|
|
Hendrik Lorentz
 Painting of Hendrik Lorentz by Menso Kamerlingh Onnes, 1916  Portrait by Jan Veth Lorentz' theory of electrons. Formulas for the Lorentz force (I) and the Maxwell equations for the divergence of the electrical field E (II) and the magnetic field B (III), La théorie electromagnétique de Maxwell et son application aux corps mouvants, 1892, p. 451. V is the velocity of light.  Lorentz' theory of electrons. Formulas for the curl of the magnetic field (IV) and the electrical field E (V), La théorie electromagnétique de Maxwell et son application aux corps mouvants, 1892, p. 452
Hendrik Antoon Lorentz ForMemRS (; 18 July 1853 – 4 February 1928) was a Dutch physicist who shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for the discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect. He derived the Lorentz transformation of the special theory of relativity, as well as the Lorentz force, which describes the combined electric and magnetic forces acting on a charged particle in an electromagnetic field. Lorentz was also responsible for the Lorentz oscillator model, a classical model used to describe the anomalous dispersion observed in dielectric materials when the driving frequency of the electric field was near the resonant frequency of the material, resulting in abnormal refractive indices.
According to the biography published by the Nobel Foundation, "It may well be said that Lorentz was regarded by all theoretical physicists as the world's leading spirit, who completed what was left unfinished by his predecessors and prepared the ground for the fruitful reception of the new ideas based on the quantum theory."[2] He received many other honours and distinctions, including a term as chairman of the International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation,[3] the forerunner of UNESCO, between 1925 and 1928. He was the father and doctoral advisor of Geertruida de Haas-Lorentz.
Early life and education
[edit]
Hendrik Lorentz was born in Arnhem, Gelderland, Netherlands, the son of Gerrit Frederik Lorentz (1822–1893), a well-off horticulturist, and Geertruida van Ginkel (1826–1861). In 1862, after his mother's death, his father married Luberta Hupkes. Despite being raised as a Protestant, he was a freethinker in religious matters and regularly attended Catholic mass in his local French church.[4] From 1866 to 1869, he attended the "Hogere Burgerschool" in Arnhem, a new type of public high school recently established by Johan Rudolph Thorbecke. His results in school were exemplary; not only did he excel in the physical sciences and mathematics, but also in English, French, and German. In 1870, he passed the exams in classical languages which were then required for admission to University.[5]
Lorentz studied physics and mathematics at Leiden University, where he was strongly influenced by the teaching of astronomy professor Frederik Kaiser; it was his influence that led him to become a physicist. After earning a bachelor's degree, he returned to Arnhem in 1871 to teach night school classes in mathematics, but he continued his studies in Leiden in addition to his teaching position. In 1875, Lorentz earned a doctoral degree under Pieter Rijke on a thesis entitled "Over de theorie der terugkaatsing en breking van het licht" (On the theory of reflection and refraction of light), in which he refined the electromagnetic theory of James Clerk Maxwell.[5][6]
Professor in Leiden
[edit]
On 17 November 1877, only 24 years of age, Lorentz was appointed to the newly established chair in theoretical physics at the University of Leiden. The position had initially been offered to Johan van der Waals, but he accepted a position at the Universiteit van Amsterdam.[5] On 25 January 1878, Lorentz delivered his inaugural lecture on "De moleculaire theoriën in de natuurkunde" (The molecular theories in physics). In 1881, he became member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences.[7]
During the first twenty years in Leiden, Lorentz was primarily interested in the electromagnetic theory of electricity, magnetism, and light. After that, he extended his research to a much wider area while still focusing on theoretical physics. Lorentz made significant contributions to fields ranging from hydrodynamics to general relativity. His most important contributions were in the area of electromagnetism, the electron theory, and relativity.[5]
Lorentz theorized that atoms might consist of charged particles and suggested that the oscillations of these charged particles were the source of light. When a colleague and former student of Lorentz's, Pieter Zeeman, discovered the Zeeman effect in 1896, Lorentz supplied its theoretical interpretation. The experimental and theoretical work was honored with the Nobel prize in physics in 1902. Lorentz' name is now associated with the Lorentz–Lorenz equation, the Lorentz force, the Lorentzian distribution, the Lorentz oscillator model and the Lorentz transformation.
Electrodynamics and relativity
[edit]
In 1892 and 1895, Lorentz worked on describing electromagnetic phenomena (the propagation of light) in reference frames that move relative to the postulated luminiferous aether.[8][9] He discovered that the transition from one to another reference frame could be simplified by using a new time variable that he called local time and which depended on universal time and the location under consideration. Although Lorentz did not give a detailed interpretation of the physical significance of local time, with it, he could explain the aberration of light and the result of the Fizeau experiment. In 1900 and 1904, Henri Poincaré called local time Lorentz's "most ingenious idea" and illustrated it by showing that clocks in moving frames are synchronized by exchanging light signals that are assumed to travel at the same speed against and with the motion of the frame[10][11] (see Einstein synchronisation and Relativity of simultaneity). In 1892, with the attempt to explain the Michelson–Morley experiment, Lorentz also proposed that moving bodies contract in the direction of motion (see length contraction; George FitzGerald had already arrived at this conclusion in 1889).[12]
In 1899 and again in 1904, Lorentz added time dilation to his transformations and published what Poincaré in 1905 named Lorentz transformations.[13][14]
It was apparently unknown to Lorentz that Joseph Larmor had used identical transformations to describe orbiting electrons in 1897. Larmor's and Lorentz's equations look somewhat dissimilar, but they are algebraically equivalent to those presented by Poincaré and Einstein in 1905.[15] Lorentz's 1904 paper includes the covariant formulation of electrodynamics, in which electrodynamic phenomena in different reference frames are described by identical equations with well defined transformation properties. The paper clearly recognizes the significance of this formulation, namely that the outcomes of electrodynamic experiments do not depend on the relative motion of the reference frame. The 1904 paper includes a detailed discussion of the increase of the inertial mass of rapidly moving objects in a useless attempt to make momentum look exactly like Newtonian momentum; it was also an attempt to explain the length contraction as the accumulation of "stuff" onto mass making it slow and contract.
|
|
|
 Primer
Primer
 Anterior
2 a 13 de 13
Siguiente
Anterior
2 a 13 de 13
Siguiente
 Último
Último

|
|
|
Lorentz and special relativity
[edit]
 Albert Einstein and Hendrik Antoon Lorentz, photographed by Ehrenfest in front of his home in Leiden in 1921 Albert Einstein and Hendrik Antoon Lorentz, photographed by Ehrenfest in front of his home in Leiden in 1921 Lorentz (left) at the International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation of the League of Nations, here with Albert Einstein Lorentz (left) at the International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation of the League of Nations, here with Albert Einstein His published university lectures in theoretical physics. Part 1. Stralingstheorie (1910-1911, Radiation theory) in Dutch, edited by his student A. D. Fokker, 1919. His published university lectures in theoretical physics. Part 1. Stralingstheorie (1910-1911, Radiation theory) in Dutch, edited by his student A. D. Fokker, 1919.
In 1905, Einstein would use many of the concepts, mathematical tools and results Lorentz discussed to write his paper entitled "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies",[16] known today as the special theory of relativity. Because Lorentz laid the fundamentals for the work by Einstein, this theory was originally called the Lorentz–Einstein theory.[17]
In 1906, Lorentz's electron theory received a full-fledged treatment in his lectures at Columbia University, published under the title The Theory of Electrons.
The increase of mass was the first prediction of Lorentz and Einstein to be tested, but some experiments by Kaufmann appeared to show a slightly different mass increase; this led Lorentz to the famous remark that he was "au bout de mon latin" ("at the end of my [knowledge of] Latin" = at his wit's end)[18] The confirmation of his prediction had to wait until 1908 and later (see Kaufmann–Bucherer–Neumann experiments).
Lorentz published a series of papers dealing with what he called "Einstein's principle of relativity". For instance, in 1909,[19][failed verification] 1910,[20][21] 1914.[22] In his 1906 lectures published with additions in 1909 in the book "The theory of electrons" (updated in 1915), he spoke affirmatively of Einstein's theory:[19]
It will be clear by what has been said that the impressions received by the two observers A0 and A would be alike in all respects. It would be impossible to decide which of them moves or stands still with respect to the ether, and there would be no reason for preferring the times and lengths measured by the one to those determined by the other, nor for saying that either of them is in possession of the "true" times or the "true" lengths. This is a point which Einstein has laid particular stress on, in a theory in which he starts from what he calls the principle of relativity, I cannot speak here of the many highly interesting applications which Einstein has made of this principle. His results concerning electromagnetic and optical phenomena agree in the main with those which we have obtained in the preceding pages, the chief difference being that Einstein simply postulates what we have deduced, with some difficulty and not altogether satisfactorily, from the fundamental equations of the electromagnetic field. By doing so, he may certainly take credit for making us see in the negative result of experiments like those of Michelson, Rayleigh and Brace, not a fortuitous compensation of opposing effects, but the manifestation of a general and fundamental principle. It would be unjust not to add that, besides the fascinating boldness of its starting point, Einstein's theory has another marked advantage over mine. Whereas I have not been able to obtain for the equations referred to moving axes exactly the same form as for those which apply to a stationary system, Einstein has accomplished this by means of a system of new variables slightly different from those which I have introduced.
Though Lorentz still maintained that there is an (undetectable) aether in which resting clocks indicate the "true time":
1909: Yet, I think, something may also be claimed in favour of the form in which I have presented the theory. I cannot but regard the ether, which can be the seat of an electromagnetic field with its energy and its vibrations, as endowed with a certain degree of substantiality, however different it may be from all ordinary matter.[19]
1910: Provided that there is an aether, then under all systems x, y, z, t, one is preferred by the fact, that the coordinate axes as well as the clocks are resting in the aether. If one connects with this the idea (which I would abandon only reluctantly) that space and time are completely different things, and that there is a "true time" (simultaneity thus would be independent of the location, in agreement with the circumstance that we can have the idea of infinitely great velocities), then it can be easily seen that this true time should be indicated by clocks at rest in the aether. However, if the relativity principle had general validity in nature, one wouldn't be in the position to determine, whether the reference system just used is the preferred one. Then one comes to the same results, as if one (following Einstein and Minkowski) deny the existence of the aether and of true time, and to see all reference systems as equally valid. Which of these two ways of thinking one is following, can surely be left to the individual.[20]
Lorentz also gave credit to Poincaré's contributions to relativity.[23]
Indeed, for some of the physical quantities which enter the formulas, I did not indicate the transformation which suits best. That was done by Poincaré and then by Mr. Einstein and Minkowski. I did not succeed in obtaining the exact invariance of the equations. Poincaré, on the contrary, obtained a perfect invariance of the equations of electrodynamics, and he formulated the "postulate of relativity", terms which he was the first to employ. Let us add that by correcting the imperfections of my work he never reproached me for them.
|
|
|
|
|
Lorentz and general relativity
[edit]
Lorentz was one of few scientists who supported Einstein's search for general relativity from the beginning – he wrote several research papers and discussed with Einstein personally and by letter.[24] For instance, he attempted to combine Einstein's formalism with Hamilton's principle (1915),[25] and to reformulate it in a coordinate-free way (1916).[26][27] Lorentz wrote in 1919:[28]
The total eclipse of the sun of May 29, resulted in a striking confirmation of the new theory of the universal attractive power of gravitation developed by Albert Einstein, and thus reinforced the conviction that the defining of this theory is one of the most important steps ever taken in the domain of natural science.
Lorentz and quantum mechanics
[edit]
Lorentz gave a series of lectures in the fall of 1926 at Cornell University on the new quantum mechanics; in these he presented Erwin Schrödinger's wave mechanics.[29]
Change of priorities
[edit]
In 1910, Lorentz decided to reorganize his life. His teaching and management duties at Leiden University were taking up too much of his time, leaving him little time for research. In 1912, he resigned from his chair of theoretical physics to become curator of the "Physics Cabinet" at Teylers Museum in Haarlem. He remained connected to Leiden University as an external professor, and his "Monday morning lectures" on new developments in theoretical physics soon became legendary.[5]
Lorentz initially asked Einstein to succeed him as professor of theoretical physics at Leiden. However, Einstein could not accept because he had just accepted a position at ETH Zurich. Einstein had no regrets in this matter, since the prospect of having to fill Lorentz's shoes made him shiver. Instead Lorentz appointed Paul Ehrenfest as his successor in the chair of theoretical physics at the Leiden University, who would found the Institute for Theoretical Physics which would become known as the Lorentz Institute.[5]
After World War I, Lorentz was one of the driving forces behind the founding of the "Wetenschappelijke Commissie van Advies en Onderzoek in het Belang van Volkswelvaart en Weerbaarheid", a committee which was to harness the scientific potential united in the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences (KNAW) for solving civil problems such as food shortage which had resulted from the war. Lorentz was appointed chair of the committee. However, despite the best efforts of many of the participants the committee would harvest little success. The only exception being that it ultimately resulted in the founding of TNO, the Netherlands Organisation for Applied Scientific Research.[5]
Lorentz was also asked by the Dutch government to chair a committee to calculate some of the effects of the proposed Afsluitdijk (Enclosure Dam) flood control dam on water levels in the Waddenzee. Hydraulic engineering was mainly an empirical science at that time, but the disturbance of the tidal flow caused by the Afsluitdijk was so unprecedented that the empirical rules could not be trusted. Originally Lorentz was only supposed to have a coordinating role in the committee, but it quickly became apparent that Lorentz was the only physicist to have any fundamental traction on the problem. In the period 1918 till 1926, Lorentz invested a large portion of his time in the problem.[30] Lorentz proposed to start from the basic hydrodynamic equations of motion and solve the problem numerically. This was feasible for a "human computer", because of the quasi-one-dimensional nature of the water flow in the Waddenzee. The Afsluitdijk was completed in 1932, and the predictions of Lorentz and his committee turned out to be remarkably accurate.[31][5] One of the two sets of locks in the Afsluitdijk was named after him.
In 1881, Lorentz married Aletta Catharina Kaiser. Her father was J.W. Kaiser, a professor at the Academy of Fine Arts. He was the Director of the museum which later became the well-known Rijksmuseum (National Gallery). He also was the designer of the first postage stamps of The Netherlands.
There were two daughters, and one son from this marriage.
Dr. Geertruida Luberta Lorentz, the eldest daughter, was a physicist. She married Professor Wander Johannes de Haas, who was the Director of the Cryogenic Laboratory at the University of Leiden.[32]
In January 1928, Lorentz became seriously ill, and died shortly after on 4 February.[5] The respect in which he was held in the Netherlands is apparent from Owen Willans Richardson's description of his funeral:
The funeral took place at Haarlem at noon on Friday, February 10. At the stroke of twelve the State telegraph and telephone services of Holland were suspended for three minutes as a revered tribute to the greatest man the Netherlands has produced in our time. It was attended by many colleagues and distinguished physicists from foreign countries. The President, Sir Ernest Rutherford, represented the Royal Society and made an appreciative oration by the graveside.
Unique 1928 film footage of the funeral procession with a lead carriage followed by ten mourners, followed by a carriage with the coffin, followed in turn by at least four more carriages, passing by a crowd at the Grote Markt, Haarlem, from the Zijlstraat to the Smedestraat, and then back again through the Grote Houtstraat towards the Barteljorisstraat, on the way to the "Algemene Begraafplaats" at the Kleverlaan (northern Haarlem cemetery), has been digitized on YouTube.[34] Amongst others, the funeral was attended by Albert Einstein and Marie Curie.[35]
Lorentz is considered one of the prime representatives of the "Second Dutch Golden Age", a period of several decades surrounding 1900 in which the natural sciences flourished in the Netherlands.[5]
Richardson describes Lorentz as:
A man of remarkable intellectual powers. Although steeped in his own investigation of the moment, he always seemed to have in his immediate grasp its ramifications into every corner of the universe. The singular clearness of his writings provides a striking reflection of his wonderful powers in this respect. He possessed and successfully employed the mental vivacity which is necessary to follow the interplay of discussion, the insight which is required to extract those statements which illuminate the real difficulties, and the wisdom to lead the discussion among fruitful channels, and he did this so skillfully that the process was hardly perceptible.[33]
M. J. Klein (1967) wrote of Lorentz's reputation in the 1920s:
For many years physicists had always been eager "to hear what Lorentz will say about it" when a new theory was advanced, and, even at seventy-two, he did not disappoint them.[36]
 Lorentz-monument Park Sonsbeek in Arnhem, the Netherlands
Einstein wrote of Lorentz:
1928: The enormous significance of his work consisted therein, that it forms the basis for the theory of atoms and for the general and special theories of relativity. The special theory was a more detailed expose of those concepts which are found in Lorentz's research of 1895.[37]
1953: For me personally he meant more than all the others I have met on my life's journey.[38]
Poincaré (1902) said of Lorentz's theory of electrodynamics:[39]
The most satisfactory theory is that of Lorentz; it is unquestionably the theory that best explains the known facts, the one that throws into relief the greatest number of known relations. It is due to Lorentz that the results of Fizeau on the optics of moving bodies, the laws of normal and abnormal dispersion and of absorption are connected with each other. Look at the ease with which the new Zeeman phenomenon found its place, and even aided the classification of Faraday's magnetic rotation, which had defied all Maxwell's efforts.
Paul Langevin (1911) said of Lorentz:[40]
It will be Lorentz's main claim to fame that he demonstrated that the fundamental equations of electromagnetism also allow of a group of transformations that enables them to resume the same form when a transition is made from one reference system to another. This group differs fundamentally from the above group as regards transformations of space and time.'
Lorentz was chairman of the first Solvay Conference held in Brussels in the autumn of 1911. Shortly after the conference, Poincaré wrote an essay on quantum physics which gives an indication of Lorentz's status at the time:[41]
At every moment the twenty physicists from different countries could be heard talking of the [quantum mechanics] which they contrasted with the old mechanics. Now what was the old mechanics? Was it that of Newton, the one which still reigned uncontested at the close of the nineteenth century? No, it was the mechanics of Lorentz, the one dealing with the principle of relativity; the one which, hardly five years ago, seemed to be the height of boldness.
In addition to the Nobel prize, Lorentz received a great many honours for his outstanding work. He was elected a Foreign Member of the Royal Society (ForMemRS) in 1905.[1] The Society awarded him their Rumford Medal in 1908 and their Copley Medal in 1918. He was elected an Honorary Member of the Netherlands Chemical Society in 1912.[42] He was an International Member of the American Philosophical Society, the United States National Academy of Sciences, and the American Academy of Arts and Sciences.[43][44][45]
|
|
|
|
|


Different cyclotron size: a) Lawrence ́s first one, b) Venezuela First one (courtesy of Dorly Coehlo), c) Fermi National Laboratory at CERN. And size matters, and Cyclotrons win as best hospital candidates due to Reactors are bigger, harder and difficult to be set in a hospital installation. Can you imagine a nuclear reactor inside a health installation? Radiation Protection Program will consume all the budget available. Size, controlled reactions, electrical control, made cyclotrons easy to install, and baby cyclotrons come selfshielded so hospital don ́t need to spend money in a extremely large bunker. Now on, we are going to talk about our first experience with the set up of a baby cyclotron for medical uses inside the first PET installation in Latin America. “Baby” means its acceleration “D” diameters are suitable to be set inside a standard hospital room dimensions, with all its needs to be safetly shielded for production transmision and synthetized for human uses for imaging in Nuclear Medicine PET routine. When we ask why Cyclotrons are better than reactors for radioisotopes production to be used in Medicine, we also have to have in mind that they has: 1. Less radioactive waste 2. Less harmful debris
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Different-cyclotron-size-a-Lawrence-s-first-one-b-Venezuela-First-one-courtesy-of_fig3_221906035

|
|
|
|
|
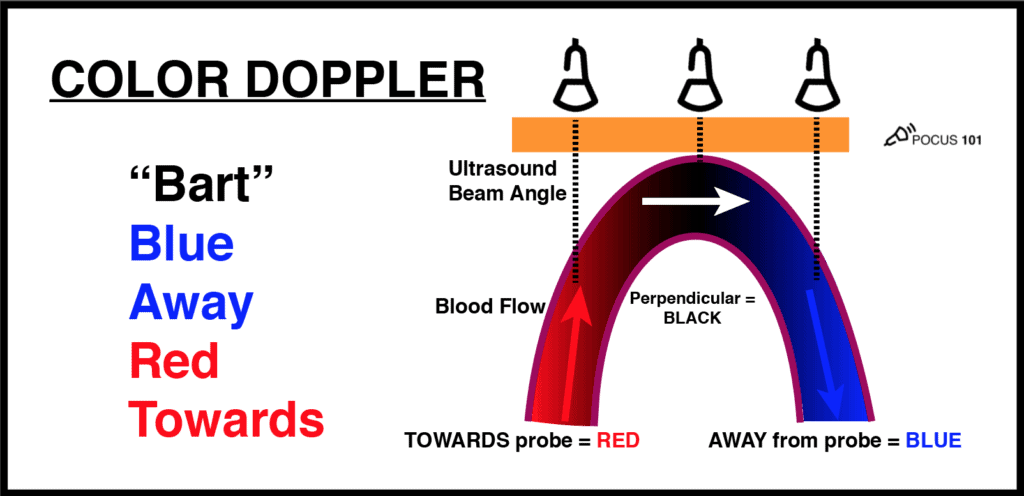
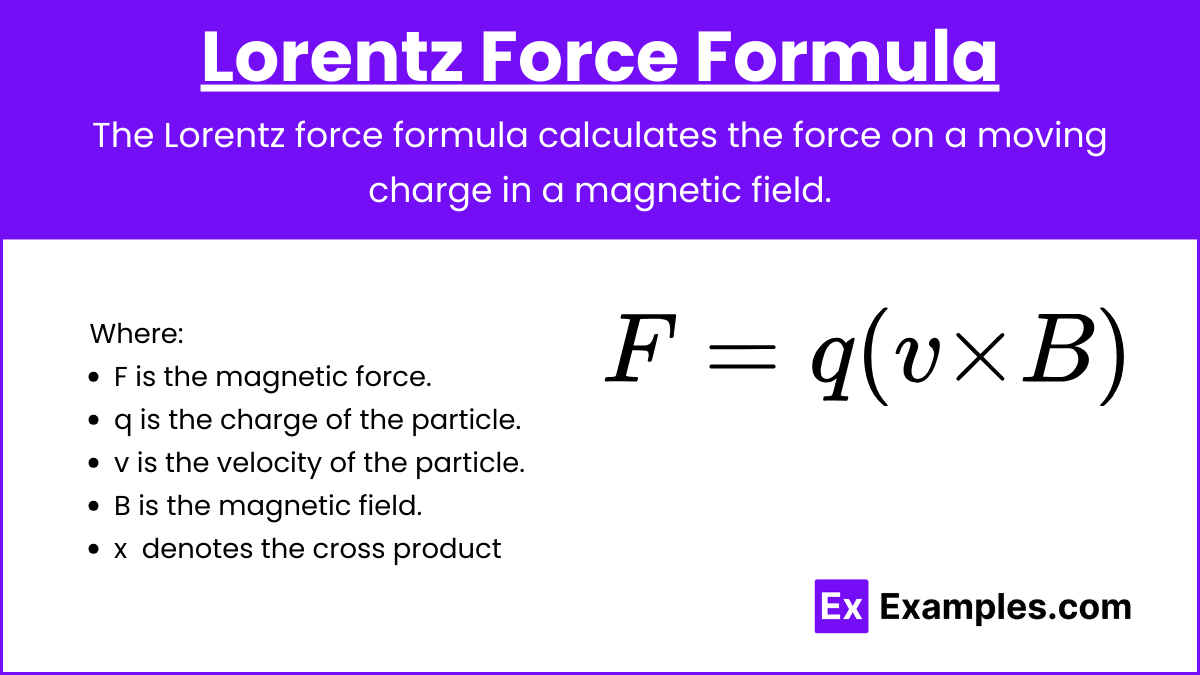
MOTORES ELÉCTRICOS. Ley de LORENTZ

La fuerza magnética está descrita por la ley de la Ley de Lorentz:
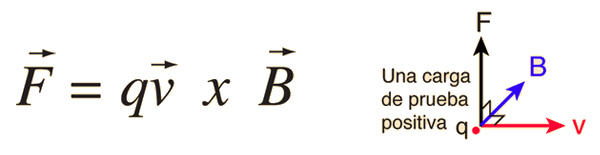
Fuerza de Lorentz
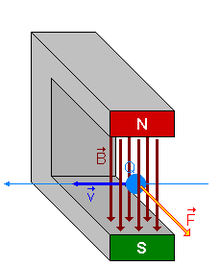
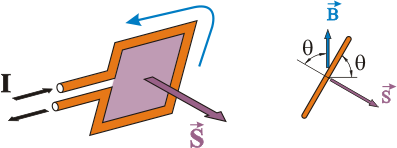
Una cantidad fija de carga q que se mueve a una velocidad constante v en un campo magnético uniforme B, experimenta una fuerza F, perpendicular tanto a la velocidad v como al campo B

Hendrik Antoon Lorentz, 1921
A veces queremos encontrar la fuerza que actúa sobre un alambre de longitud L por el que pasa una corriente I que se encuentra dentro de un campo magnético. Podemos lograrlo al reordenar la expresión previa. Si recordamos que la velocidad es la distancia dividida entre el tiempo, y puesto que la corriente I es la cantidad de carga que fluye por unidad de tiempo, entonces
q.v.B = q.(L/t).B = (q/t).L.B = I.L.B
Así obtenemos otra expresión para la Fuerza de Lorentz:

Estas fuerzas se pueden utilizar para provocar un PAR DE FUERZAS que hagan girar una espira, siendo este efecto el principio de funcionamiento de los motores eléctricos.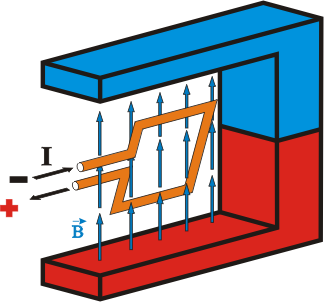

Par de fuerzas de Lorentz sobre una espira

Motor CC
Examen hasta aquí
El valor del momento de fuerza viene dado por el producto de la fuerza por la distancia que separa ambas líneas de acción:
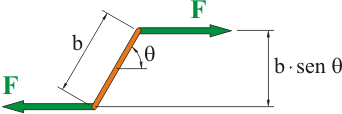 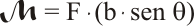
A continuación, se sustituye la fuerza por su valor, teniendo en cuenta que la intensidad y el campo magnético son siempre perpendiculares. Después se reorganizan los términos de la expresión:

Ahora, el producto de la longitud de la espira por su anchura da como resultado la superficie de la misma. Con ésto se obtiene una expresión que es independiente de la forma de la espira, y sólo influye su superficie:
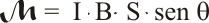
Y, ya para acabar, se transforma esta igualdad en un producto vectorial si se considera la superficie como un vector cuyo módulo es el valor de superficie, dirección perpendicular al plano de la espira y sentido definido por la regla de la mano derecha según el sentido de la intensidad, previamente invertida:
 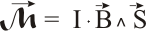 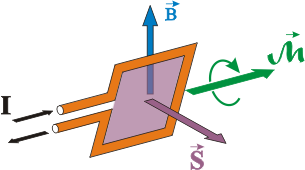
Con lo cual, además, tenemos la dirección del momento de giro como un vector, y nuevamente por la regla de la mano derecha este vector indica el sentido de giro. Cuando hay varias espiras, la expresión se multiplica por el número de las mismas:


Me gusta esto:
|
|
|
|
|
- ARCHIVE
Lorenz-force motors
In 1831, Michael Faraday discovered that subjecting a coil to a moving magnetic field induces a current. Today, electromagnetic induction powers most
In 1831, Michael Faraday discovered that subjecting a coil to a moving magnetic field induces a current. Today, electromagnetic induction powers most electric motors, along with a phenomenon described in Ampere's law (involving the forces generated between the magnetic field surrounding a current-carrying conductor and an external magnetic field.) But the interaction of the magnetic and mechanical forces inherent to this design is not always the most efficient.
That's why some motors use Lorenz forces instead. Named after the Nobel laureate, this force is that experienced by a point charge moving along a wire in a magnetic field, at right angles to both the current and magnetic vector. Current in a Lorenz motor may be viewed as a procession of moving charges subject to Lorentz force, thereby transduced to a force on the conductor itself. This force is then multiplied by the number of coil conductors.
Note: Versions of Lorenz-force motors are sometimes also called pancake motors; Timken has used them in cutting-edge vehicle designs detailed here.
Q&A
In short, Lorentz and Faraday motors both use electromagnetic properties to create mechanical work, but the way the forces are applied in a traditional Faraday motor means it is always trying to reshape itself. By contrast, the lack of steel in Lorentz-force motors allows application of electromagnetic forces with almost no mechanical energy losses — and no electrical lamination “buzzing” noise.
Q: How powerful are Lorenz-force motors?
A: It's been held that power density is not achieved by coils alone. However, the forming, interleaving, precision layer winding, and square magnet (or litz) wire in Lorenz stators eliminates the need for steel poles to concentrate flux created by current in the coil. Stacking of coil and rotor segments multiplies torque in a compact package, and extra multiplication is possible with integral planetary gearheads — in virtually the same footprint as an induction motor.
Q: How does the performance of Lorenz-force motors differ from traditional motors?
A: Eliminating poles to concentrate flux means the motors effectively eliminate core saturation, without exotic steels. No saturation means a linear current/torque relationship over an unusually wide range resulting in high torque at low rpm, including at stall. This allows the use of high current to produce proportionally high torque, for better efficiency and less waste heat. Together, extended torque linearity and higher torque translate into excellent damping and reduced overshoot in servo applications. (Because the controller doesn't have to compensate for saturation or iron losses, it gets back everything it puts in.) Performance is consistent in all modes: constant or variable speed, steady state, intermittent, and reversible.
Lorenz-force motors are also responsive, precise (in terms of speed and torque), and repeatable (to within two arc-seconds). Their low coil inductance and thus electrical time constant translate to better precision and bandwidth in servo applications.
Q: Why aren't Lorenz-force motors the norm?
A: The majority of motor applications today require only brute horsepower. And until recently, most motors only needed to provide rotation and torque — for which conventional motors are quite efficient under the right circumstances. But this is changing.
In a growing number of applications, motors are being called on to provide motion control in addition to horsepower. This has led to increased use of specialty motors that accelerate quickly, present little inertia, and produce torque proportional to current with no torque ripple. Although today's applications may justify the more costly winding configurations of Lorenz motors, there is one caveat. Lorenz motors have no core losses and thus no inductive heating, but the elimination of steel from the heat-generating portion of the motor makes it more difficult to remove the heat caused by winding I2R losses. Another concern is that off-the-shelf amplifiers may not be suitable for Lorentz force motors owing to the extremely low inductance due to the lack of iron.
This month's handy tips provided by J.E.Marth,V.P.of Engineering at Bodine Electric Co., and Edmund Glück. For more information, visit www.bodine.com.
|
|
|
|
|
Viktor Schauberger: The Man Who Invented Flying Discs For The Nazis
- ENGLISH NEWS
- TECHNOLOGY GAME SCIENCE
VN EN
Some historical figures leave behind little real information, but many secrets and mysteries.
 Ảnh minh họa
One such person was a scientist, thinker, philosopher, and inventor, and the author of innovative technological ideas. He was hired to work for the Third Reich and allegedly built for the Nazis a flying machine that looked like a disc-shaped UFO for the Nazis.
And then this man suddenly disappeared from history as quickly and mysteriously as he appeared. It is officially believed that he died a natural death, but there are many theories that he was either deliberately killed or his death was faked, but in fact was kidnapped for his own purposes.
The Mysterious Disappearance Of Viktor Schauberger
A man named Viktor Schauberger was born in Austria in 1885 and initially had an experience that had nothing to do with his future fame as the inventor of Hitler’s UFOs. He grew up in a hereditary family of foresters living in a vast area of remote wilderness in Holzschlag, Upper Austria, and spent most of his youth and middle years tending more than 10,000 hectares of land.

During this time, constantly being in nature, he began to make many observations that profoundly changed his life and outlook. In particular, he was absolutely fascinated by water, which he regarded as an independent living organism, calling it the “Blood of the Earth” and the source of all living things.
He especially focused on such properties of water as its spiral forms, eddies, fast currents, eddies, and easy harmony with the surrounding world.
He obsessively studied the movements and effects of water, continuing to form many theories, and then he began to craft completely innovative types of spiral-cut water gutters, the design of which was based on his own hydrodynamic system.
According to this system, an inward-moving and swirling water vortex could be used for power and thrust, which was the beginning of his revolutionary new idea for a new type of engine that relied on implosion (an explosion directed inward) rather than conventional explosions.
Viktor Schauberger was completely self-taught, he never took any university courses, but he soon gained international recognition thanks to some of his ideas, patents, and inventions, and controversy. He was critical of the many inventions available in his era, believing that they work against the laws of nature and are destructive.
Instead, he embraced the idea that humanity and nature can live together using alternative energy sources, such as using natural processes and live in harmony with them. His motto was “Kapieren und kopieren” (To comprehend and copy nature). Schauberger believed that many inventions of mankind were contrary to nature, and later he stated that even the propeller was an imperfect invention:
“As nature best demonstrated in the case of the winged maple seed, today’s propeller is a pressure rotor, and therefore a brake rotor, whose purpose is to allow the heavy maple seed to slowly fall to the ground like a parachute and move away from the wind.
No bird has such a rotating object on its head, nor a fish on its tail. This brake rotor was only used by a person for forward propulsion. As the propeller spins, drag increases in proportion to the square of the rotation speed. It is also a sign that this supposed propulsion device is not built naturally and is therefore out of place. “
Schauberger sought to bring his ideas to life by coming up with a detailed theory according to which water vortices can build on each other to create more and more forces, which, in turn, will create a force opposite to gravity. In essence, Schauberger was explaining how to create anti-gravity, which he called diamagnetism.
He used these theories to create fantastic inventions such as a water blast turbine that sucked in air in a spiral, reaching enormous forces. He also invented the machine that created a typhoon-like suction force to control the temperature in a room, and a power generator. These machines created energy from water and air using spiral pipes and nozzles.
All of this worked on the principles of clean energy and working with nature, apparently with little or no pollution and being completely sustainable.
It might seem odd that such a radical promoter of green energy and work with nature caught the attention of the Nazis, who were not particularly concerned with preserving the environment. But he really piqued their interest, and in 1934 the Nazis approached him with a tempting offer to work for them for a good salary. Schauberger agreed.
Furthermore. In 1938, Nazi Party member Julius Streicher allegedly personally ordered him to build an aircraft that could use a vortex engine. This device had to have the shape of a disk and move completely differently from all modern aircraft while hovering in the air in one place (levitation), performing precise maneuvers, and accelerating at high speeds.

Basically, they wanted Schauberger to build a futuristic anti-gravity ship using his own natural theories, and since they were the Nazis, he had no choice but to agree once again, receiving an exorbitant amount of money.
In 1940, Schauberger created the first prototype of his artificial UFO, called Repulsin A, which used friction between vortices and the surrounding air to force the air downward, creating an overall lifting and propelling effect, more or less producing a kind of mini-tornado, on the energy of which this ship moved.
However, it was found that the vortex motor was unstable, and the fan inside the device could not spin as fast as required because the blades were pushing out too much air. At the time, no way was found to circumvent the problem of generating more intense rotational energy, and the device was deemed too impractical.

Indeed, during the testing of the ship, although it could indeed levitate, it was almost impossible to control or move forward, usually quickly spinning out of control or even flying through the roof of the test hangar.
According to rumors, the Nazis were furious at Schauberger’s inability to solve these problems, which caused the inventor to be temporarily imprisoned. But then he came under the personal attention of Heinrich Himmler, who drew Schauberger to work on another miracle of technology – a new type of silent mini-submarine, and then ordered to continue work on a new version of the anti-gravity device called Vril-7.
It is not known how far Schauberger went with the Vril-7, as the end of World War II halted all secret Nazi research (at least official), with most of his work, prototypes, and plans destroyed so that they would not fall into the hands of the Allies.

The Americans, knowing how important Schauberger was to the Germans, arrested him and took him to the United States, intensively interrogating him, but were never able to get much information from him. However, they were able to use all the information they received to the maximum. The fundamental principles that Schauberger used were later applied to several projects, including the Avro Canada VZ-9 Avrocar, which was a vertical takeoff and landing aircraft developed during the Cold War era, and others.
Schauberger, while in the United States, tried for several more years on various civilian vortex technology projects such as generators, water purification systems and air purification devices, before eventually returning to Austria on September 25, 1958, almost penniless.
He died quite suddenly, just five days after his return to his homeland, taking all his secrets with him to the grave.
Since then, various conspiracy theories have regularly emerged about Schauberger, including that his research went much further than anticipated, and that many of the UFOs that were seen during the Second World War were in fact Schauberger’s experimental devices.
But all these are just hypotheses and unverified rumors, for sure no one knows anything. He remains in many ways a ghost person, the true scope of his work is unknown, and his research is enigmatic.
https://www.xaluannews.com/modules.php?name=News&file=article&sid=3296405 |
|
|
|
|
Subestación eléctrica de maniobras Magdalena I (Parque Solar Magdalena I)
NOVIEMBRE 17, 2021 PV MAGAZINE
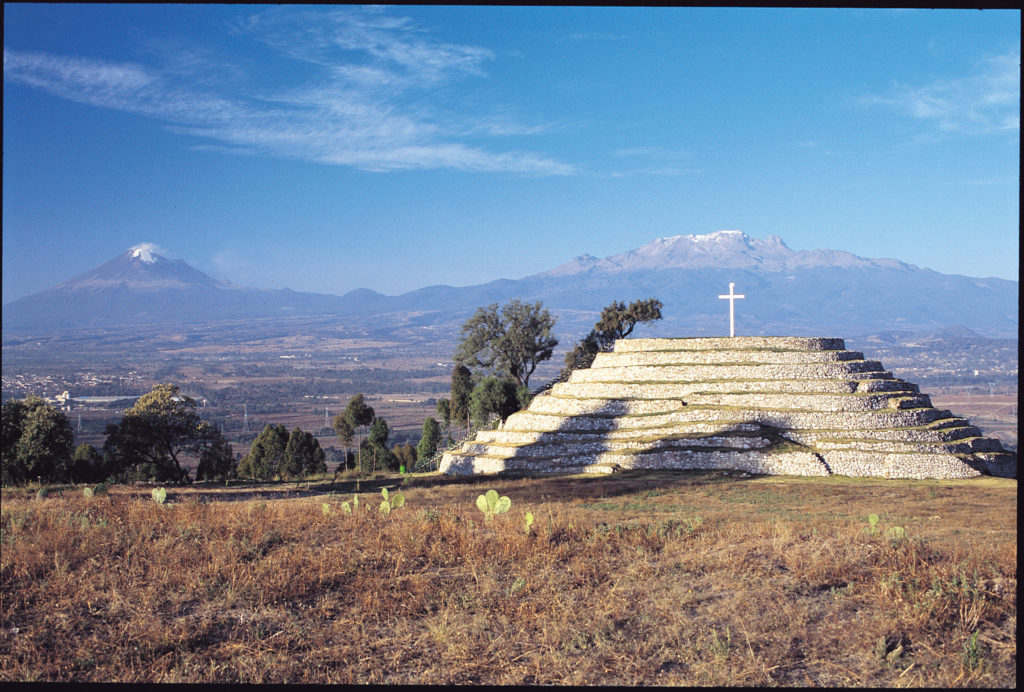
Pirámide de la Espiral Xochitecatl, Tlaxcala
Fotografía: Gobierno del estado de Tlaxcala
La Dirección General de Impacto y Riesgo Ambiental de la Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales informa que ha recibido la documentación de la firma promovente Más Energía, para el proyecto de la Subestación eléctrica de maniobras Magdalena I (Parque Solar Magdalena I).
El proyecto consiste en la construcción, operación y mantenimiento de una subestación eléctrica de maniobras, dos accesos, y una línea eléctrica de entronque de 400 Kv que se interconectará a una línea de transmisión eléctrica existente de 400 Kv propiedad de la Comisión Federal de Electricidad para desahogar la energía eléctrica que se genera en la planta fotovoltaica parque solar Magdalena I al Sistema Eléctrico Nacional.
Este contenido está protegido por derechos de autor y no se puede reutilizar. Si desea cooperar con nosotros y desea reutilizar parte de nuestro contenido, contacte: editors@pv-magazine.com.
 
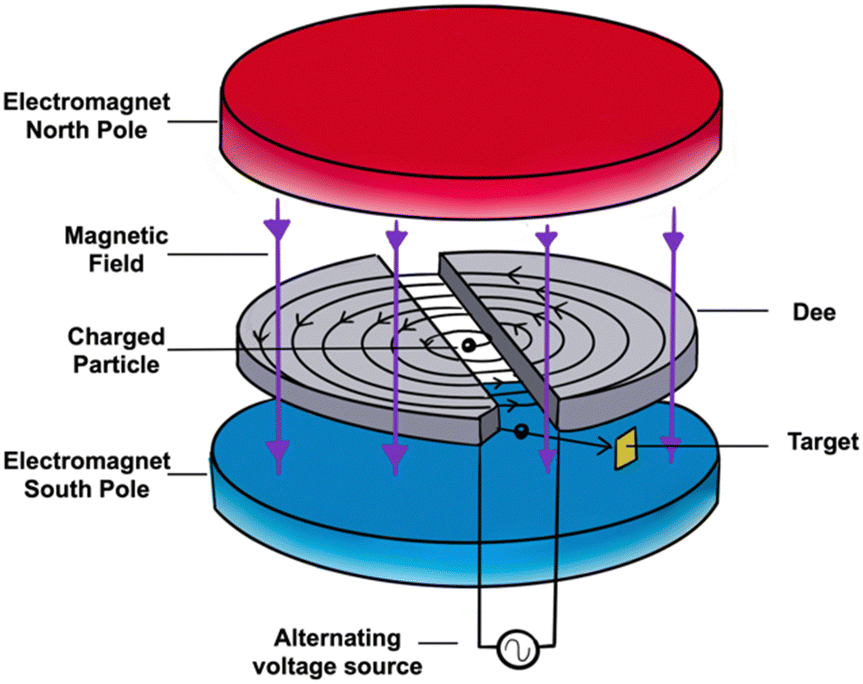
6 Schematic representation of a cyclotron. The distance between the pole pieces of the magnet is shown larger than reality to allow seeing what is inside
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Schematic-representation-of-a-cyclotron-The-distance-between-the-pole-pieces-of-the_fig3_237993541
|
|
|
 Primer
Primer
 Anterior
2 a 13 de 13
Siguiente
Anterior
2 a 13 de 13
Siguiente
 Último
Último

|

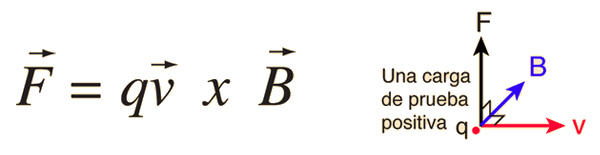

![]()





![]()
![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()
























 Ảnh minh họa
Ảnh minh họa