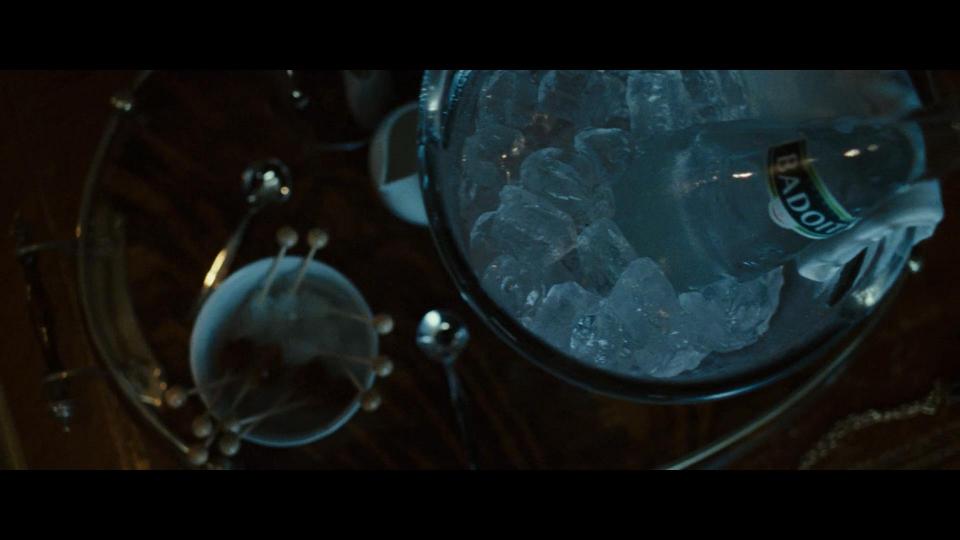|
|

 
Source: Facts.net
Welcome to our daily historical journey! In this article, we will explore the intriguing events and interesting facts that occurred on September 27th throughout history. It’s fascinating to delve into the past and uncover the significant milestones, memorable moments, and noteworthy achievements that shape our world today. From groundbreaking discoveries and technological advancements to political events and cultural milestones, September 27th has proven to be a day of great importance. This day holds a treasure trove of historical significance, and by exploring the events that unfolded on this date, we gain a deeper understanding of our collective past. So, join us as we embark on a captivating journey through time to discover all the facts and events that have taken place on September 27th in history.
HISTORICAL EVENTS
-
1954: The U.S. Army opens the first nuclear power station at Shippingport, Pennsylvania.
-
1964: The Warren Commission releases its report, concluding that Lee Harvey Oswald acted alone in the assassination of President John F. Kennedy.
-
1996: Taliban forces seize control of Kabul, the capital of Afghanistan.
-
2008: SpaceX launches the Falcon 1, becoming the first privately-funded liquid-fueled rocket to reach orbit.
-
2014: Hong Kong pro-democracy protests, also known as the “Umbrella Movement,” begin after China announces plans for strict control over Hong Kong’s elections.
SCIENTIFIC BREAKTHROUGHS
-
1825: George Stephenson successfully operates the first practical steam locomotive, the “Locomotion No. 1,” on the Stockton and Darlington Railway in England.
-
1942: The first successful controlled nuclear chain reaction is achieved by a team led by Enrico Fermi at the University of Chicago.
-
1998: The first robotic mission to Mars, NASA’s Mars Pathfinder, deploys the Sojourner rover and begins transmitting valuable scientific data back to Earth.
-
2007: NASA’s Dawn spacecraft is launched, embarking on a mission to study the protoplanet Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres.
-
2015: Scientists announce the discovery of liquid water on Mars, raising the possibility of potential microbial life on the planet.
  Enrico Fermi, Italian-American physicist, received the 1938 Nobel Prize in physics for identifying new elements and discovering nuclear reactions by his method of nuclear irradiation and bombardment. He was born in Rome, Italy, on September 29, 1901, and died in Chicago, Illinois, on November 28, 1954.
|
|
|
|
|

I love the adventure stories with twisted plots, mysteries, puzzles. That is why I love the stories created by Dan Brown and his major character Professor Robert Langdon who was very well played by Tom Hanks in the series of successful movies. Moreover, in my travel adventures I managed to visit most of the countries, places, museums, etc, and even CERN, which are described in the books and movies. And when I watch the movies I travel back in time together with Professor Langdon.
So, today I invite you to solve great mysteries of Leonardo, Illuminati, and Dante. It’s time to refresh your knowledge of history and arts. Welcome aboard!
Jacques Saunière, a Louvre curator, is pursued through the Grand Gallery by an albino Catholic monk named Silas, who demands the location of the Priory’s “keystone” to find and destroy the Holy Grail. Saunière gives him a false lead and is murdered. The police find his body posed like Da Vinci’s Vitruvian Man. Police captain Bezu Fache has his lieutenant, Jérôme Collet, summon American symbologist Robert Langdon, who is in Paris for a lecture on the interpretation of symbols, to examine Saunière’s body.
Langdon is shown the body and a secret message, readable only by blacklight. It contains an out-of-order Fibonacci sequence. Sophie Neveu, a police cryptographer and Saunière’s granddaughter, tells Langdon that Fache planted a tracker on him after finding the words, “P.S. Find Robert Langdon” at the end of Saunière’s secret message. Fache believes that Langdon murdered Saunière. Sophie throws away the tracker, distracting the police while they sneak around the Louvre, finding more clues in Leonardo da Vinci’s works. Langdon deduces that Saunière was the grand master of the Priory of Sion. And our adventure begins.
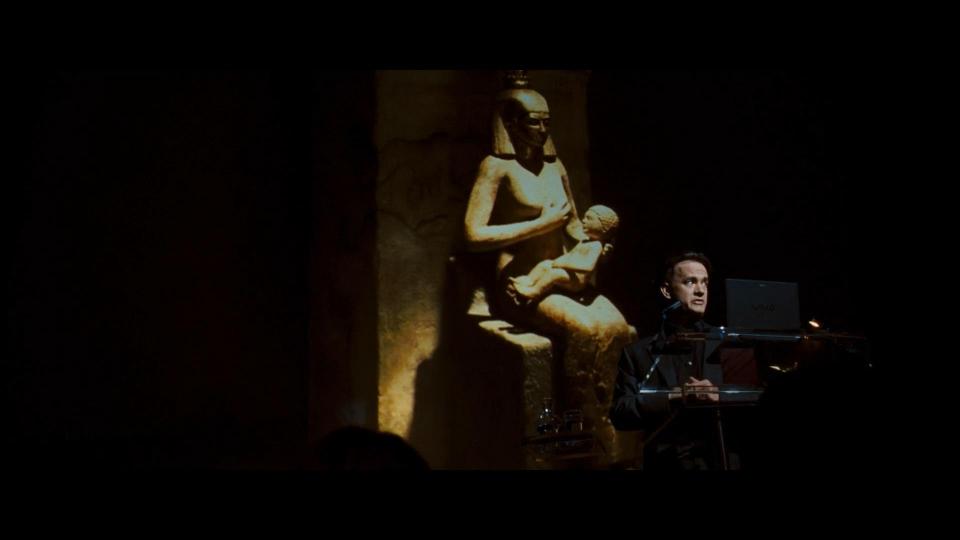
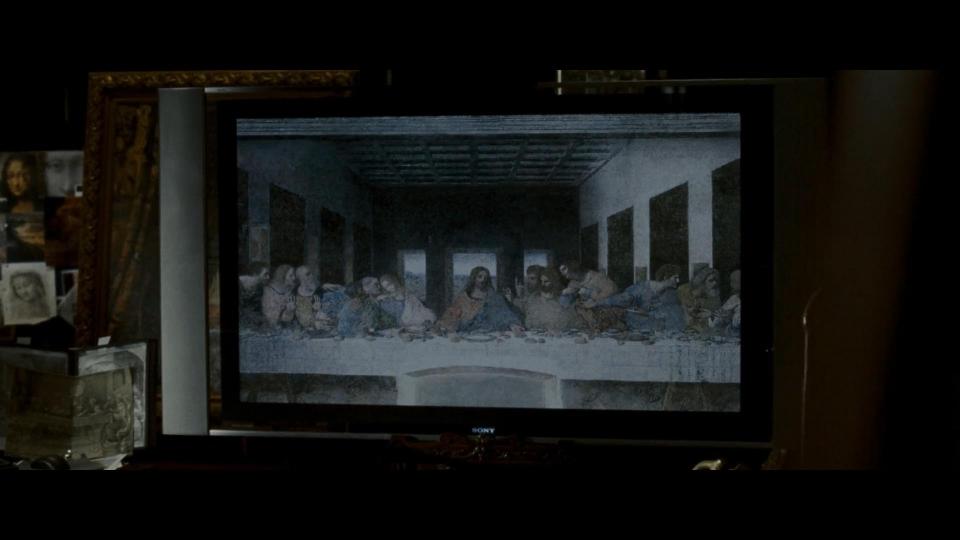
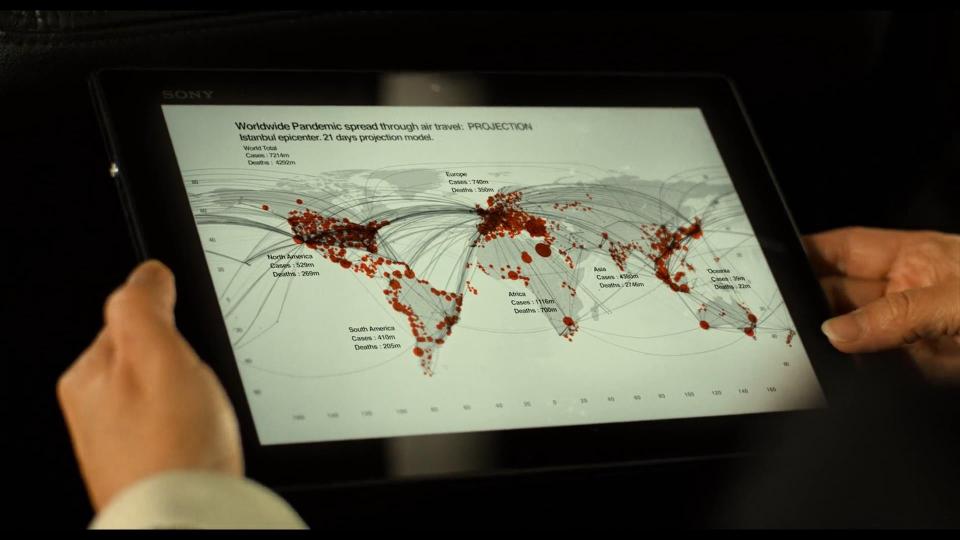
We meet Professor Robert Langdon for the first time during his lecture. He uses Sony laptop for his presentation.
In one of the next scenes of the movie we can clearly see the van with Bosch logo. Same is for the famous French water – Badoit. We can see it in a bucket full of ice.
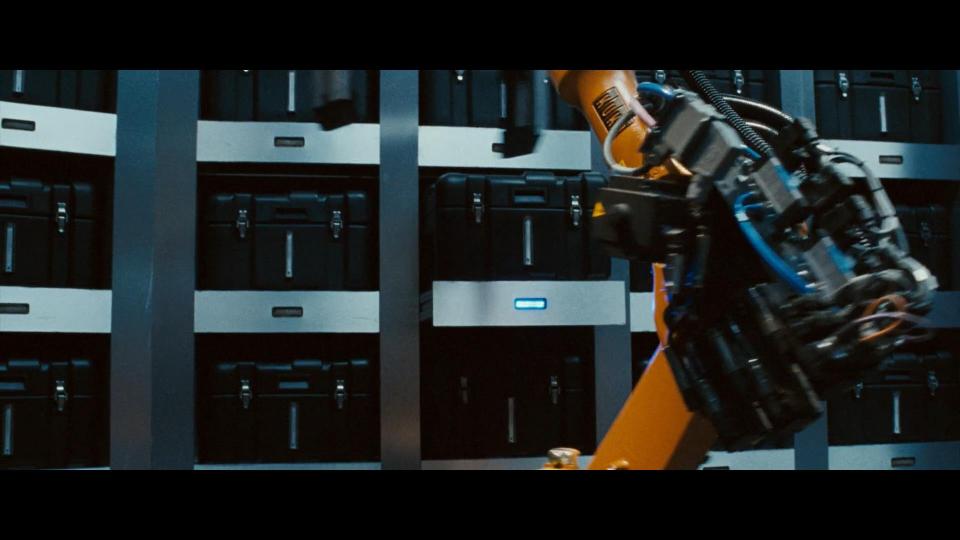
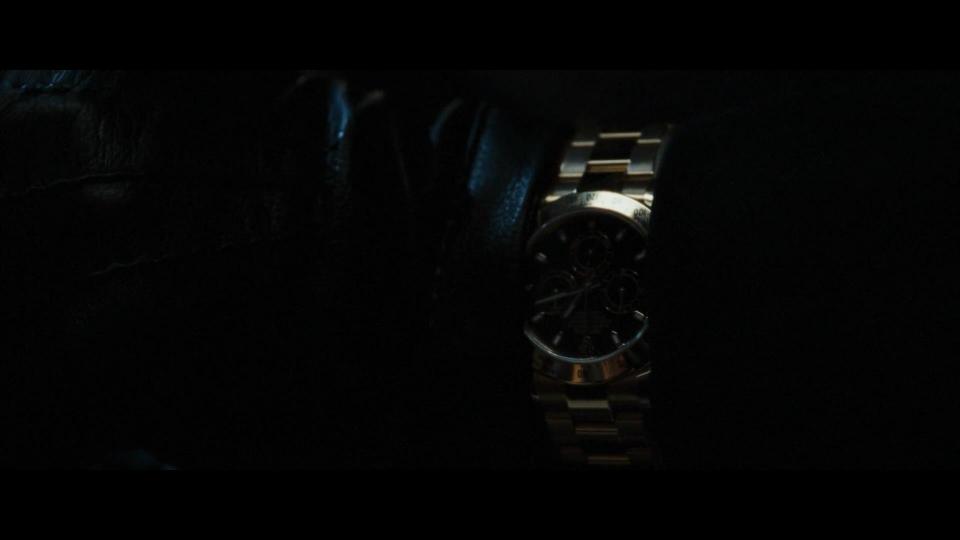
When Robert Langdon and Sophie Neveu (Audrey Tautou) come to the bank to retrieve the cryptex, we can see how KUKA robot picks the right box that belonged to Jacques Saunière. When the bank employee helps the main characters to pass the police, we can get a glimpse of his Rolex watch.
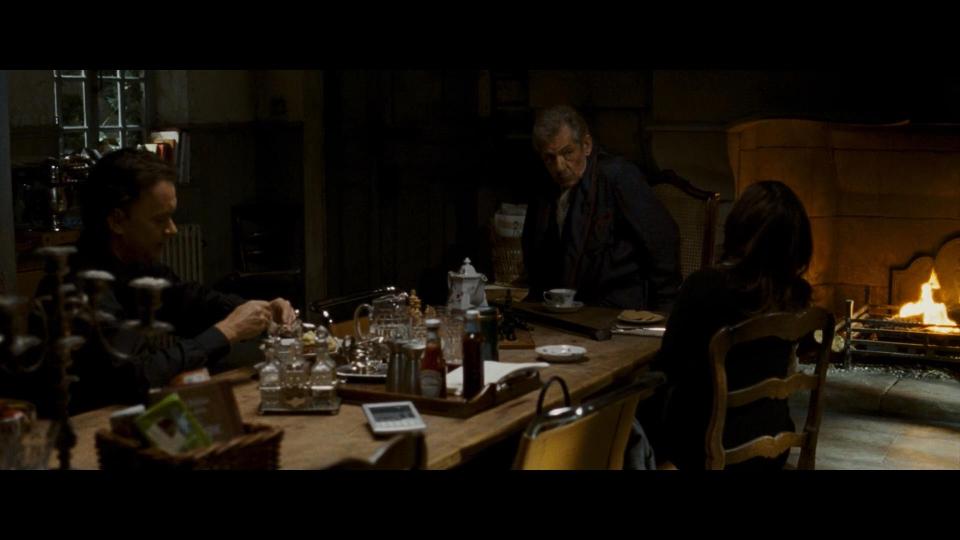
At Sir Leigh Teabing’s (Ian McKellen) house our guests learn more about The Last Supper painting secrets. Their host is also a fan of Sony, so we may see various TV sets and displays in the house. While enjoying their evening tea, we can as well see Heinz there, of course.
When Robert Langdon and Sophie look for a tomb in London, they borrow a Sony Ericsson smartphone to search for more information.
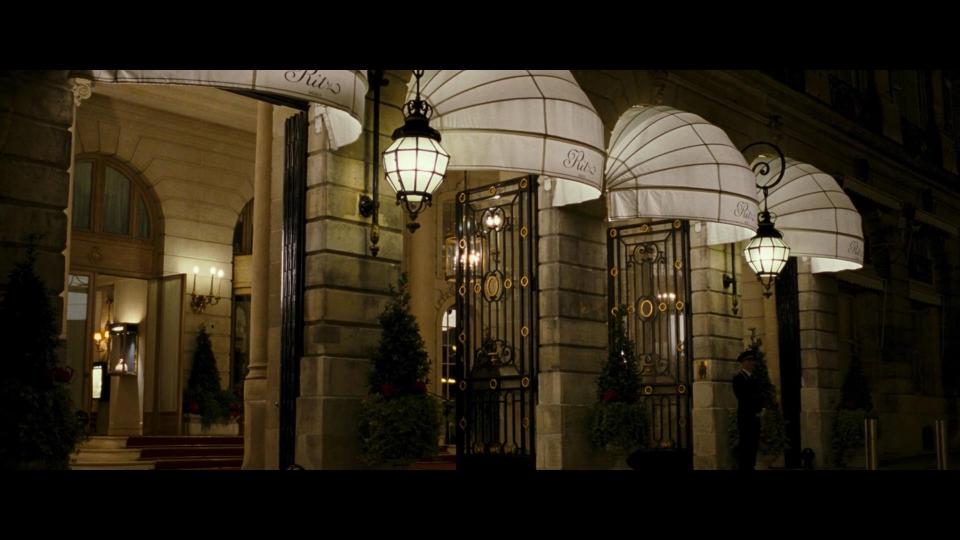
In the final scene of the movie we see that Robert lives in Ritz hotel in Paris, and from there he starts his evening walk to follow the Arago medallions and come to the Louvre.
The Catholic Church mourns the sudden death of Pope Pius XVI, and prepares for the papal conclave to elect his successor in Vatican City. Father Patrick McKenna (Ewan McGregor), the camerlengo, takes temporary control of the Vatican during the sede vacante period.
Meanwhile, at CERN, scientists Father Silvano Bentivoglio and Dr. Vittoria Vetra (Ayelet Zurer) create three canisters of antimatter. As Vetra goes to evaluate the experiment, she discovers that Silvano has been murdered, and one of the canisters was stolen. Shortly thereafter, four of the preferiti, the favored candidates to be elected pope, are kidnapped by a man claiming to represent the Illuminati. He sends the Vatican a warning, claiming he will murder each of the cardinals from 8 p.m. to midnight, when the stolen antimatter will explode and destroy the city, hidden somewhere within.
Unlike two other movies, there are only few product placements in Angels & Demons. And they can be divided in two categories – Sony and TV channels.
That is why we see Sony computers and displays in the first scene in CERN.
And when the events of the movie accelerate, we can see various TV channels broadcasting from Vatican City. These are Canal+, CNN, and Reuters.
And this is it for Angels & Demons. More product placements are waiting in Inferno.
Some time after helping the Vatican dealing with an antimatter threat, Harvard University professor Robert Langdon awakens in a hospital room in Florence, Italy, with no memory of what has transpired over the last few days, but being plagued with hellish visions. Dr. Sienna Brooks (Felicity Jones), the doctor tending to him, reveals that he is suffering from amnesia as a result of a bullet wound to the head. An orderly says the police are there to question Langdon but the officer turns out to be Vayentha, an assassin, who shoots the orderly while coming up the hallway. Brooks helps Langdon to escape, and they flee to her apartment.
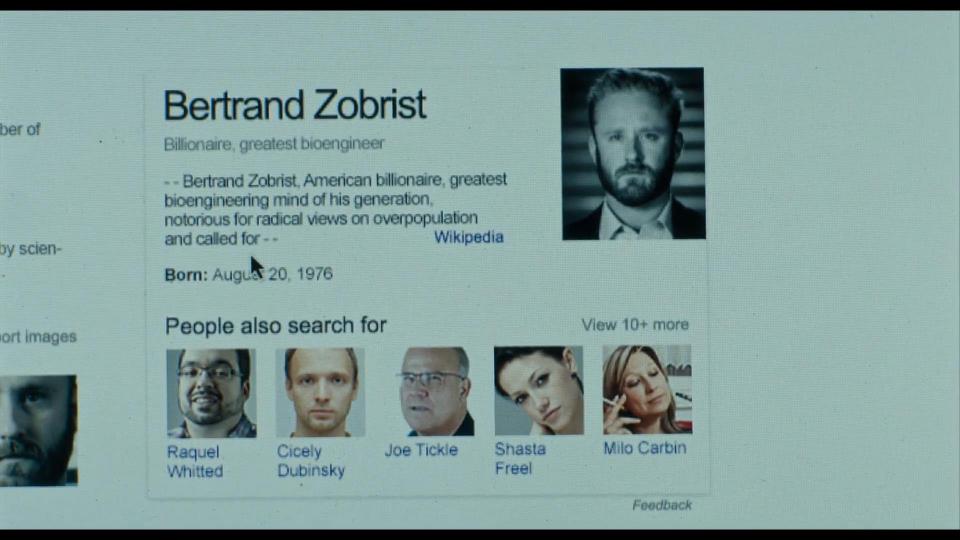
Among Langdon’s personal belongings, Langdon and Brooks find a Faraday pointer, a miniature image projector with a modified version of Sandro Botticelli’s Map of Hell, which itself is based on Dante’s Inferno. They soon realize this is the first clue in a trail left by Bertrand Zobrist, a dangerously unstable villain who believed that rigorous measures were necessary to reduce the Earth’s growing population, and who committed suicide three days earlier after being chased by armed government agents.
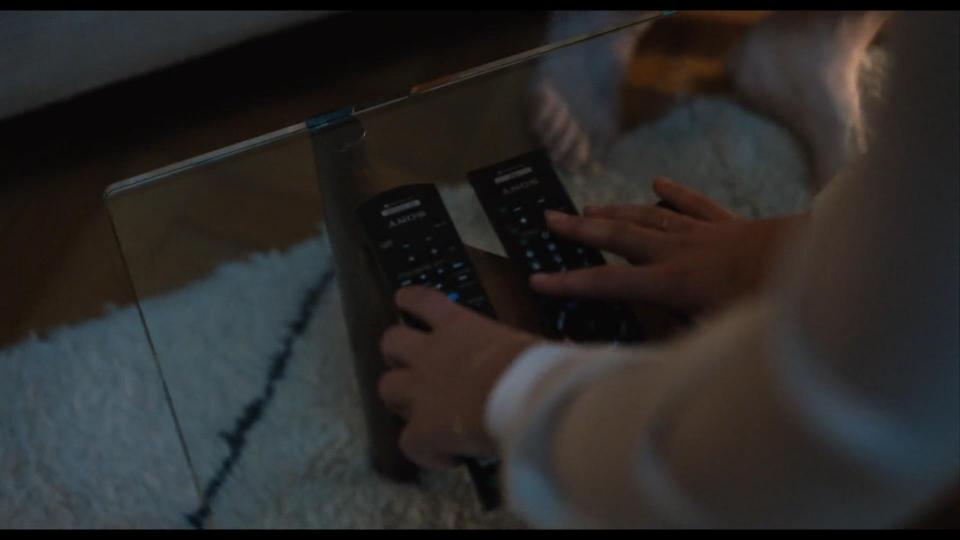
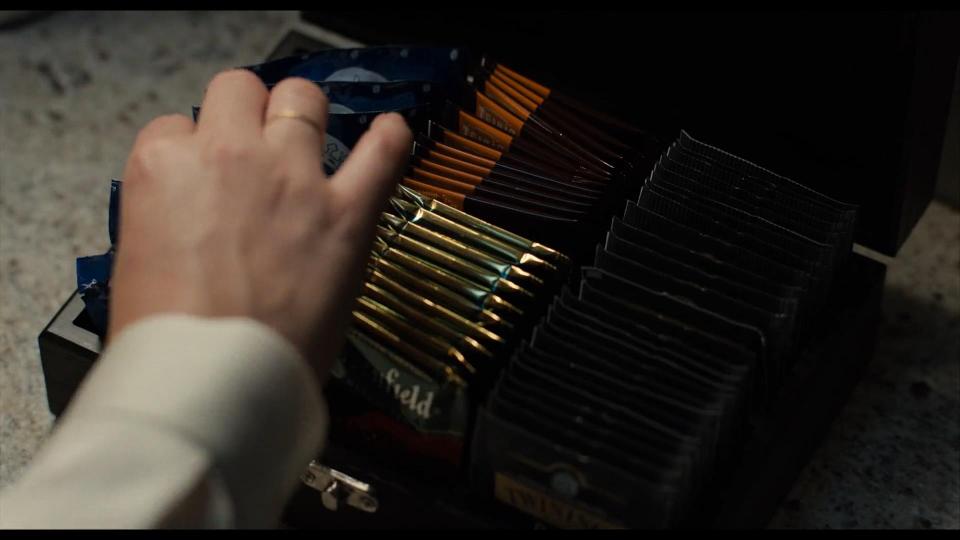
When Robert Langdon wakes up in Sienna’s house, we can find various brands across her apartment. First of all we see Sony TV remote controls. And when Professor asks for coffee, Sienna goes to the kitchen where we spot tea brands like Greenfield and Twinings.
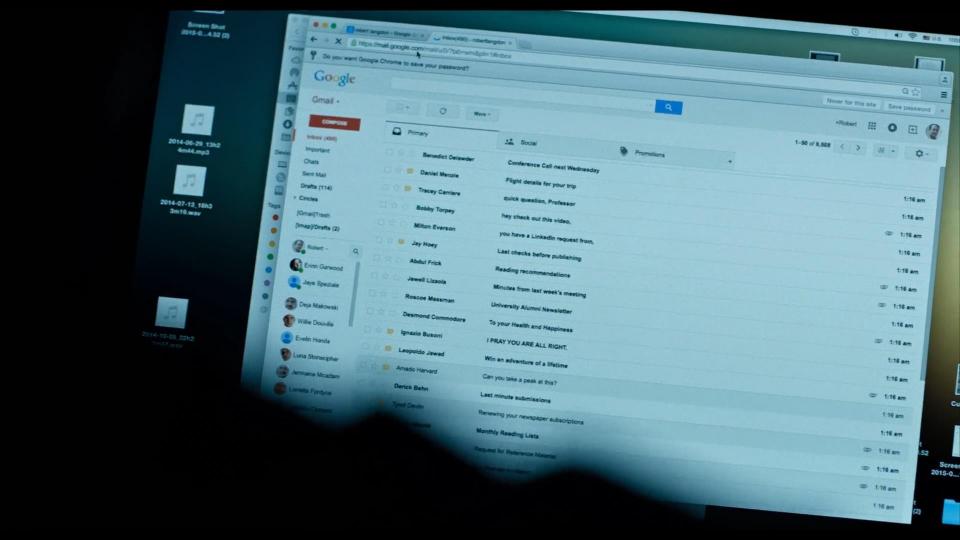
While Sienna is looking for some clothes for Robert, he decides to use her Apple MacBook to check his Google mail.
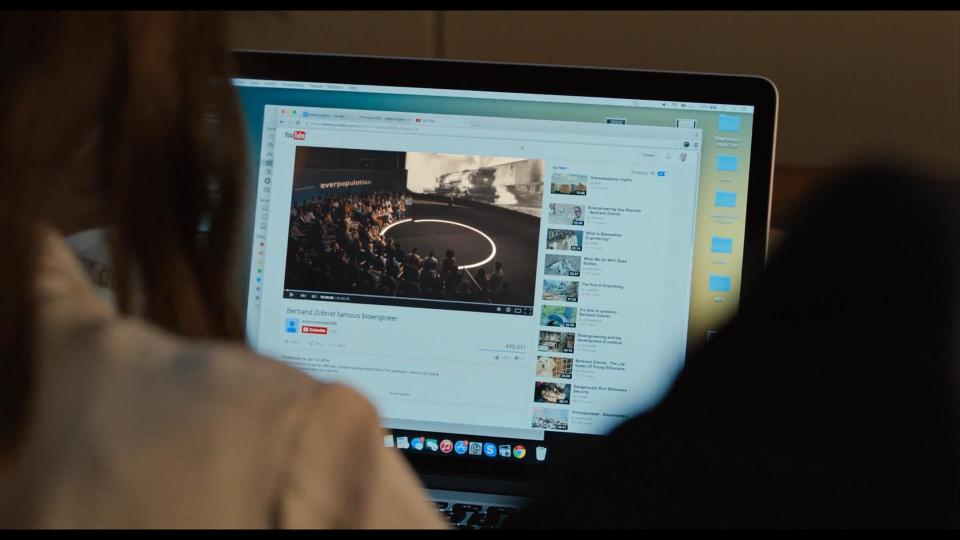
When Robert and Sienna decide to call to the consulate, we see that Sienna uses Sony smartphone. When they realize that they can trust no one, they start their investigation. First, they search for the information about Zobrist. Google, Wikipedia, and YouTube are very helpful even in the movies.
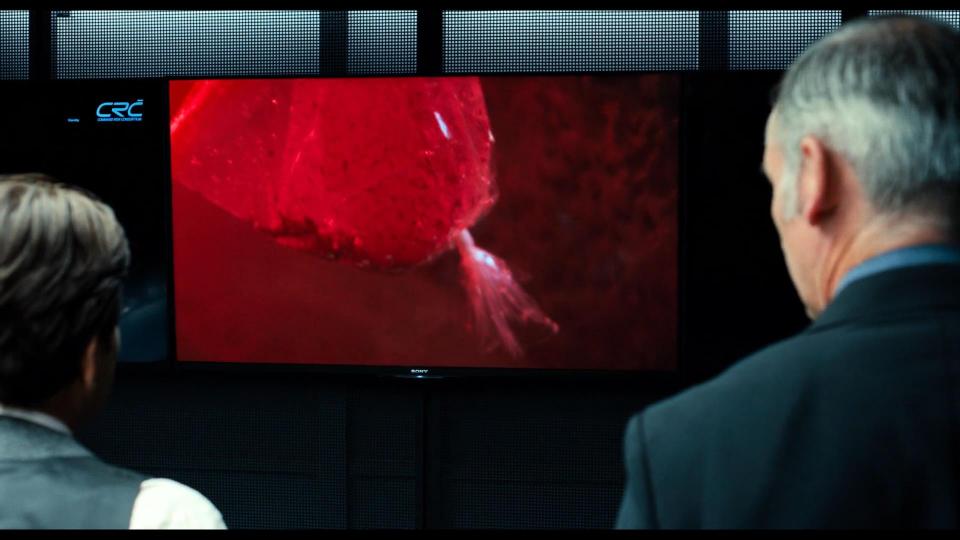
Later in the movie we see more Sony product placements – a TV set in Command Risk Consortium, a smartphone and a tablet used by Elizabeth Sinskey.
When Robert Langdon and Sienna Brooks try to escape from their enemies with the help of Christoph Bouchard, they make everyone believe they are going to fly to Switzerland via Swiss, but instead they take an Italo speed train to Venice.
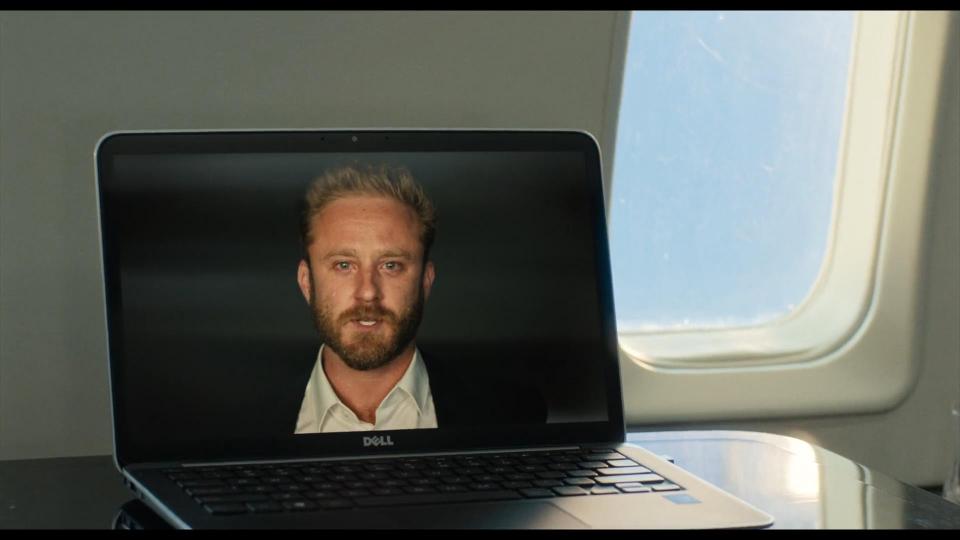
When finally the truth is revealed and memory is restored, Robert and Elizabeth go to Istanbul to stop Sienna from unleashing the virus. Elizabeth shares Zobrist’s message with Robert. They watch it together on a Dell laptop.
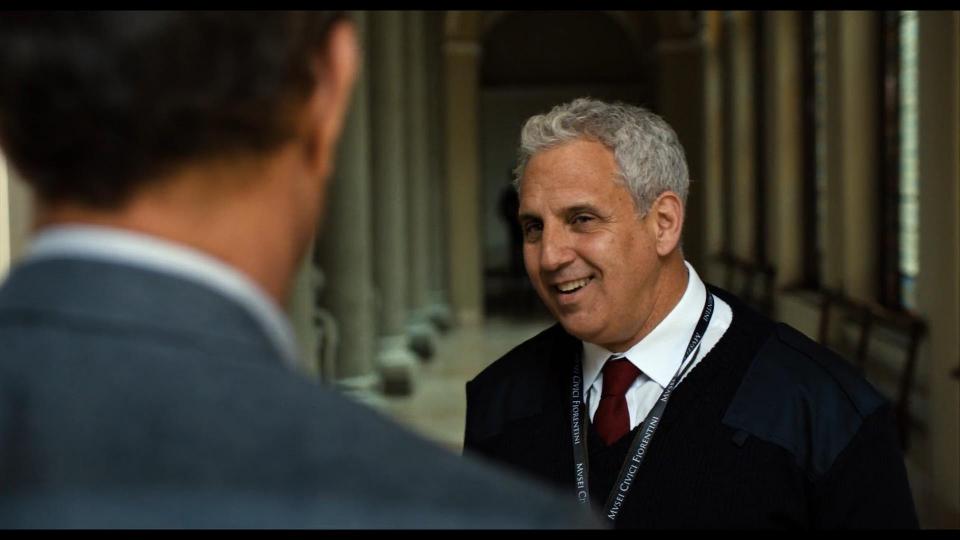
In the final scene when Professor returns Dante’s mask to the museum, we can see the museum employee wearing the tag with the Florentine Civic Museums branding.
Unfortunately, there is no news about the future movies with Tom Hanks. And no news about any new books. Looking forward to new adventures of Professor Langdon.
I highly recommend you to visit Product Placement section of the website. You will find more amazing movie series analysed there.
https://www.marketing-psycho.com/robert-langdon-product-placement/ |
|
|
|
|
Midnight in Paris
| Midnight in Paris |

Theatrical release poster
|
| Directed by |
Woody Allen |
| Written by |
Woody Allen |
| Produced by |
|
| Starring |
|
| Cinematography |
Darius Khondji |
| Edited by |
Alisa Lepselter |
Production
companies |
|
| Distributed by |
Sony Pictures Classics (United States)
Alta Films (Spain)[1] |
| Release dates |
- May 11, 2011 (Cannes)
- May 13, 2011 (Spain)
- May 20, 2011 (United States)
|
| Running time |
94 minutes[2] |
| Countries |
|
| Language |
English |
| Budget |
$17 million[1] |
| Box office |
$151.7 million[1] |
Midnight in Paris is a 2011 fantasy comedy film written and directed by Woody Allen. Set in Paris, the film follows Gil Pender (Owen Wilson), a screenwriter and aspiring novelist, who is forced to confront the shortcomings of his relationship with his materialistic fiancée (Rachel McAdams) and their divergent goals, which become increasingly exaggerated as he travels back in time to the 1920s each night at midnight.[3]
Produced by the Spanish group Mediapro and Allen's US-based Gravier Productions, the film stars Wilson, McAdams, Kathy Bates, Adrien Brody, Carla Bruni, Tom Hiddleston, Marion Cotillard, and Michael Sheen. It premiered at the 2011 Cannes Film Festival and was released in the United States on May 20, 2011.[3][4] The film opened to critical acclaim. In 2012, it won the Academy Award for Best Original Screenplay and the Golden Globe Award for Best Screenplay. It was nominated for three other Academy Awards: Best Picture, Best Director and Best Art Direction.[5]
In 2010, disillusioned screenwriter Gil Pender and his fiancée, Inez, vacation in Paris with Inez's wealthy parents. Gil, struggling to finish his debut novel about a man who works in a nostalgia shop, finds himself drawn to the artistic history of Paris, especially the Lost Generation of the 1920s, and has ambitions to move there, which Inez dismisses. By chance, they meet Inez's friend, Paul, and his wife, Carol. Paul speaks with great authority but questionable accuracy on French history, annoying Gil but impressing Inez.
Intoxicated after a night of wine tasting, Gil decides to walk back to their hotel, while Inez goes with Paul and Carol by taxi. At midnight, a 1920s car pulls up beside Gil and delivers him to a party for Jean Cocteau, attended by other people of the 1920s Paris art scene. Zelda Fitzgerald, bored, encourages her husband Scott and Gil to leave with her. They head to a cafe where they run into Ernest Hemingway and Juan Belmonte. After Zelda and Scott leave, Gil and Hemingway discuss writing, and Hemingway offers to show Gil's novel to Gertrude Stein. As Gil leaves to fetch his manuscript, he returns to 2010; the cafe is now a laundromat.
The next night, Gil tries to repeat the experience with Inez, but she leaves before midnight. Returning to the 1920s, Gil accompanies Hemingway to visit Gertrude Stein, who critiques Pablo Picasso's new painting of his lover Adriana. Gil becomes drawn to Adriana, a costume designer who also had affairs with Amedeo Modigliani and Georges Braque. Having heard the first line of Gil's novel, Adriana praises it and admits she has always longed for the past.
Gil continues to time travel the following nights. Inez grows jaded with Paris and Gil's constant disappearing, while her father grows suspicious and hires a private detective to follow him. Adriana leaves Picasso and continues to bond with Gil, who is conflicted by his attraction to her. Gil explains his situation to Salvador Dalí, Man Ray, and Luis Buñuel; as surrealists, they do not question his claim of coming from the future. Gil later suggests the plot of "The Exterminating Angel" to Buñuel.
While Inez and her parents travel to Mont Saint Michel, Gil meets Gabrielle, an antique dealer and fellow admirer of the Lost Generation. He later finds Adriana's diary at a book stall, which reveals that she was in love with Gil and dreamed of being gifted earrings before making love to him. To seduce Adriana, Gil tries to steal a pair of Inez's earrings but is thwarted by her early return to the hotel room.
Gil buys new earrings and returns to the past. After he gives Adriana the earrings, a horse-drawn carriage arrives, transporting them to the Belle Époque, an era Adriana considers Paris's Golden Age, they go to the Moulin Rouge where they meet Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Paul Gauguin, and Edgar Degas, who all agree that Paris's best era was the Renaissance. Adriana is offered a job designing ballet costumes; thrilled, she proposes to Gil that they stay, but he, observing the unhappiness of Adriana and the other artists, realizes that chasing nostalgia is fruitless because the present is always "a little unsatisfying." Adriana decides to stay, and they part ways.
Gil rewrites the first two chapters of his novel. He retrieves his draft from Stein, who praises his rewrite. Still, he says that on reading the new chapters, Hemingway does not believe that the protagonist does not realize that his fiancée, based on Inez, is having an affair with the character based on Paul. Gil returns to 2010 and confronts Inez, who admits to sleeping with Paul but disregards it as a meaningless fling. Gil breaks up with her and decides to move to Paris. The detective following him takes a "wrong turn" and ends up being chased by the palace guards of Louis XVI just before a revolution breaks out. While walking by the Seine at midnight, Gil encounters Gabrielle. As it begins to rain, he offers to walk her home and learns that they share a love for Paris in the rain.
Main cast
|
|
|
|
|
Gran colisionador de hadrones
 Estructura detallada de los precolisionadores, colisionadores y aceleradores del LHC
El Gran Colisionador de Hadrones (LHC; en inglés: Large Hadron Collider) es el acelerador de partículas más grande y de mayor energía que existe y la máquina más grande construida por el ser humano en el mundo.12 Fue construido por la Organización Europea para la Investigación Nuclear (CERN) entre 1989 y 2001 en colaboración con más de 10 000 científicos y cientos de universidades y laboratorios, así como más de 100 países de todo el Mundo.3 Se encuentra en un túnel de 27 kilómetros de circunferencia y a una profundidad máxima de 175 metros bajo tierra, debajo de la frontera entre Francia y Suiza, cerca de Ginebra.
Las primeras colisiones se lograron en 2010 a una energía de 3,5 teraelectronvoltios (TeV) por haz, aproximadamente cuatro veces el récord mundial anterior, alcanzados en el Tevatron.45 Después de las correspondientes actualizaciones, alcanzó 6,5 TeV por haz (13 TeV de energía de colisión total, el récord mundial actual).6789 A finales de 2018, entró en un período de parada de dos años, que finalmente se ha prolongado hasta 2022, con el fin de realizar nuevas actualizaciones, con lo cual se espera posteriormente alcanzar energías de colisión aún mayores.
El colisionador tiene cuatro puntos de cruce, alrededor de los cuales se colocan siete detectores, cada uno diseñado para ciertos tipos de experimentos en investigación. El LHC hace colisionar protones, pero también puede utilizar haces de iones pesados (por ejemplo de plomo) realizándose colisiones de átomos de plomo normalmente durante un mes al año. El objetivo de los detectores del LHC es permitir a los físicos probar las predicciones de las diferentes teorías de la física de partículas, incluida la medición de las propiedades del bosón de Higgs10 y la búsqueda de una larga serie de nuevas partículas predicha por las teorías de la supersimetría,11 así como también otros problemas no resueltos en la larga lista de elementos en la física de partículas.
 Túnel del Gran Colisionador de Hadrones (LHC) de la Organización Europea para la Investigación Nuclear (CERN) con todos los imanes e instrumentos. La parte del túnel que se muestra se encuentra debajo del LHC P8, cerca del LHCb.
El término "hadrón" se refiere a aquellas partículas subatómicas compuestas de quarks unidos por la fuerza nuclear fuerte (así como los átomos y las moléculas se mantienen unidos por la fuerza electromagnética).12 Los hadrones más conocidos son los bariones, como pueden ser los protones y los neutrones. Los hadrones también incluyen mesones como el pion o el kaón, que fueron descubiertos durante los experimentos de rayos cósmicos a fines de la década de 1940 y principios de la de 1950.13
Un "colisionador" es un tipo de acelerador de partículas con dos haces enfrentados de partículas que chocan entre sí. En la física de partículas, los colisionadores se utilizan como herramientas de investigación: aceleran las partículas a energías cinéticas muy altas que les permiten impactar con otras partículas.1 El análisis de los subproductos de estas colisiones, captados por los sensores, brinda a los científicos una buena evidencia de la estructura del mundo subatómico y de las leyes de la naturaleza que los gobiernan. Muchos de estos subproductos se producen sólo mediante colisiones de alta energía y se descomponen después de períodos de tiempo muy breves. Por lo tanto, muchos de ellos son difíciles o casi imposibles de detectar de otra manera.14
|
|
|
|
|
Governor General David Johnston (right) with actor Michael J.Fox at Rideau Hall on May 27, 2011 during an Order of Canada ceremony.
PATRICK DOYLE / THE CANADIAN PRESS
OTTAWA—Actor Michael J. Fox is now an officer of the Order of Canada.
The Edmonton-born actor and activist is among 43 people who received their medals from Gov. Gen. David Johnston at a Rideau Hall ceremony.
Others include rock legend Robbie Robertson, hockey commentator Howie Meeker, Acadian filmmaker Phil Comeau, former cabinet minister Anne McLellan and Trudeau biographer Stephen Clarkson.
Fox was honoured for his efforts on behalf of those suffering from Parkinson’s disease, as well as his television and film work.
Fox, diagnosed with Parkinson’s two decades ago, called the award a great honour.
He chuckled that he felt like an imposter when he glanced around at his fellow inductees.
“I don’t begin for a second to put myself in the league of any of these people,” he said. “When I listen to what they’ve done, that’s Canadian to me. It’s a seriousness and a sense of humour, it’s a lot of contradictions.”
He said Canada always makes him think “of vast spaces and tight communities.”
“We think of ourselves huddled against the elements and helping each other. It’s very moving to be part of it.”
https://www.thestar.com/entertainment/michael-j-fox-receives-order-of-canada/article_8f612aa5-9d87-5133-9984-8c2b1b3eaa4f.html |
|
|
|
|
Knights Templar and Switserland
"The current Knights Templar Headquarters are in Geneva. This country befits and holds similar many of the most common and closely guarded values of the original Knights Templar. The oldest abbey established in Switzerland is Sion, in the Valais Canton. There is a twin peaks overlooking the town, meaning new Jerusalem or holy place in the Alps. The twin mountains house the cathedral of Sion and the Castle Tourbillion. These date back to the beginning times of Swiss Confederation formation around 1291. A time when the Templars were known to be looking to establish a European mainland stronghold outside of the Holy Land as they were being pushed out of the Levant by the Muslims and the Christians had lost their stomach to fight on any longer.
These are suggestions that certain historians and conspiracists alike deem to be true that suggest that the Knights Templar did in fact form Switzerland. The evidence and likelihood seem pretty plausible to me. The county of Valais in the city of Sion has a particular Templar tie in the founding history. Rumors have always floated that this is where the Templars originally set up shop after their flight from France.
- In the history of the first Swiss Cantons there are tales of white coated knights mysteriously appearing and helping the locals to gain their independence against foreign domination.
- The founding of the early Switzerland pinpoints exactly to the period when the Templars were being persecuted in France by King Philip IV of France.
- Switzerland is directly to the east of France and would have been particularly easy for fleeing Templar brothers from the whole region of France to get to.
- The Templars were one of the earliest known banking systems in early day Europe. King Phillip in fact was deeply in debt to the Templars.
- Not only were the Templars big into banking, but also in farming, engineering, and clock making (of an early type). These same aspects can be seen as importance to the commencement and gradual forming of the separate states that would eventually be Switzerland.
- The Swiss don’t really know the ins and outs of their earliest history (or suggest that they don’t.)
- They are famous for being secretive and independent as were the Templars.
- The famous Templar Cross is incorporated into the flags of many of the Swiss Cantons. As are other emblems, such as keys and lambs, that were particularly important to the Knights Templar.
- The Swiss were and are famous for their religious tolerance – and so were the Templars"
https://www.templarsnow.com/2015/01/knights-templar-and-switserland.html |
|
|
|
|
|
History and geography of Sion in Switzerland
Are you ready to discover the history and geography of Sion in Switzerland?
This city, founded several centuries ago, is a place rich in history that has influenced Swiss and European cultures. Embark on an exciting adventure in the Valais region.
On your journey through these cultural wonders, you’ll explore the castles of Valère and Tourbillon, one of the town’s historic gems. You will also learn all about the emergence of the canton’s most important city and its evolution.

History of Sion in Switzerland
Sion is a town in the canton of Valais, Switzerland, and is the administrative capital of the canton. It was founded at the turn of the century and is considered an important place for historical and geographical research.
The first written mention of Sion as a town dates back to the year 1160, and in 1189 the county became the episcopal principality of Sion. By this time, the town had already prospered to become a politically important and strategic site.
Over the centuries, through destruction, fire and regional power struggles, its population gradually grew and it experienced several periods of development.
Integrated into the Germanic Holy Roman Empire at the beginning of the 11th century, the principality of Sion was at the centre of conflicts between Switzerland and Savoy, between counts, episcopates and local communities, until the creation of the Republic of the Seven Tithings*.
In 1798, the Upper Valais, including Sion, united with the Lower Valais to create a single canton and join the Helvetic Republic.
The construction of the Valère and Tourbillon castles between the 11th and 13th centuries also played a major role in the history of the town and its establishment as the central place of the region.
Origins and development of the town
Sion is an ancient Roman city built around the Castrum Sedunum by Roman legionaries around the year 40. The Latin name is said to have originated with the Seduni a Celtic people who had settled in the Valais since the 1st century BC.
Until the seat of the episcopate was moved to Sion in the 5th century, the town remained in the shadow of the present-day towns of Martigny and Massongex, both of which were located on the axis of the Great St Bernard Pass, a passageway between the Valais and the Aosta Valley since the Neolithic period.
Development and expansion of the town
The arrival of the train in the Rhone Valley from the Lake Geneva port of Bouveret in the 19th century stimulated the development of the town, as it did for Martigny and the other towns on the railway axis. A provisional station was built in 1860 and the final version was completed in 1873.
The establishment and gradual improvement of rail and road links between neighbouring towns and in the valley from Geneva facilitated trade and travel throughout the region.
Since then, Sion has steadily developed its tertiary sector and its tourist capacities, to the detriment of the agricultural sector and in particular the dairy industry, which has seen its importance decline for several decades. Only the wine industry has been able to survive this agricultural decline.

Geography and heritage of Sion in Switzerland
Sion is located in the heart of the Valais, in the southwest of Switzerland. The town is situated at an altitude of 512 metres on the right bank of the river Rhône, for the historic centre, and shares the two banks over the whole of the commune.
Geographical location and climate
Nestled in the valley of the nascent Rhone and protected from the influences of the high peaks of the Alps, the climate is generally temperate throughout the year, with average temperatures varying between 6°C in winter and 19°C in summer.

Where is Sion?
Location map of the city of Sion in the Swiss Valais:
Physical and natural characteristics
The surrounding landscape is mostly composed of mountains covered by alpine forest, offering an unimaginable variety to admire: impressive rocks and peaks, limpid bodies of water with turquoise reflections, magical valleys invaded by daffodils and thousand-year-old glaciers like the Aletsch.
Important places and monuments
The most visible and most important site of the town is located on the heights of the town, with the castle of Tourbillon and the fortified basilica of Valère.
The castle, dating from the 13th century, is built on the ramparts of the lower town and its magnificent towers dominate the town.
The basilica dates from the 12th century and has been undergoing a complete restoration since 1987.
The Tourbillon and Valère castles, the Sorcerers’ Tower, Notre-Dame de Sion Cathedral with the old town, the Town Hall and the Rue du Grand-Pont, are the places not to be missed during a visit to the town’s heritage.

Culture in Sion, Switzerland
Spoken languages and dialects
The spoken language is French and the regional language, Valaisan, is used. German and Romansh are also spoken in a minority.
Cuisine and gastronomy
Sion offers a wide variety of culinary delights from all over the Valais and Switzerland.
Local specialities include rösti potatoes, tartiflettes, fondue of course, but also game (rabbit, venison, etc.), dried meat or Valais rye bread.
As the most important wine-producing region in Switzerland, it is difficult to escape from one of the 60 grape varieties that the Valais has to offer and which the Sion region has been able to take advantage of, for example with the wine tour of the region starting from the city.
Arts, music and entertainment
The artistic culture is very present in Sion. The town has several museums to discover, such as the Valais Art Museum, the History Museum, the Nature Museum and the Fellini Foundation.
The music scene has also developed rapidly in recent years, with numerous concerts and festivals throughout the year, from classical music at PALP to Opéra Viva under the stars.
Discovering the city is an enriching experience thanks to its prolific past and its current dynamics: passing through Sion on a journey along the Rhône River will delight travellers, whether for a short time or for a longer stay.
Along the Rhône

https://ontherhone.com/en/history-geography-sion-valais-switzerland/ |
|
|
|
|
Valère Basilica
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Valère Basilica (French: Basilique de Valère), also called Valère castle (French: Chteau de Valère), is a fortified Roman Catholic church situated in Sion in the canton of Valais in Switzerland. It is located on a hill and faces the Chteau de Tourbillon, situated on the opposite hill. It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance.[1]
 The Valère and Tourbillon castles as seen from Sion.
The castle of Valère is located on the Valère hill at 615 meters (2,018 ft) above sea level and dominates the town of Sion in the canton of Valais, Switzerland.[2] The castle's church is located at the top of the hill, while the fortified village and its walls surround it. The relief of the Valère hill is very uneven and access to the castle is only possible from the north-east.[3]
Since 1977, the site has been included in the Federal Inventory of Sites and Monuments of National Importance due to the large number of protected species present on Valère Hill.[4] The fauna of the hill includes the European green lizard (Lacerta viridis), the European mantis (Mantis religiosa), the scarce swallowtail (Iphiclides podalirius), the green-underside blue (Glaucopsyche alexis), the blue-winged grasshopper (Oedipoda caerulescens), the rock bunting (Emberiza cia), the common redstart (Phoenicurus phoenicurus), the common raven (Corvus Corax) and the common kestrel (Falco tinnunculus). Valère's flora is composed of a feather grass (Stipa) species, Ephedra distachya, Indian fig (Opuntia humifusa), hoary berteroa (Berteroa incana), early star-of-Bethlehem (Gagea bohemica), cotton thistle (Onopordum acanthium), motherwort (Leonurus cardiaca) and patience dock (Rumex patientia).[5]
4.9 hectares (530,000 sq ft) of the Tourbillon Hill are also included in the catalogue of protected places in the category of dry meadows and pastures of national importance. This area was so classified in 2017 with the aim of conserving Switzerland's dry meadows and pastures, almost 95% of which have disappeared since 1900.[6]
 11th century Byzantine robe, silk with griffins. Valère treasury.
The Diocese was founded in Octodurum, now called Martigny, in the early 4th century. In 589 the bishop, St. Heliodorus, transferred the see to Sion, as Octodurum was frequently endangered by the inundations of the Rhone and the Drance. Very little is known about the early Bishops and the early churches in Sion. However, in the late 10th century the last King of Upper Burgundy Rudolph III, granted the County of Valais to Bishop Hugo (998–1017). The combination of spiritual and secular power made the Prince-Bishops the most powerful nobles in the Upper Rhone valley. Sion became the political and religious center of the region. By the 12th century they began building impressive churches and castles in Sion to represent their power and administer their estates.[7] Valère, as the residence of the cathedral chapter in Sion, was one-third of the administrative center of the powerful Diocese of Sion. In the 12th century the Cathedral Notre Dame de Sion (du Glarier) was built in the town below Valère hill.[8] Glarier Cathedral became the seat of the Diocese of Sion, while the Prince-Bishop of Sion lived in Tourbillon Castle.[9]
The name Valère is first mentioned in 1049 as the site of the cathedral chapter in Sion. The first parts of the church were built between 1100 and 1130 in the Romanesque style. The next construction phase began after 1130 and included the semi-circular apse, the walls and windows and a roof. The third phase saw the church expand and the style changed to the new Gothic style. Between 1235 and 1267 the nave expanded and was flanked with two aisles. During the 13th century, the choir was covered with a Gothic ribbed vault and a rood screen was installed to separate the chancel from the nave. The famous organ was installed around 1430–1435 and other than a modification in the 1700s is essentially unchanged. The murals date from about 1435 as well.[10] The Gothic marble statue of the Madonna with the baby Jesus was added in the 15th century over the high altar. The current choir stalls were added in the mid-17th century.[11]
The church obtained the rank of minor basilica in the Roman Catholic tradition on 7 October 1987, during the visit of Pope John Paul II.
The Valère Basilica has been restored with the larch structures preserved and tested by Sylvatest in 2000.[12][13]
 The Basilica's Organ
The Pipe organ on the west side of the Valère Basilica, believed to have been built in 1435, is one of the oldest functioning in the world. It was probably brought to the church by Guillaume de Rarogne, who eventually ended up as the bishop of Sion. Its pipes are arranged to form a rough outline of a church; the larger pipes form two towers, and the smaller ones create a triangular church roof. The organ was modified in the 1700s to play Baroque music, but otherwise remains essentially unchanged.[10] It was renovated in 1954.[citation needed]
|
|
|
|
|
Church of St. Théodule, Sion
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Church of St. Théodule (French: église Saint-Théodule; German: St. Theodul) is a Roman Catholic church located in Sion in the canton of Valais, Switzerland.
The church is located in the historic center of Sion, south from the Cathedral of Our Lady of Sion.
 Choir vault
The first church on the site was built during the High Middle Ages on the ruins of a Roman bath.[1] The current building was built from 1514 to 1516 on the site of a former building. The vault of the choir (before 1502 – finished in 1514), symbolic of the Flamboyant Gothic style, was made by a builder from Valsesia[2] who was identified with Ulrich Ruffiner [de], perhaps erroneously.[3] The nave was vaulted in 1644 by Adrien III of Reidmatten. The church was renovated in 1960–64.[1]
The church was listed among the Cultural Property of National Significance.
The church has a single nave and a polygonal choir. The buttresses which support the nave have niches and canopies for statues, though most have been removed. A small stair tower is built into the southern wall on the western end of the church.[1]
|
|
|
 Primer Primer
 Anterior
41 a 55 de 55
Següent Anterior
41 a 55 de 55
Següent
 Darrer
Darrer

|