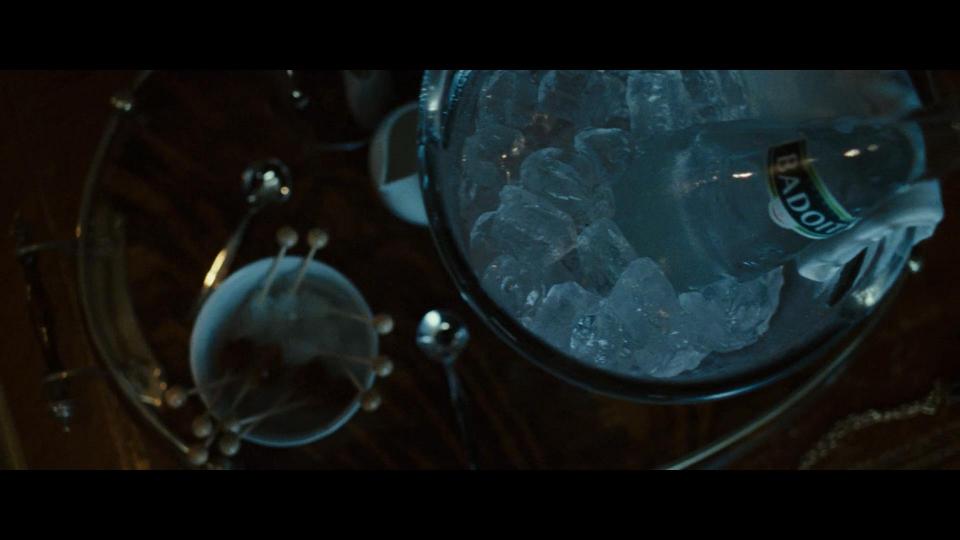|
|
“Banking secrecy has its roots in Calvinism”
 Calvin's influence spread well beyond Geneva RDB Calvin's influence spread well beyond Geneva RDB
Today's Switzerland - and its cherished bank secrecy - still reflect the influence of church reformer Jean Calvin, an economic think tank director tells swissinfo.
This content was published onApril 26, 2009 - 10:21
6 minutes
Xavier Comtesse, who heads the western Swiss branch of Avenir Suisse, says Calvin stood for morality in the granting of credit, but also for protection of the personal sphere.
This year marks the 500th birthday of the religious reformer whose ideas shaped the Protestant Church. In his honour Protestant denominations have designated 2009 Calvin Year.
Calvin, who spent much of his time working in Geneva, not only influenced democracy in Switzerland but modern-day thinking on both moral and financial matters, Comtesse believes.
swissinfo: What is the basis of Calvin’s Protestantism?
Xavier Comtesse: It is based on the Bible written in the language of the people, on the separation of church and state, and on the understanding that the grassroots faithful – who fund the community – choose their own priests.
This Calvinist form of institutional organisation has also over time had an influence on non-religious areas of the Swiss mentality. All state institutions remain separate from religious ones, and bottom up participation in political decisions continues from communal to national level.
Both lead to an emancipation of the people, an ’empowerment’, as we say today.
swissinfo: What would Switzerland look like today without Calvin?
X.C.: I don’t think we’d have direct democracy without this popular emancipation that was spurred on by Calvin. We would probably be a republic [with an elected president], like our neighbours. Of course when talking about German-speaking Switzerland we should mention [Zurich reformer Huldrych] Zwingli just as much as Calvin.
This communication from community organisations up to the highest state level is typical for us Swiss.
swissinfo: To what extent was Geneva more significant than Zurich?
X.C.: In those days French-speaking Switzerland did not exist. Geneva was the place to be – across the whole country. Basel was worth considering, but Zurich wasn’t. Neither was Bern nor Lausanne.
That is also why Calvin is rated so much more important internationally than Zwingli. Even in the post-Napoleonic period Zurich was smaller than Geneva both in the number of inhabitants and economically.
swissinfo: How did Calvin stamp the mark of the Reformation and the image of Switzerland on the world?
X.C.: I know most about his influence on the United States. There Calvinism is very pronounced with around 15 million Calvinists – called Presbyterians in Anglo-Saxon countries.
There are also communities in Scotland and South Korea. Worldwide there are said to be around 50 million Presbyterians. But there are very few of them in Switzerland.
swissinfo: What was Calvin’s influence on the economy and banking?
X.C.: As a reaction to the papal selling of indulgences as a mean of raising money for Rome, Calvin was one of the first church leaders to permit the granting of loans with interest – albeit tied to high moral standards.
That forged a link with the present: extortionate interest didn’t come into question, therefore the loans had to be cheap. As in religion and politics, the thinking behind this banking was to protect the citizen through high moral standards.
Also considered worth protecting by Protestantism was the personal sphere. Add this to being able to bank and you get banking secrecy.
swissinfo: Historically banking secrecy was meant to protect citizens from state interference.
X.C.: Exactly. And that’s why there are many misunderstandings concerning the term. The description ‘banking secrecy’ is actually incorrect – ‘protection of the private sphere by the bank’ would be more appropriate.
Such legal protection is not unique to Switzerland. In France for example a wife has no right to any information about her husband’s bank account – French legal law considers that his private sphere.
We Swiss simply go one step further. We protect against any state despotism. This way of thinking has historical roots in Protestantism, which in Calvin’s time sought to protect the people against the despotism of the powerful Catholic Church.
swissinfo: What remains from these Calvinist ethics today – bearing in mind the drama playing out in the world of banking and finance?
X.C.: At the moment we’re in a moral crisis. As a result we’ll soon have to grapple more with social responsibility.
That will be a form of secular Calvinism with new, still moral, but no longer religious characteristics. Regarding quality for example – new ISO standards in the area of quality attempt to rectify deficits in the area of responsibility.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is based in Geneva – like many other international institutions. This is also part of Calvin’s legacy.
Another ‘Geneva’ institution is the World Wide Web – invented at Cern. This also works ‘Calvinistically’ insofar as it enables direct access to information to the population, or rather the user.
Until now, powerful intermediaries were needed for this access. The internet has reformed access to the markets – similar to Calvin’s reformation of direct access to God.
swissinfo-interview: Alexander Künzle
|
|
|
|
|
CRIPTOCOMUNISMO – MARK ALIZART
Descargar libro (epub)
Por Mark Alizart
Las criptomonedas a menudo son consideradas “revolucionarias” y es posible que lo sean. Y no solamente en un sentido metafórico, sino también histórico, político e incluso filosófico.
De hecho, la promesa de Satoshi Nakamoto de que es posible comerciar sin la intermediación de banqueros parece que podría desencadenar una revolución en la economía de la misma manera que Martin Lutero comenzó su revolución en la Iglesia en 1517, al afirmar que los creyentes podían tener una relación directa con Dios sin sacerdotes como intermediarios, o como Oliver Cromwell, George Washington o Maximilien de Robespierre provocaron una revolución en el Estado en los tiempos modernos al declarar que la gente podía gobernarse a sí misma sin príncipes como intermediarios.
Obviamente, el White Paper que en el 2009 dio origen a Bitcoin, la criptomoneda más famosa, no nos dice cómo obtener la vida eterna. Tampoco los pequeños cálculos de un pequeño inversor preocupado por sus ahorros parecen tener mucho en común con la lucha por la libertad. Sin embargo, la revolución que encarna es real. La economía es un aspecto fundamental de nuestras sociedades. Incluso comparte rasgos con las esferas religiosas y políticas.

Si las hostias tienen forma de moneda es porque originalmente se fundían en los mismos moldes1. El primer “banco central” de la historia, el Bank of England, fue fundado por los Puritanos ingleses en 1694. A menudo se cree, desde Max Weber, que el capitalismo fue conducido a las fuentes bautismales por la “ética del trabajo” protestante, pero el aporte más notable de la Reforma a la economía, más bien, fue la ingeniería financiera moderna2. Al volver a poner a la fe (fide) y a la culpabilidad en el centro de la vida religiosa, el protestantismo permitió que socios que se tienen “confianza” (con-fide) puedan darse “crédito” entre sí (crede, “creer”, “tener la fide”) para sus deudas (tanto morales como financieras). Por cierto, fue un protestante, John Law, quien a comienzos del siglo XVIII introdujo en Francia el primer papel moneda3. Y es también el concepto protestante de fe, en el sentido que supone confiar, ceder y, por lo tanto, ser libre, el que permitió que las democracias liberales se construyeran y emanciparan de la monarquía.
De hecho, el invento de Satoshi, en la medida en que también trata con la confianza y la fe, es un digno heredero de la historia teológica y política de Occidente4. Incluso puede que represente su cumplimiento. Mientras que la Reforma y la Revolución se basaron en un concepto subjetivo de fe, Bitcoin es un algoritmo de fe. Al permitir liberarse matemáticamente de los “terceros de confianza”, Bitcoin es una máquina de producir fe y libertad5.
Dicho esto, muchas ideas equivocadas rodean a las revoluciones y lo que ellas implican, y los “fanáticos” de las criptomonedas –palabra que podemos usar puesto que de hecho es una nueva religión y un nuevo partido– podrían decepcionarse respecto de las suyas.
Si las revoluciones del pasado nos enseñan algo, es que no son un camino en una sola dirección hacia la emancipación, la libertad [freedom] o la liberación [liberty]. La Reforma no puso fin al tráfico de personas en la religión, aunque hirió gravemente a la Iglesia; las revoluciones inglesa, estadounidense y francesa tampoco pusieron fin al Estado como tal, aunque detuvieron a la monarquía. De la misma manera, es dudoso que Bitcoin simplemente signifique el fin de los bancos centrales, del sistema financiero mundial y del Estado policial, solo para dar a luz a un mundo nuevo y valiente de individuos empoderados liberados de pagar impuestos y obedecer la ley, como lo expresaron muchos profetas libertarios, bitcoiners de alt-right y criptoculturistas.
Ciertamente, hubo campesinos que durante la Edad Media se reunieron en torno a los gurús de la Reforma como Thomas Müntzer, quienes dedujeron de las tesis de Lutero que ahora era posible vivir libres de toda autoridad moral y clerical. También hubo enragésrevolucionarios que creían que su libertad recién obtenida les daba el derecho de cortar tantas cabezas como quisieran, especialmente aquellas más altas que las suyas. Eventualmente, sin embargo, todos descubrirían más temprano que tarde que estaban equivocados sobre el significado más profundo de la Reforma y la Revolución. El protestantismo iba a introducir aún más rigor en la religión que el catolicismo, hasta el punto de que los protestantes terminarían siendo conocidos como “puritanos”. Se abolieron los sacerdotes, se destruyeron las catedrales, los altares, el incienso y el latín de la iglesia, solo para ser reemplazados por una práctica religiosa que, al eliminar todos los signos visibles, solo se hizo más ascética, y tuvo que ser observada en todo momento y en todos los aspectos de la vida secular. Del mismo modo, la democracia demostraría ser aún más compleja y enrevesada que el antiguo régimen. Los príncipes fueron abolidos solo para ver la burocracia desenfrenada, con enjambres de funcionarios y libros de leyes más gruesos que el diccionario y la guia telefónica combinados.
Ahora se podría argumentar que el regreso de la Iglesia y del Estado, después de la Reforma y las Revoluciones liberales que intentaron destruirlos, significa que fracasaron en lo que se suponía que debían hacer. La verdad es que este retorno fue una herramienta, no un error. Lutero no quería derrocar la ley de Dios, quería cumplirla. Rousseau no quería que la ley de la Naturaleza reemplazara la ley de los hombres, quería asegurarse de que se observara la ley de los hombres. De hecho, ambos habían entendido que la libertad era, paradójicamente, la mejor manera de hacer cumplir la ley de Dios y el gobierno de los hombres porque, en última instancia, la libertad no consiste en ser libre de toda ley, sino en imponerse libremente leyes a uno mismo, como la palabra “autonomía” lo dice claramente: una “ley” (nomos) impuesta sobre “uno mismo” (auto).
Lo mismo puede decirse sobre el proyecto de Satoshi. Quiere restaurar la confianza, no destruirla. Quiere restaurar las instituciones en las que podemos creer, no quemarlas. Y de una manera muy convincente, lo hace de la misma manera que la Reforma y las Revoluciones, al reemplazar las viejas instituciones por otras nuevas, que solo son más robustas porque son instituciones elegidas e impuestas libremente sobre nosotros. Bitcoin nos libera al encadenarnos, como la bien llamada blockchain lo establece claramente. La Cripto nos libera uniéndonos unos a otros. Es una institución de libertad, no la libertad de todas las instituciones.
Por lo tanto, no hay duda de que las criptomonedas traerán consigo un nuevo viento de cambio, extendiendo la libertad en todo el mundo, pero no de la forma en que los niñitos del Tea Party lo han soñado. Lo hará sometiendo nuestras vidas a una nueva ley, una nueva Iglesia y un nuevo Estado, aún más austeros que los de la Reforma de Lutero, más rigurosos que los de la República de Rousseau. Y esta es la razón por la cual este ensayo afirma que el régimen teológico-político que la Cripto finalmente establecerá no es el “criptoanarquismo”. Por el contrario, es un régimen conocido precisamente por hacer que las personas reconozcan que viven en comunidades y no como átomos separados, y por querer que compartan lo que tienen en común, en lugar de separarlo para su propio beneficio; un régimen que también se consideró revolucionario, incluso si no logró dar lugar a la revolución que sus creyentes esperaban, es decir, el comunismo, o más precisamente: el criptocomunismo.
https://confoederatio.noblogs.org/post/2020/10/04/criptocomunismo/ |
|
|
|
|
Subestación eléctrica de maniobras Magdalena I (Parque Solar Magdalena I)
NOVIEMBRE 17, 2021 PV MAGAZINE
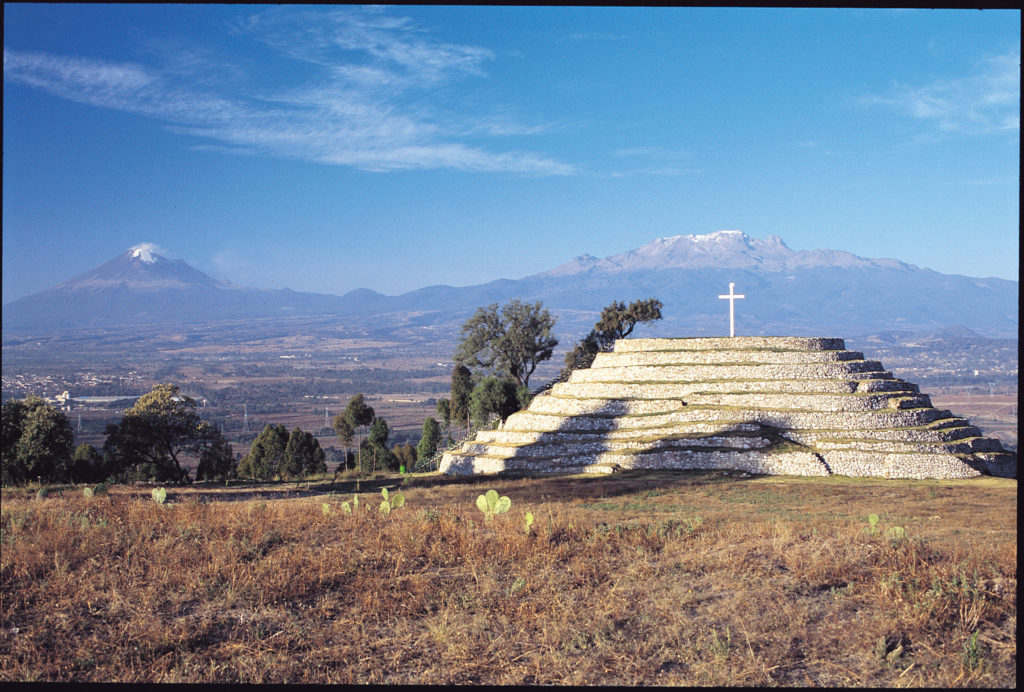
Pirámide de la Espiral Xochitecatl, Tlaxcala
Fotografía: Gobierno del estado de Tlaxcala
La Dirección General de Impacto y Riesgo Ambiental de la Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales informa que ha recibido la documentación de la firma promovente Más Energía, para el proyecto de la Subestación eléctrica de maniobras Magdalena I (Parque Solar Magdalena I).
El proyecto consiste en la construcción, operación y mantenimiento de una subestación eléctrica de maniobras, dos accesos, y una línea eléctrica de entronque de 400 Kv que se interconectará a una línea de transmisión eléctrica existente de 400 Kv propiedad de la Comisión Federal de Electricidad para desahogar la energía eléctrica que se genera en la planta fotovoltaica parque solar Magdalena I al Sistema Eléctrico Nacional.
Este contenido está protegido por derechos de autor y no se puede reutilizar. Si desea cooperar con nosotros y desea reutilizar parte de nuestro contenido, contacte: editors@pv-magazine.com.
 
6 Schematic representation of a cyclotron. The distance between the pole pieces of the magnet is shown larger than reality to allow seeing what is inside
https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Schematic-representation-of-a-cyclotron-The-distance-between-the-pole-pieces-of-the_fig3_237993541
|
|
|
|
|
First Lady of The United States
Eleanor Roosevelt
Rolex Oyster Perpetual
I once heard a rumor that both U.S. President Franklin Roosevelt and Harry Truman wore Rolex watches. Of course, I spent a zillion hours looking for examples of them wearing Rolex watches, but to date the first U.S. President I documented wearing a Rolex was Dwight Eisenhower. When Nick Gould recently shared the following images with me of former First Lady, Eleanor Roosevelt wearing a Rolex Oyster Perpetual, I almost fell out of my chair. Nick mentioned Charlie Dunne shared them with him.
Eleanor Roosevelt is pictured below with her husband, President Roosevelt on January 20, 1941 as they return to the White House following his third term election.
Eleanor Roosevelt was one of the most beloved First Ladies of The United States and in the photo below we see the U.S. Presidents and First Ladies attending here funeral. From left to right we see Lady Bird Johnson, Jaqueline & John F. Kennedy, Lyndon Baines Johnson, Harry Truman, as well as Mamie and Dwight Eisenhower.
https://www.rolexmagazine.com/2021/02/first-lady-of-united-states-eleanor.html#/page/1 |
|
|
|
|

I love the adventure stories with twisted plots, mysteries, puzzles. That is why I love the stories created by Dan Brown and his major character Professor Robert Langdon who was very well played by Tom Hanks in the series of successful movies. Moreover, in my travel adventures I managed to visit most of the countries, places, museums, etc, and even CERN, which are described in the books and movies. And when I watch the movies I travel back in time together with Professor Langdon.
So, today I invite you to solve great mysteries of Leonardo, Illuminati, and Dante. It’s time to refresh your knowledge of history and arts. Welcome aboard!
Jacques Saunière, a Louvre curator, is pursued through the Grand Gallery by an albino Catholic monk named Silas, who demands the location of the Priory’s “keystone” to find and destroy the Holy Grail. Saunière gives him a false lead and is murdered. The police find his body posed like Da Vinci’s Vitruvian Man. Police captain Bezu Fache has his lieutenant, Jérôme Collet, summon American symbologist Robert Langdon, who is in Paris for a lecture on the interpretation of symbols, to examine Saunière’s body.
Langdon is shown the body and a secret message, readable only by blacklight. It contains an out-of-order Fibonacci sequence. Sophie Neveu, a police cryptographer and Saunière’s granddaughter, tells Langdon that Fache planted a tracker on him after finding the words, “P.S. Find Robert Langdon” at the end of Saunière’s secret message. Fache believes that Langdon murdered Saunière. Sophie throws away the tracker, distracting the police while they sneak around the Louvre, finding more clues in Leonardo da Vinci’s works. Langdon deduces that Saunière was the grand master of the Priory of Sion. And our adventure begins.
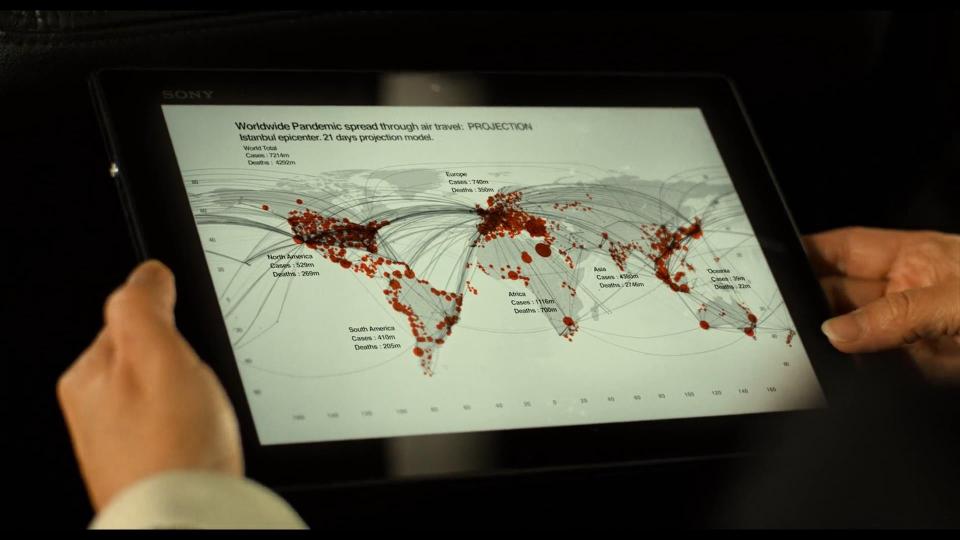
We meet Professor Robert Langdon for the first time during his lecture. He uses Sony laptop for his presentation.
In one of the next scenes of the movie we can clearly see the van with Bosch logo. Same is for the famous French water – Badoit. We can see it in a bucket full of ice.
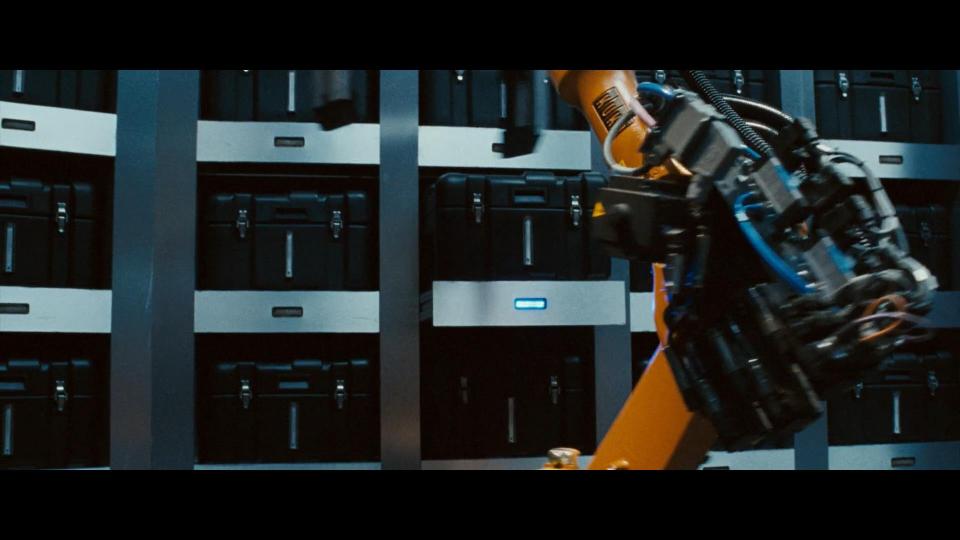
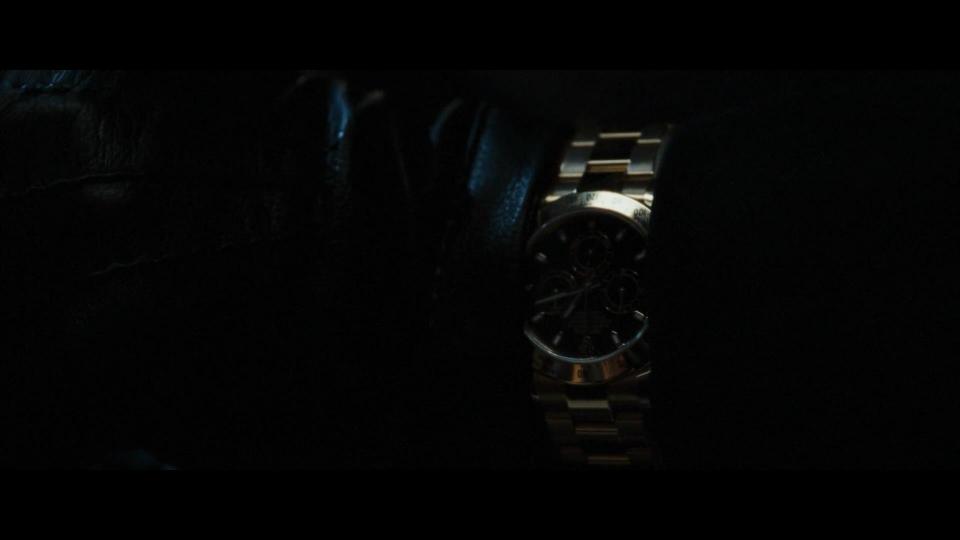
When Robert Langdon and Sophie Neveu (Audrey Tautou) come to the bank to retrieve the cryptex, we can see how KUKA robot picks the right box that belonged to Jacques Saunière. When the bank employee helps the main characters to pass the police, we can get a glimpse of his Rolex watch.
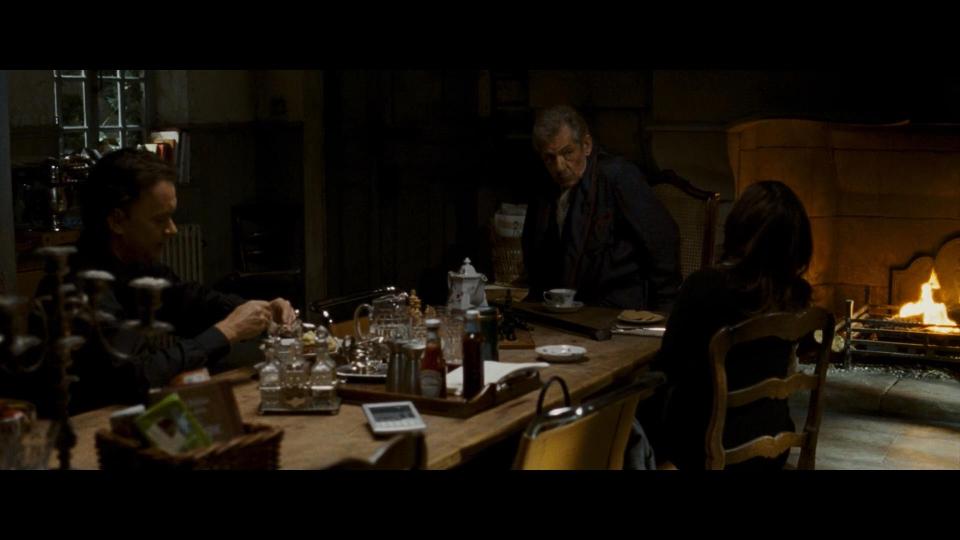
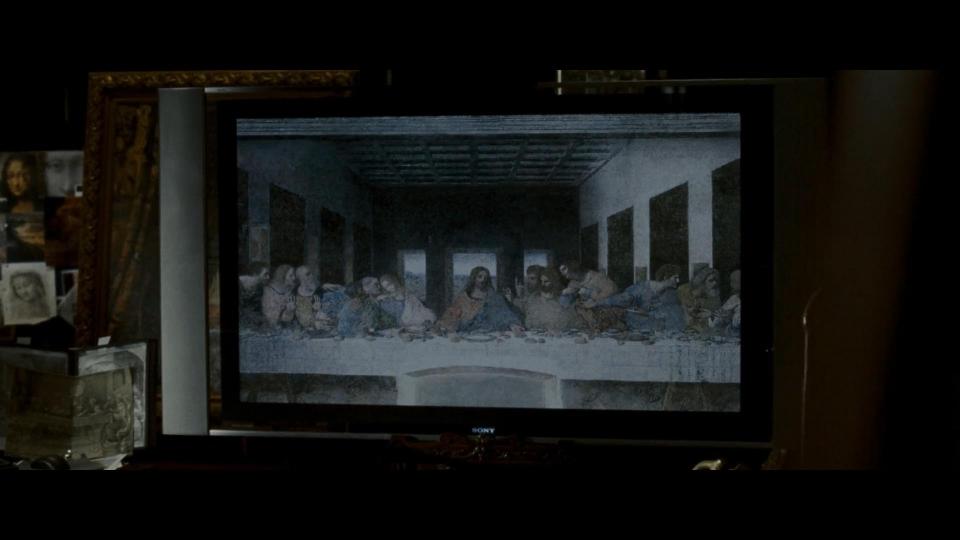
At Sir Leigh Teabing’s (Ian McKellen) house our guests learn more about The Last Supper painting secrets. Their host is also a fan of Sony, so we may see various TV sets and displays in the house. While enjoying their evening tea, we can as well see Heinz there, of course.
When Robert Langdon and Sophie look for a tomb in London, they borrow a Sony Ericsson smartphone to search for more information.
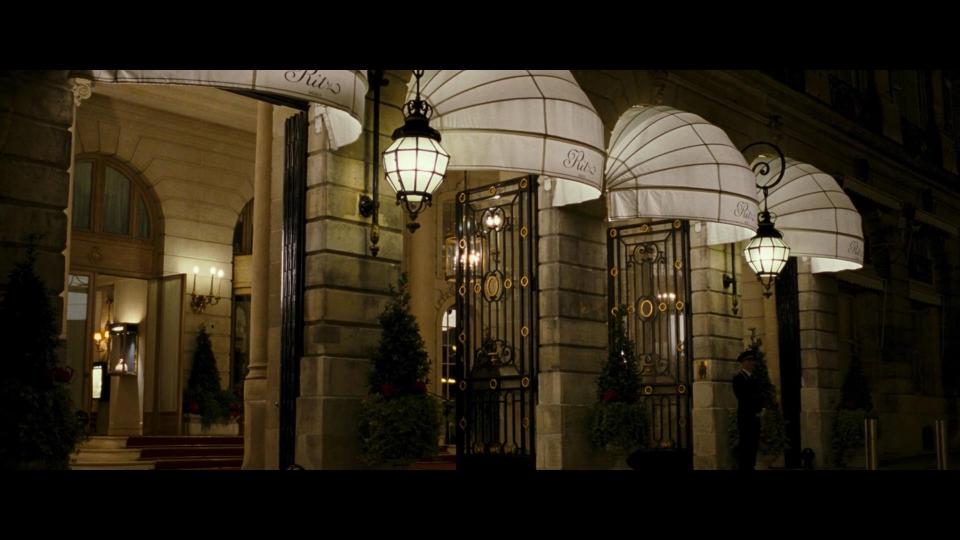
In the final scene of the movie we see that Robert lives in Ritz hotel in Paris, and from there he starts his evening walk to follow the Arago medallions and come to the Louvre.
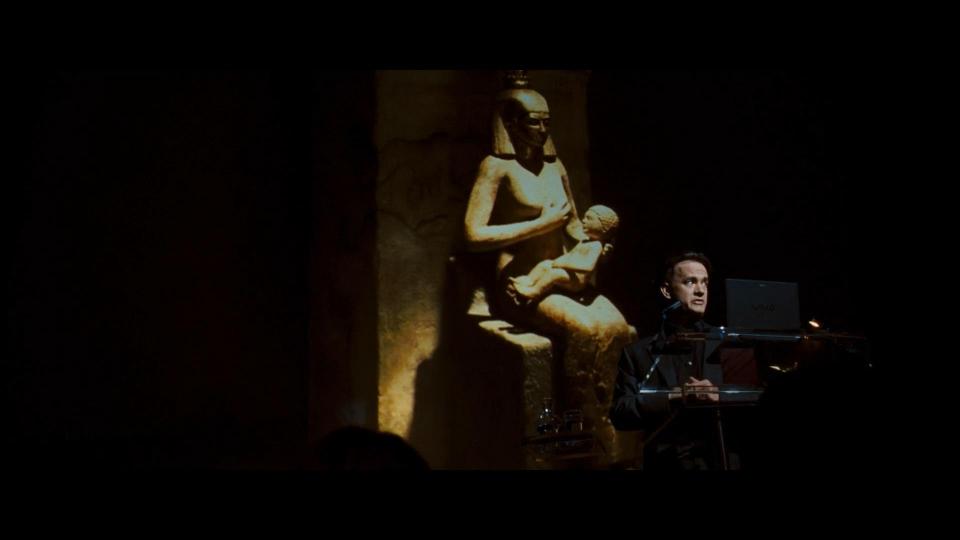
The Catholic Church mourns the sudden death of Pope Pius XVI, and prepares for the papal conclave to elect his successor in Vatican City. Father Patrick McKenna (Ewan McGregor), the camerlengo, takes temporary control of the Vatican during the sede vacante period.
Meanwhile, at CERN, scientists Father Silvano Bentivoglio and Dr. Vittoria Vetra (Ayelet Zurer) create three canisters of antimatter. As Vetra goes to evaluate the experiment, she discovers that Silvano has been murdered, and one of the canisters was stolen. Shortly thereafter, four of the preferiti, the favored candidates to be elected pope, are kidnapped by a man claiming to represent the Illuminati. He sends the Vatican a warning, claiming he will murder each of the cardinals from 8 p.m. to midnight, when the stolen antimatter will explode and destroy the city, hidden somewhere within.
Unlike two other movies, there are only few product placements in Angels & Demons. And they can be divided in two categories – Sony and TV channels.
That is why we see Sony computers and displays in the first scene in CERN.
And when the events of the movie accelerate, we can see various TV channels broadcasting from Vatican City. These are Canal+, CNN, and Reuters.
And this is it for Angels & Demons. More product placements are waiting in Inferno.
Some time after helping the Vatican dealing with an antimatter threat, Harvard University professor Robert Langdon awakens in a hospital room in Florence, Italy, with no memory of what has transpired over the last few days, but being plagued with hellish visions. Dr. Sienna Brooks (Felicity Jones), the doctor tending to him, reveals that he is suffering from amnesia as a result of a bullet wound to the head. An orderly says the police are there to question Langdon but the officer turns out to be Vayentha, an assassin, who shoots the orderly while coming up the hallway. Brooks helps Langdon to escape, and they flee to her apartment.
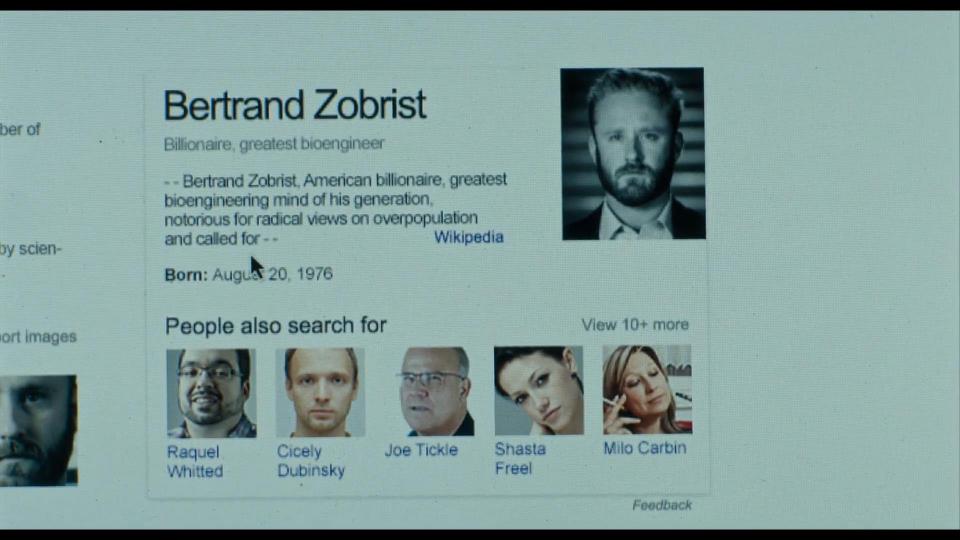
Among Langdon’s personal belongings, Langdon and Brooks find a Faraday pointer, a miniature image projector with a modified version of Sandro Botticelli’s Map of Hell, which itself is based on Dante’s Inferno. They soon realize this is the first clue in a trail left by Bertrand Zobrist, a dangerously unstable villain who believed that rigorous measures were necessary to reduce the Earth’s growing population, and who committed suicide three days earlier after being chased by armed government agents.
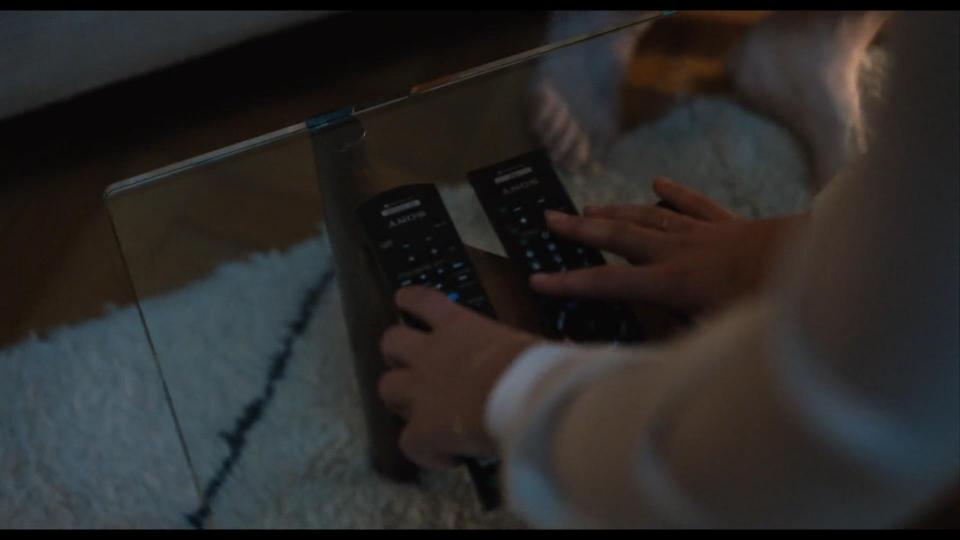
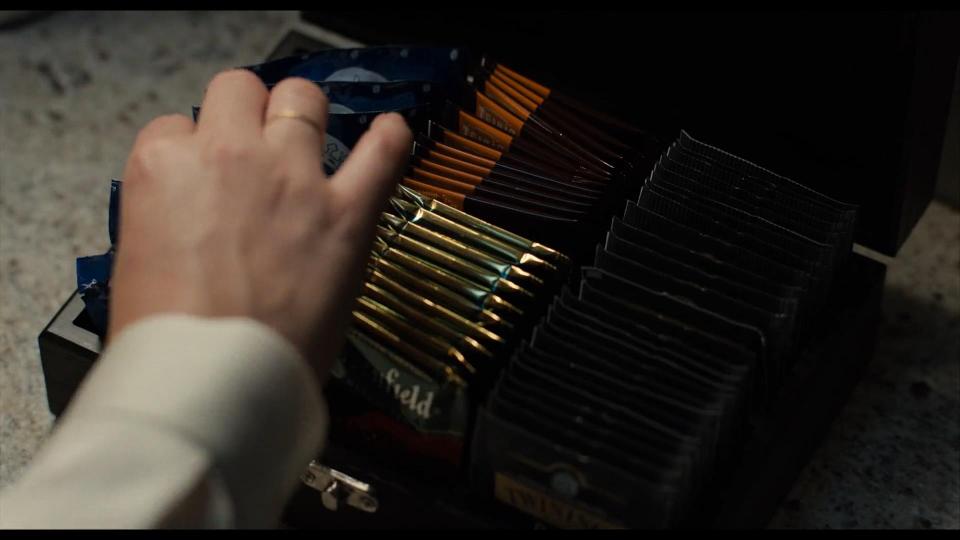
When Robert Langdon wakes up in Sienna’s house, we can find various brands across her apartment. First of all we see Sony TV remote controls. And when Professor asks for coffee, Sienna goes to the kitchen where we spot tea brands like Greenfield and Twinings.
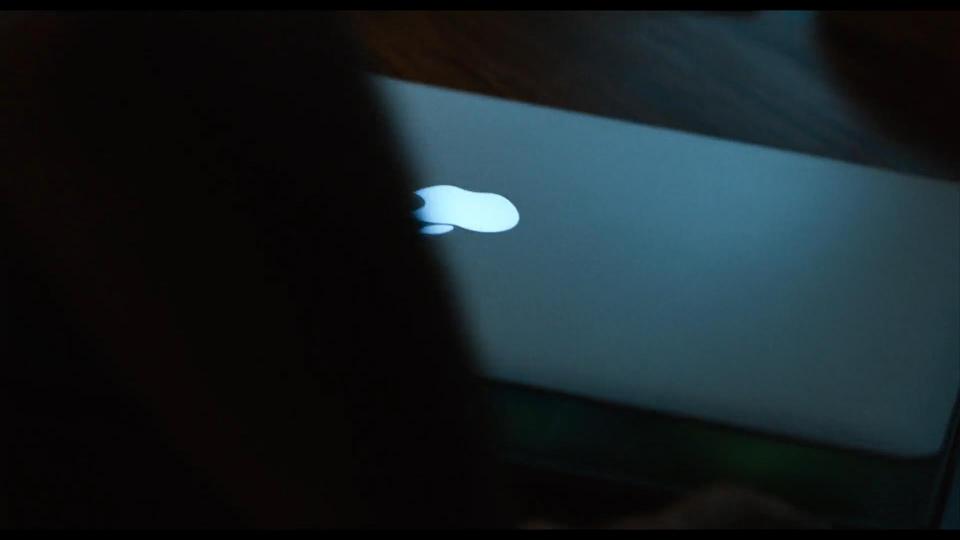
While Sienna is looking for some clothes for Robert, he decides to use her Apple MacBook to check his Google mail.
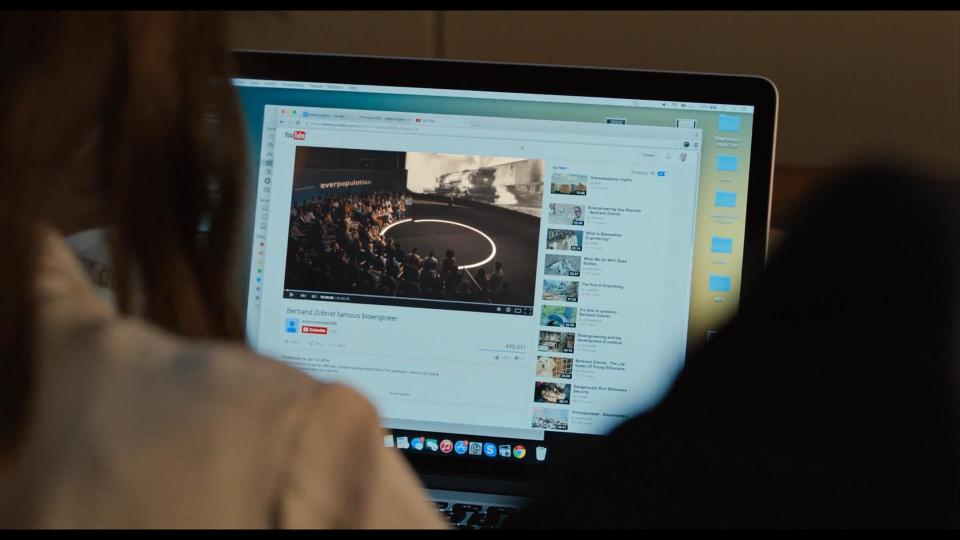
When Robert and Sienna decide to call to the consulate, we see that Sienna uses Sony smartphone. When they realize that they can trust no one, they start their investigation. First, they search for the information about Zobrist. Google, Wikipedia, and YouTube are very helpful even in the movies.
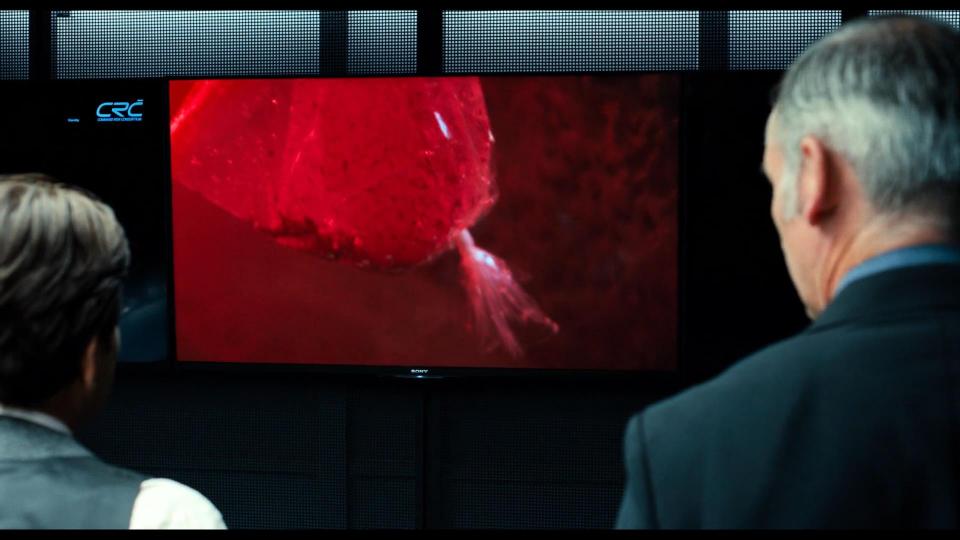
Later in the movie we see more Sony product placements – a TV set in Command Risk Consortium, a smartphone and a tablet used by Elizabeth Sinskey.
When Robert Langdon and Sienna Brooks try to escape from their enemies with the help of Christoph Bouchard, they make everyone believe they are going to fly to Switzerland via Swiss, but instead they take an Italo speed train to Venice.
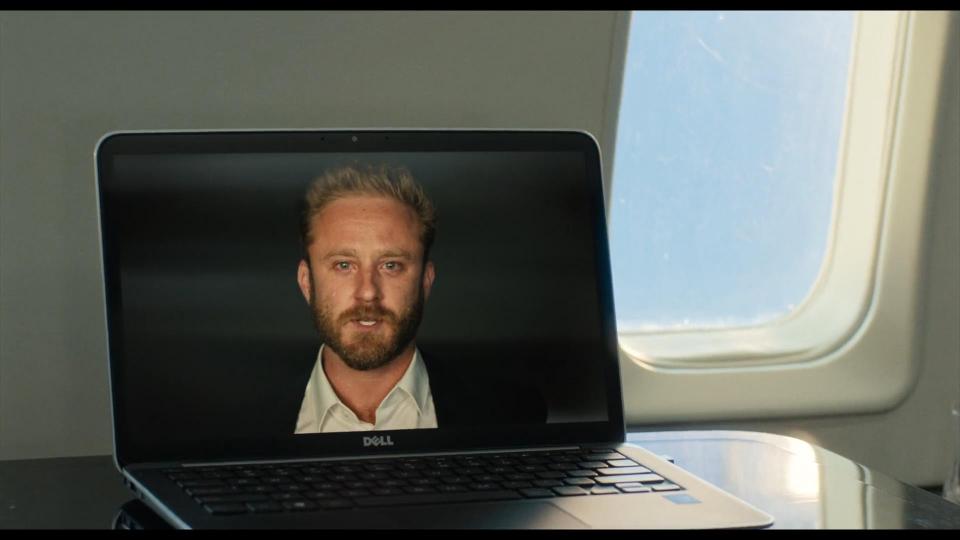
When finally the truth is revealed and memory is restored, Robert and Elizabeth go to Istanbul to stop Sienna from unleashing the virus. Elizabeth shares Zobrist’s message with Robert. They watch it together on a Dell laptop.
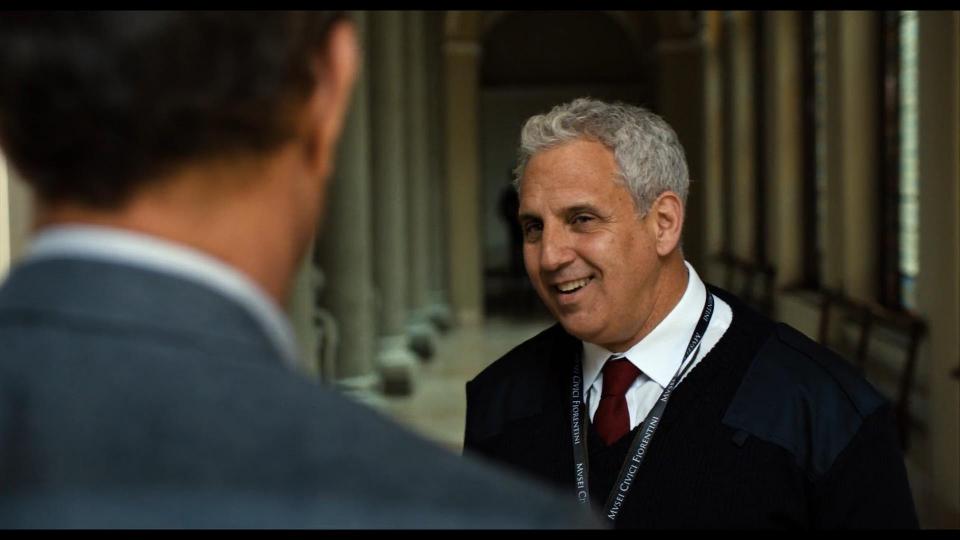
In the final scene when Professor returns Dante’s mask to the museum, we can see the museum employee wearing the tag with the Florentine Civic Museums branding.
Unfortunately, there is no news about the future movies with Tom Hanks. And no news about any new books. Looking forward to new adventures of Professor Langdon.
I highly recommend you to visit Product Placement section of the website. You will find more amazing movie series analysed there.
https://www.marketing-psycho.com/robert-langdon-product-placement/ |
|
|
|
|
The Da Vinci Code (2006) clip with quote And do all the drivers wear a Rolex? Yarn is the best search for video clips by quote. Find the exact moment in a ...
The Da Vinci Code (2006) clip with quote And do all the drivers wear a Rolex? Yarn is the best search for video clips by quote. Find the exact moment in a ...
The Da Vinci Code (2006) clip with quote And do all the drivers wear a Rolex? Yarn is the best search for video clips by quote. Find the exact moment in a ...
31 may 2008 — Am I mistaken or is the driver in the security van of Da Vinci Code wearing a Rolex TT??
In "The Da Vinci Code ... Collet : (looks at Vernet's wrist and the camera gives us a clear view of that 116523 on Vernet's wrist) And do all the drivers wear a ...
... WATCH MORE: ▻ Subscribe to Now Playing: bit.ly/OfficialNowPlaying ... Here you will find all of the most memorable moments, scenes ...
|
|
|
|
|
Earth from Space – Arc de Triomphe, Paris
Status Report
May 13, 2022

Arc de Triomphe, Paris.
ESA
This striking, high-resolution image of the Arc de Triomphe, in Paris, was captured by Planet SkySat – a fleet of satellites that have just joined ESA’s Third Party Mission Programme in April 2022.
The Arc de Triomphe, or in full Arc de Triomphe de l’Étoile, is an iconic symbol of France and one of the world’s best-known commemorative monuments. The triumphal arch was commissioned by Napoleon I in 1806 to celebrate the military achievements of the French armies. Construction of the arch began the following year, on 15 August (Napoleon’s birthday).
The arch stands at the centre of the Place Charles de Gaulle, the meeting point of 12 grand avenues which form a star (or étoile), which is why it is also referred to as the Arch of Triumph of the Star. The arch is 50 m high and 45 m wide.
The names of all French victories and generals are inscribed on the arch’s inner and outer surfaces, while the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier from World War I lies beneath its vault. The tomb’s flame is rekindled every evening as a symbol of the enduring nature of the commemoration and respect shown to those who have fallen in the name of France.
The Arc de Triomphe’s location at the Place Charles de Gaulle places it at the heart of the capital and the western terminus of the Avenue des Champs-Élysées (visible in the bottom-right of the image). Often referred to as the ‘most beautiful avenue in the world’, the Champs-Élysées is known for its theatres, cafés and luxury shops, as the finish of the Tour de France cycling race, as well as for its annual Bastille Day military parade.
This image, captured on 9 April 2022, was provided by Planet SkySat – a fleet of 21 very high-resolution satellites capable of collecting images multiple times during the day. SkySat’s satellite imagery, with 50 cm spatial resolution, is high enough to focus on areas of great interest, identifying objects such as vehicles and shipping containers.
SkySat data, along with PlanetScope (both owned and operated by Planet Labs), serve numerous commercial and governmental applications. These data are now available through ESA’s Third Party Mission programme – enabling researchers, scientists and companies from around the world the ability to access Planet’s high-frequency, high-resolution satellite data for non-commercial use.
Within this programme, Planet joins more than 50 other missions to add near-daily PlanetScope imagery, 50 cm SkySat imagery, and RapidEye archive data to this global network.
Peggy Fischer, Mission Manager for ESA’s Third Party Missions, commented, “We are very pleased to welcome PlanetScope and SkySat to ESA’s Third Party Missions portfolio and to begin the distribution of the Planet data through the ESA Earthnet Programme.
“The high-resolution and high-frequency imagery from these satellite constellations will provide an invaluable resource for the European R&D and applications community, greatly benefiting research and business opportunities across a wide range of sectors.”
To find out more on how to apply to the Earthnet Programme and get started with Planet data, click here.
– Download the full high-resolution image.
|
|
|
 Primer Primer
 Anterior
21 a 35 de 35
Siguiente Anterior
21 a 35 de 35
Siguiente
 Último
Último

|