Louis Blériot makes the first flight across the English Channel in a heavier-than-air machine
On July 25, 1909, French aviator Louis Blériot made history by becoming the first person to fly across the English Channel in a heavier-than-air aircraft. He piloted his Blériot XI monoplane from Calais, France, to Dover, England, covering the distance in about 37 minutes.
This achievement demonstrated the potential of aviation and marked a significant milestone in the development of powered flight. Blériot’s successful crossing captured the public’s imagination and paved the way for future advancements in aviation technology and commercial air travel.
1917 – Mata Hari sentenced to death for espionage
On July 25, 1917, the renowned dancer and courtesan Mata Hari was sentenced to death by a French military court for espionage during World War I.
Accused of spying for Germany, she was portrayed as a dangerous femme fatale, although the evidence against her was largely circumstantial.
Her trial and execution highlighted the paranoia and fear of espionage that pervaded wartime Europe. Mata Hari’s story has since become legendary, symbolizing the intrigue and moral complexities of espionage during the war.
1943 – Benito Mussolini dismissed as Italian premier; arrested
On July 25, 1943, Italian dictator Benito Mussolini was dismissed from power by King Victor Emmanuel III and subsequently arrested.
This event marked a turning point in World War II, as Mussolini’s downfall signaled the collapse of the Fascist regime in Italy. It also led to Italy’s eventual surrender to the Allies.
The dismissal was influenced by military defeats and widespread dissatisfaction with Mussolini’s leadership. His arrest set the stage for a period of political turmoil in Italy and a shift in the balance of power in the war.
1956 – Suez Crisis: Egyptian President Nasser nationalized the Suez Canal
On July 25, 1956, Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser nationalized the Suez Canal, previously controlled by British and French interests. This bold move aimed to fund the construction of the Aswan High Dam and assert Egypt’s sovereignty.
The nationalization led to the Suez Crisis, where Britain, France, and Israel launched a military intervention to regain control of the canal. The crisis highlighted the waning influence of European colonial powers and the rising importance of Middle Eastern geopolitics during the Cold War. It also marked a significant moment in the decolonization movement.
1965 – Bob Dylan controversially used electric instruments at the Newport Folk Festival
On July 25, 1965, Bob Dylan performed with an electric band at the Newport Folk Festival, marking a significant shift in his musical style. This performance was controversial, as Dylan was primarily known for his acoustic folk music.
The audience’s reaction was mixed, with some embracing the new sound and others feeling betrayed. This moment is often seen as a pivotal point in rock music history, symbolizing the merging of folk and rock genres and highlighting Dylan’s evolving artistry.
1978 – Birth of Louise Brown, the first test-tube baby
On July 25, 1978, Louise Brown, the world’s first baby conceived through in vitro fertilization (IVF), was born in England. Her birth marked a groundbreaking achievement in reproductive technology, offering hope to millions of couples struggling with infertility.
The successful use of IVF opened new possibilities for assisted reproductive treatments and sparked discussions about the ethical and social implications of such technologies. Louise Brown’s birth is celebrated as a milestone in medical science.
1984 – Cosmonaut Svetlana Savitskaya became the first woman to perform a spacewalk
On July 25, 1984, Soviet cosmonaut Svetlana Savitskaya became the first woman to perform a spacewalk. During her mission aboard the Salyut 7 space station, she conducted an extravehicular activity (EVA) that lasted nearly four hours.
This achievement not only highlighted her skills and bravery but also underscored the contributions of women in space exploration. Savitskaya’s spacewalk was a significant step forward for gender equality in the field of astronautics.
1994 – Israel and Jordan sign the Washington Declaration, formally ending the state of war
On July 25, 1994, Israel and Jordan signed the Washington Declaration, officially ending the state of war between the two nations. This agreement was a crucial step towards peace in the Middle East, facilitated by the United States.
It laid the groundwork for the Israel-Jordan Peace Treaty later that year, fostering improved diplomatic and economic relations. The declaration represented a significant move towards regional stability and cooperation.
2000 – Air France Flight 4590 crashes on takeoff in Paris, killing 113
On July 25, 2000, Air France Flight 4590, a Concorde supersonic airliner, crashed shortly after takeoff from Charles de Gaulle Airport in Paris. All 109 passengers and crew on board, along with four people on the ground, were killed.
The crash was caused by a strip of metal left on the runway by another aircraft, which led to a tire explosion and subsequent fuel tank rupture. This tragic event marked the beginning of the end for the Concorde program, highlighting safety concerns and contributing to the aircraft’s eventual retirement in 2003.
https://www.havefunwithhistory.com/july-25/
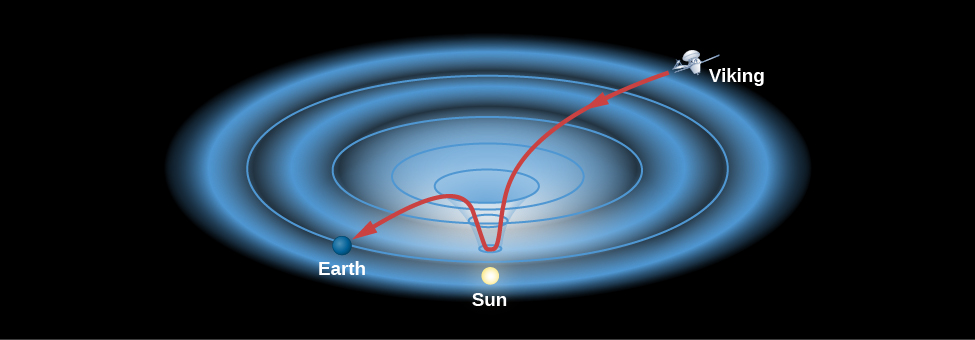
 A report, “Viking relativity experiment: verification of signal retardation by solar gravity” published in 1979 by researchers at MIT and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, analyzed 14 months of data obtained from radio ranging to Viking to verify the prediction of the general theory of relativity.
A report, “Viking relativity experiment: verification of signal retardation by solar gravity” published in 1979 by researchers at MIT and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, analyzed 14 months of data obtained from radio ranging to Viking to verify the prediction of the general theory of relativity.


 Cifra
Cifra











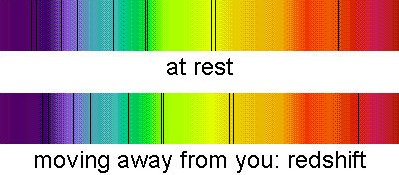














































 Full MoonImage credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio.
Full MoonImage credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio.





