|
Réponse |
Message 1 de 136 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 122 de 136 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 123 de 136 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 124 de 136 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 125 de 136 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 126 de 136 de ce thème |
|
The Polaris Dawn mission will launch on August 28 (
Image: (Image: Getty))
SpaceX delayed the much-anticipated Polaris Dawn mission, which will see a crew of four attempt the first-ever private spacewalk, due to a helium leak at the launch site.
The issue meant that the planned launch on Tuesday morning was pushed to Wednesday to allow for a thorough investigation of the issue and to implement additional safety checks.
In an announcement, SpaceX stated: "Teams are taking a closer look at a ground-side helium leak on the Quick Disconnect umbilical.
"Falcon and Dragon remain healthy and the crew continues to be ready for their multi-day mission to low-Earth orbit. Next launch opportunity is no earlier than Wednesday, 28 August."
Spacex's CEO and renowned entrepreneur Elon Musk posted on social media regarding the groundbreaking journey, reports the Express US. He said: "An incredible amount of work has gone into this historic mission by an amazing team. We are triple-checking everything to make sure there is nothing more we can do to improve crew safety."
 The flight will launch on a Falcon 9 rocket ( The flight will launch on a Falcon 9 rocket (
Image:
(Image: Getty))
Furthermore, he highlighted the significance of the mission, tweeting: "Crew safety is absolutely paramount and this mission carries more risk than usual, as it will be the furthest humans have traveled from Earth since Apollo and the first commercial spacewalk! ".
Reaffirming their commitment to the schedule, SpaceX aims to maintain the initial early morning launch timing of 3:38 am ET on Wednesday at the storied Launch Complex 39A of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. More options are also on the table with additional lift-off times of 5:23 am ET and 7:09 am ET.
If the preferred launch windows aren't workable, they've got a fallback on Thursday, August 29. Just three days into the space mission, an EVA is scheduled to test out SpaceX's cutting-edge spacesuits.
Designed for deep space escapades and to shield against intense cosmic radiation in the Van Allen belts, these EVA suits are at the forefront of aerospace innovation alongside the Polaris Dawn spacecraft.
Tech mogul Jared Isaacman, a pioneer in private space travel, is commandeering and bankrolling this five-day cosmic voyage. No stranger to the stars after his self-financed 2021 flight on a Crew Dragon craft, Isaacman is the seasoned spacefarer of the group.
Despite recent delays, Isaacman shared from isolation that the team is geared up and waiting for liftoff as soon as the glitch is sorted out.
He stated on X: "The best aerospace engineers in the world are working on the issue, and we promise to put on a great show soon enough. When the call comes, we won't hesitate to strap in."
https://www.themirror.com/news/us-news/spacex-forced-delay-polaris-dawn-664786 |
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 127 de 136 de ce thème |
|
Elon Musk’s Impact on the Future of Space Exploration
By Betty Bassett
Photo by SpaceX on Unsplash
Elon Musk's journey to becoming one of the most influential figures in space exploration began long before SpaceX's first rocket launch. As a child, Musk was captivated by the worlds crafted in science fiction novels. These stories did more than entertain; they instilled a belief in the boundless potential of humanity. Musk often cites books like "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy" and "Foundation" as pivotal in shaping his outlook. These narratives, filled with interstellar travel and advanced civilizations, laid the groundwork for Musk's aspirations. He envisioned a future where humanity would not be confined to Earth, but would instead become a multi-planetary species.
Musk's philosophical foundation is deeply rooted in the concept of existential risk—the idea that humanity must safeguard its future against possible extinction events. This belief drives his relentless pursuit of space exploration. For Musk, spreading human life to other planets is not just an ambition but a necessity. It is this sense of urgency that fuels his endeavors, pushing boundaries and defying conventions.
His vision for humanity extends beyond survival. He dreams of a future where humans are explorers and innovators, constantly pushing the frontiers of knowledge and existence. This vision is not merely about escaping a doomed Earth but about inspiring a new era of growth and discovery. Musk’s Mars colonization plans, often viewed with skepticism, are underpinned by this philosophy. He believes that establishing a self-sustaining colony on Mars would be the first step towards securing humanity’s future and igniting a wave of optimism and progress.
Technological Innovations
SpaceX's technological advancements are the tangible manifestations of Musk's grand vision. One of the most groundbreaking innovations is the development of reusable rockets. Traditional rockets are expendable; they burn vast resources and are discarded after a single use. SpaceX's Falcon 9, however, revolutionized this model by being capable of landing back on Earth and being reused for multiple missions. This innovation drastically reduces the cost of space travel, making it more accessible and sustainable.
In addition to reusable rockets, SpaceX has made significant strides in spacecraft design. The Dragon spacecraft, designed to carry cargo and crew to the International Space Station (ISS), represents a leap forward in safety, efficiency, and reliability. The Crew Dragon variant is equipped with advanced life support systems, touchscreen controls, and emergency abort capabilities, ensuring the safety of astronauts in unprecedented ways.
Moreover, SpaceX is pioneering the integration of AI and automation in space travel. Autonomous systems onboard SpaceX's rockets and spacecraft can perform complex maneuvers, monitor systems, and respond to anomalies without human intervention. This reduces the risk of human error and enhances the efficiency of space missions. AI's role in SpaceX's operations extends to mission planning and analysis, optimizing trajectories, and ensuring mission success.
Economic Disruptions
SpaceX's business model has disrupted the aerospace industry in ways previously thought impossible. By focusing on cost reduction through reusability and vertical integration, SpaceX has lowered the barriers to entry for space exploration. Traditional aerospace companies, reliant on government contracts and outdated technologies, have been forced to innovate or risk obsolescence.
Private funding has played a crucial role in SpaceX's success. Unlike traditional space programs that rely heavily on public funding, SpaceX has attracted significant investment from private entities. This has allowed the company to pursue ambitious projects without the constraints of governmental budget cycles. The influx of private capital has also sparked a renaissance in the aerospace sector, with numerous startups emerging to explore new frontiers in space technology.
The economic implications of space tourism are another significant aspect of SpaceX's influence. With plans to send private citizens on spaceflights, SpaceX is opening up space travel to non-astronauts. This not only generates substantial revenue but also fosters a broader public interest in space exploration. The concept of space tourism is transforming from a futuristic fantasy to a viable industry, with SpaceX at the forefront of this revolution.
Cultural Impacts
Elon Musk's influence extends beyond the technical and economic realms; it permeates culture and public perception. Through his charismatic persona and visionary statements, Musk has captured the public's imagination. Space travel, once the domain of government agencies and elite astronauts, is now seen as a potential future for ordinary people. Musk's presence on social media and his interactions with the public have humanized space exploration, making it more relatable and exciting.
The media has played a pivotal role in shaping the SpaceX narrative. Coverage of SpaceX's milestones, from successful rocket landings to ambitious Mars plans, has been extensive and often sensational. This media attention has not only amplified public interest but also influenced other industries to consider the possibilities of space. The portrayal of Musk as a maverick entrepreneur has further cemented his status as a cultural icon, inspiring a new generation of scientists, engineers, and dreamers.
Cultural shifts towards space exploration as a viable future are evident in education and entertainment. Universities and schools are increasingly offering programs focused on aerospace engineering and space sciences, driven by the excitement surrounding SpaceX. Films, documentaries, and literature are exploring themes of space travel and colonization, reflecting and fueling public interest. Musk's vision is gradually becoming a part of the cultural zeitgeist, influencing how we think about our future.
Challenges and Criticisms
Despite SpaceX's successes, the journey has not been without challenges and criticisms. The technical and logistical hurdles of space exploration are immense. Achieving reusability, developing advanced spacecraft, and planning interplanetary missions involve overcoming numerous engineering and scientific obstacles. Each launch and landing is fraught with risks, and failures can have significant repercussions.
Ethical considerations also emerge in Musk's approach to space exploration. The environmental impact of rocket launches, the potential for space debris, and the ethical implications of colonizing other planets are topics of concern. Critics argue that more attention should be given to addressing these issues, ensuring that the pursuit of space exploration does not compromise ethical standards. The future of space travel must consider not only technological and economic factors but also ethical, environmental, and societal dimensions.
The Future of Space Exploration
The future of space exploration is likely to be shaped by collaborations between SpaceX and governmental space agencies. Partnerships with NASA, ESA, and other international agencies can leverage the strengths of both public and private sectors. Such collaborations can enhance the scope and scale of space missions, combining resources, expertise, and innovative approaches.
International cooperation will be crucial in addressing the challenges of space exploration. Establishing norms and agreements on space traffic management, resource utilization, and planetary protection will ensure that space remains a domain of peaceful exploration and scientific advancement. SpaceX's role in fostering such cooperation can set a precedent for future endeavors.
Musk's long-term vision extends beyond near-Earth space. His plans for Mars colonization are ambitious, involving the development of the Starship spacecraft capable of carrying large numbers of people and cargo to the Red Planet. This vision encompasses the establishment of a self-sustaining colony, transforming Mars into a second home for humanity. While this goal may seem distant, the progress made by SpaceX suggests that it is within the realm of possibility.
The tangible progress made by SpaceX, from reusable rockets to ambitious Mars missions, has proven that space exploration is not just a distant dream but an imminent reality. Musk's focus on making space travel more affordable and accessible opens up unprecedented opportunities for scientific research, economic development, and international cooperation. As private enterprises and governmental agencies work together, the potential for transformative breakthroughs grows, paving the way for a new era of discovery and exploration.
Reference:
Chang, Kenneth. "SpaceX’s Giant Rocket Sticks Its Landing in a Critical Milestone for Elon Musk." The New York Times, 22 Dec. 2015, www.nytimes.com/2015/12/22/science/space/spacex-rocket-landing.html.
Davenport, Christian. The Space Barons: Elon Musk, Jeff Bezos, and the Quest to Colonize the Cosmos. PublicAffairs, 2018.
Fernholz, Tim. Rocket Billionaires: Elon Musk, Jeff Bezos, and the New Space Race. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2018.
Grush, Loren. "Elon Musk’s Starship Update: ‘The Holy Grail of Space’." The Verge, 28 Sept. 2019, www.theverge.com/2019/9/28/20887814/elon-musk-spacex-starship-update-2019-prototype.
Heiney, Anna. "SpaceX Makes History: Falcon 9 Successfully Delivers Crew Dragon to Orbit." NASA, 30 May 2020, www.nasa.gov/feature/spacex-makes-history-falcon-9-successfully-delivers-crew-dragon-to-orbit.
Mehta, Aaron. "SpaceX’s Starlink Satellites Are Increasingly Responsible for Close Encounters in Orbit." CNET, 27 Apr. 2021, www.cnet.com/news/spacexs-starlink-satellites-are-increasingly-responsible-for-close-encounters-in-orbit/.
Musk, Elon. "Making Humans a Multi-Planetary Species." New Space, vol. 5, no. 2, 2017, pp. 46-61. DOI: 10.1089/space.2017.29009.emu.
Sheetz, Michael. "SpaceX Raises $850 Million, Jumping Valuation to about $74 Billion." CNBC, 17 Feb. 2021, www.cnbc.com/2021/02/17/spacex-raises-850-million-jumping-valuation-to-about-74-billion.html.
United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA). "Treaty on Principles Governing the Activities of States in the Exploration and Use of Outer Space, including the Moon and Other Celestial Bodies." United Nations, 27 Jan. 1967, www.unoosa.org/oosa/en/ourwork/spacelaw/treaties/introouterspacetreaty.html.
Wall, Mike. "Elon Musk’s Grand Plan to Make Humanity a Multiplanet Species." Space.com, 28 Sept. 2016, www.space.com/34253-elon-musk-plan-multiplanet-species.html.
Hashtags:
#SpaceExploration
#ElonMusk
#SpaceX
#MarsMission
#ReusableRockets
#Starship
#Falcon9
#Starlink
#GlobalConnectivity
#FutureOfSpace
#PrivateSpaceflight
#SpaceInnovation
#TechRevolution
#SpaceEconomy
#STEMEducation
#SpaceDebris
#EnvironmentalImpact
#SpaceLaw
#MultiplanetarySpecies
#SpaceGovernance
#SpaceEthics
#CulturalImpact
#SpaceTech
#SpaceRace
#NextGenExplorers
#MarsColonization
https://medium.com/@bettybassett63/elon-musks-impact-on-the-future-of-space-exploration-by-betty-bassett-bc70c67749ad |
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 128 de 136 de ce thème |
|
https://www.cnbc.com/2022/02/11/elon-musk-spacexs-starship-is-solution-to-efficient-space-travel.html |
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 129 de 136 de ce thème |
|
Elon Musk’s Tesla has moved some of its Bitcoin into new wallets, sparking speculation that the EV maker is poised to sell off its cryptocurrency reserves. Blockchain data platform Arkham Intelligence detected the movement after Tesla’s Bitcoin wallets saw some activity for the first time in over two years.
Tesla has transferred its entire stash of 11,509 BTC, valued at $765 million at the time of the transfer, to several new wallets. The surprise transactions, including test transfers, totaled 26 and have stirred a debate that the automaker is gearing up to offload its remaining Bitcoin stash.
Will Tesla Sell Off Its Bitcoins?
Tesla’s latest Bitcoin shuffle has drawn widespread attention. However, amidst the speculations, neither Musk nor the company has commented on the move. The activity represents Tesla’s first on-chain Bitcoin activity since early 2022.
The purchase of $1.5 billion worth of Bitcoin by Tesla in 2021 made headlines, saying it was part of its long-term investment plan. However, the company sold 85% of its Bitcoin stash in 2022. Most of the sales occurred when the crypto traded at about $23,000 per coin.
If the transfer results in sales, the company can profit as high as $515 million.
Perspective Based on Past Tesla Bitcoin Sales
Tesla certainly hasn’t shied away from selling some of its Bitcoin. During the first quarter of 2022, the company sold 10% of its Bitcoin. The firm later sold 75% of its Bitcoin in July 2022.
The company recorded losses from these sales as Bitcoin’s price was much lower at the time. Though Tesla had sell-offs in the past, the latest transfer indicates a probable change in its crypto strategy.
It’s unclear whether the EV automaker will sell its BTC assets or just transfer them for another purpose. Nonetheless, this surprise move has put the auto manufacturer in hot seats in the crypto space.
Elon Musk Faces Crypto Scrutiny After The BTC Transfers
Tesla’s transactions have caught many off guard. This is because Musk is considered an Influential proponent of cryptocurrencies. Elon Musk openly touts himself as an admirer of cryptocurrencies and declares his love for $DOGE, making him the meme cryptocurrency’s influential proponent.
In July 2024, Musk said Bitcoin and some other cryptocurrencies have merits, but he added he still favors Dogecoin. His praise of the meme coin was so great that investors sued him for financial losses.
Despite Musk seeming crypto-friendly, Tesla’s Bitcoin moves have left many guessing, particularly because his company has adopted conflicting attitudes toward digital asset storage.
Crypto Quant CEO Says Tesla’s BTC Sale Won’t Affect The Market
The CEO of Crypto Quant, Ki Young Ju, has rivaled many expectations regarding the potential sale of Tesla’s BTC. In his post, Young said that if Tesla decided to sell, the market pressure would be easily absorbed.
He pointed to the June sale of 50,000 BTC seized from Movie2k.to by the German government, which fetched $816 million. According to Ju, that sale was digested with minimal disruption to the market and thus demonstrated that it could do the same with Tesla’s smaller holdings.
Tesla’s Bitcoin is worth $515 million, a far lower value than the German government is selling. Whatever the case, Ju says that the crypto market will not bat an eyelid at a transaction of this nature.
https://www.the-blockchain.com/2024/10/16/tesla-moves-765m-worth-of-bitcoin-to-new-wallets-move-sparks-sales-debate/ |
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 130 de 136 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 131 de 136 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 132 de 136 de ce thème |
|
La primera misión privada a Marte se lanzará en 2026
Impulse y Relativity Space apuntan a un objetivo sin precedentes en la carrera espacial: llegar a Marte
Curiosidades29/05/2023 Studio341News Studio341News
Recordemos que la NASA ya ha iniciado sus preparativos para volver a la Luna, enviando a la primera mujer y al próximo hombre en 2025 con las misiones Artemis y como objetivo más lejano se encuentra viajar a Marte a finales de la década de 2030 o principios de la de 2040. Imaginar a la NASA llegando a Marte inmersos aún en el viaje a la Luna parece difícil. De hecho, el propio fundador de la compañía SpaceX, Elon Musk, había predicho que pondríamos un pie en Marte para 2026. En una entrevista publicada en la revista Time (en 2021), Musk, tras ser nombrado “Persona del año”, decía lo siguiente: “me sorprendería si no aterrizamos en Marte dentro de cinco años".
Si bien no parece que vayan a salir las cosas tal y como él pensaba, pues la Starship, la nave espacial más potente y grandiosa jamás construida por el ser humano, no está teniéndolo fácil para seguir sorteando las fases necesarias hasta poder contar con una nave completamente operativa para los viajes espaciales. Su primer vuelo de prueba, que tuvo lugar el 20 de abril de 2023, acabó en una explosión imprevista pocos minutos después del despegue. Sin embargo, Musk afirmó que este vuelo de prueba era solo para recopilar datos y que realizarían muchas modificaciones en los vehículos futuros. Existen varios (numerosos, más bien) naves espaciales en distintas etapas de producción en la base de construcción de SpaceX y su siguiente objetivo, será precisamente alcanzar la órbita. Aunque se desconoce en qué momento se producirá este siguiente paso.

Carrera espacial
Mientras tanto, hay dos empresas que parecen haber tomado la delantera de forma sutil en la carrera espacial y que se han unido en la que será la primera misión comercial a Marte. Y tan pronto como 2026. Son Impulse Space y Relativity Space.
Impulse Space: Fundada por Tom Mueller, miembro fundador de SpaceX, en septiembre de 2021. La empresa desarrolla motores de cohetes químicos y módulos de aterrizaje planetarios para llevar cargas útiles a Marte. Su objetivo es ofrecer servicios en el espacio confiables y económicos.
Relativity Space: Fundada en 2015 por Tim Ellis y Jordan Noone (ambos ingenieros aeroespaciales), han desarrollado una plataforma de fabricación de cohetes llamada "Stargate", que utiliza impresoras 3D de gran escala para fabricar componentes de cohetes de forma rápida y eficiente. En marzo de 2023, sin ir más lejos, lanzaron el "Terran 1", el primer cohete impreso en 3D que, aunque realizó un vuelo bastante exitoso, no logró alcanzar la órbita.

Ahora, las dos pequeñas compañías espaciales privadas se han unido para lograr el hito de ser los primeros en llegar a Marte. Respecto a la participación de Relativity Space, aunque su intención era lanzar la misión incluso en 2025, este retraso no parece haber esquivado su objetivo principal que es centrar toda su atención en el desarrollo del cohete Terran-R que se espera debute, por tanto, en 2026. Terran-R es mayor que Terran-1. Estará impreso en 3D pero contará con mucha más carga útil: 33,5 toneladas. En cuanto a Impulse Space, se sabe que contribuirá con su Mars Cruise Vehicle y Mars Lander para la próxima misión comercial a Marte.
Juntas, desean crear un corredor de transporte permanente entre los dos planetas, la Tierra y Marte. El objetivo es entregar carga de varios clientes a Marte durante cada ventana balística, que se abre una vez cada 26 meses. Así, las compañías intentarán lanzar una misión cada 26 meses para que coincida con la ventana de lanzamiento para enviar misiones a Marte. Si todo sale según lo previsto, Impulse y Relativity Space harán historia, aunque es posible que no sean las primeras empresas privadas en enviar una misión a otro planeta. Rocket Lab, una compañía con sede en Nueva Zelanda, planea enviar la primera misión privada a Venus con el cohete Electron y la nave espacial Photon de Rocket Lab. Y tampoco podemos olvidar la misión Juice de la Agencia Espacial Europea (ESA) con destino Júpiter que buscará rastros de vida en sus lunas heladas y que fue lanzada con éxito en abril de 2023.
https://studio341news.com/contenido/295/la-primera-mision-privada-a-marte-se-lanzara-en-2026 |
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 133 de 136 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 134 de 136 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 135 de 136 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 136 de 136 de ce thème |
|
With new contracts, SpaceX will become the US military’s top launch provider
The military's stable of certified rockets will include Falcon 9, Falcon Heavy, Vulcan, and New Glenn.
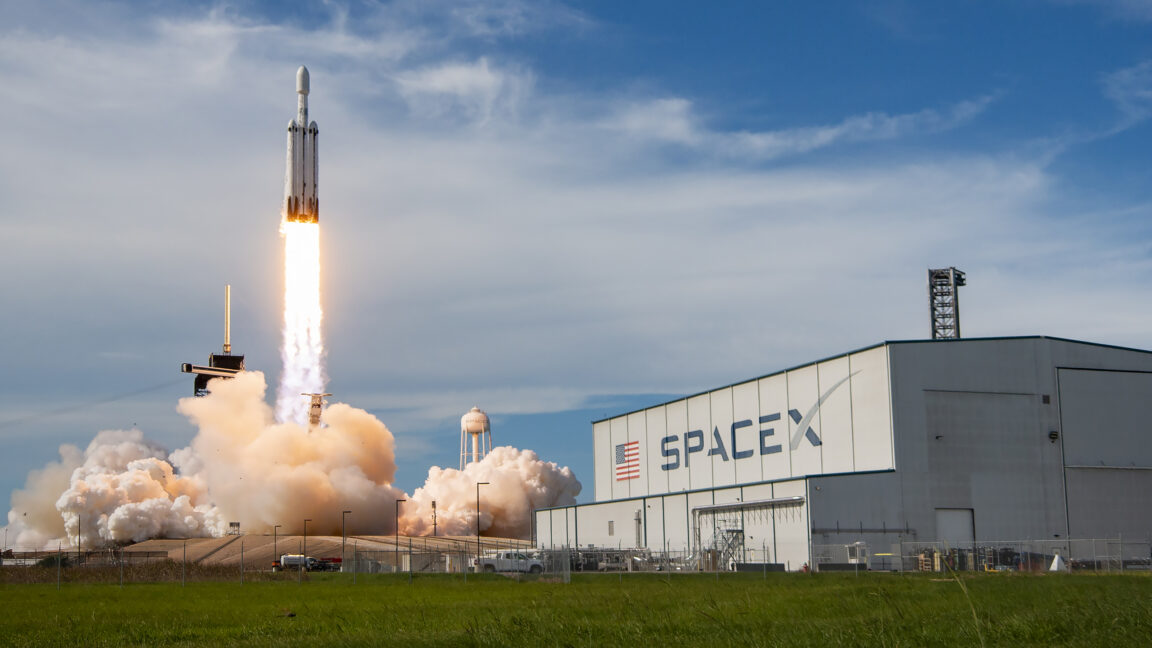
A SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket lifts off on June 25, 2024, with a GOES weather satellite for NOAA. Credit: SpaceX
The US Space Force announced Friday it selected SpaceX, United Launch Alliance, and Blue Origin for $13.7 billion in contracts to deliver the Pentagon's most critical military to orbit into the early 2030s.
These missions will launch the government's heaviest national security satellites, like the National Reconnaissance Office's large bus-sized spy platforms, and deploy them into bespoke orbits. These types of launches often demand heavy-lift rockets with long-duration upper stages that can cruise through space for six or more hours.
The contracts awarded Friday are part of the next phase of the military's space launch program once dominated by United Launch Alliance, the 50-50 joint venture between legacy defense contractors Boeing and Lockheed Martin.
After racking up a series of successful launches with its Falcon 9 rocket more than a decade ago, SpaceX sued the Air Force for the right to compete with ULA for the military's most lucrative launch contracts. The Air Force relented in 2015 and allowed SpaceX to bid. Since then, SpaceX has won more than 40 percent of missions the Pentagon has ordered through the National Security Space Launch (NSSL) program, creating a relatively stable duopoly for the military's launch needs.
The Space Force took over the responsibility for launch procurement from the Air Force after its creation in 2019. The next year, the Space Force signed another set of contracts with ULA and SpaceX for missions the military would order from 2020 through 2024. ULA's new Vulcan rocket initially won 60 percent of these missions—known as NSSL Phase 2—but the Space Force reallocated a handful of launches to SpaceX after ULA encountered delays with Vulcan.
ULA's Vulcan and SpaceX's Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets will launch the remaining 42 Phase 2 missions over the next several years, then move on to Phase 3, which the Space Force announced Friday.
Spreading the wealth
This next round of Space Force launch contracts will flip the script, with SpaceX taking the lion's share of the missions. The breakdown of the military's new firm fixed-price launch agreements goes like this:
- SpaceX will get 28 missions worth approximately $5.9 billion
- ULA will get 19 missions worth approximately $5.4 billion
- Blue Origin will get seven missions worth approximately
That equates to a 60-40 split between SpaceX and ULA for the bulk of the missions. Going into the competition, military officials set aside seven additional missions to launch with a third provider, allowing a new player to gain a foothold in the market. The Space Force reserves the right to reapportion missions between the three providers if one of them runs into trouble.
The Pentagon confirmed an unnamed fourth company also submitted a proposal, but wasn't selected for Phase 3.
Rounded to the nearest million, the contract with SpaceX averages out to $212 million per launch. For ULA, it's $282 million, and Blue Origin's price is $341 million per launch. But take these numbers with caution. The contracts include a lot of bells and whistles, pricing them higher than what a commercial customer might pay.
According to the Pentagon, the contracts provide "launch services, mission unique services, mission acceleration, quick reaction/anomaly resolution, special studies, launch service support, fleet surveillance, and early integration studies/mission analysis."
Essentially, the Space Force is paying a premium to all three launch providers for schedule priority, tailored solutions, and access to data from every flight of each company's rocket, among other things.
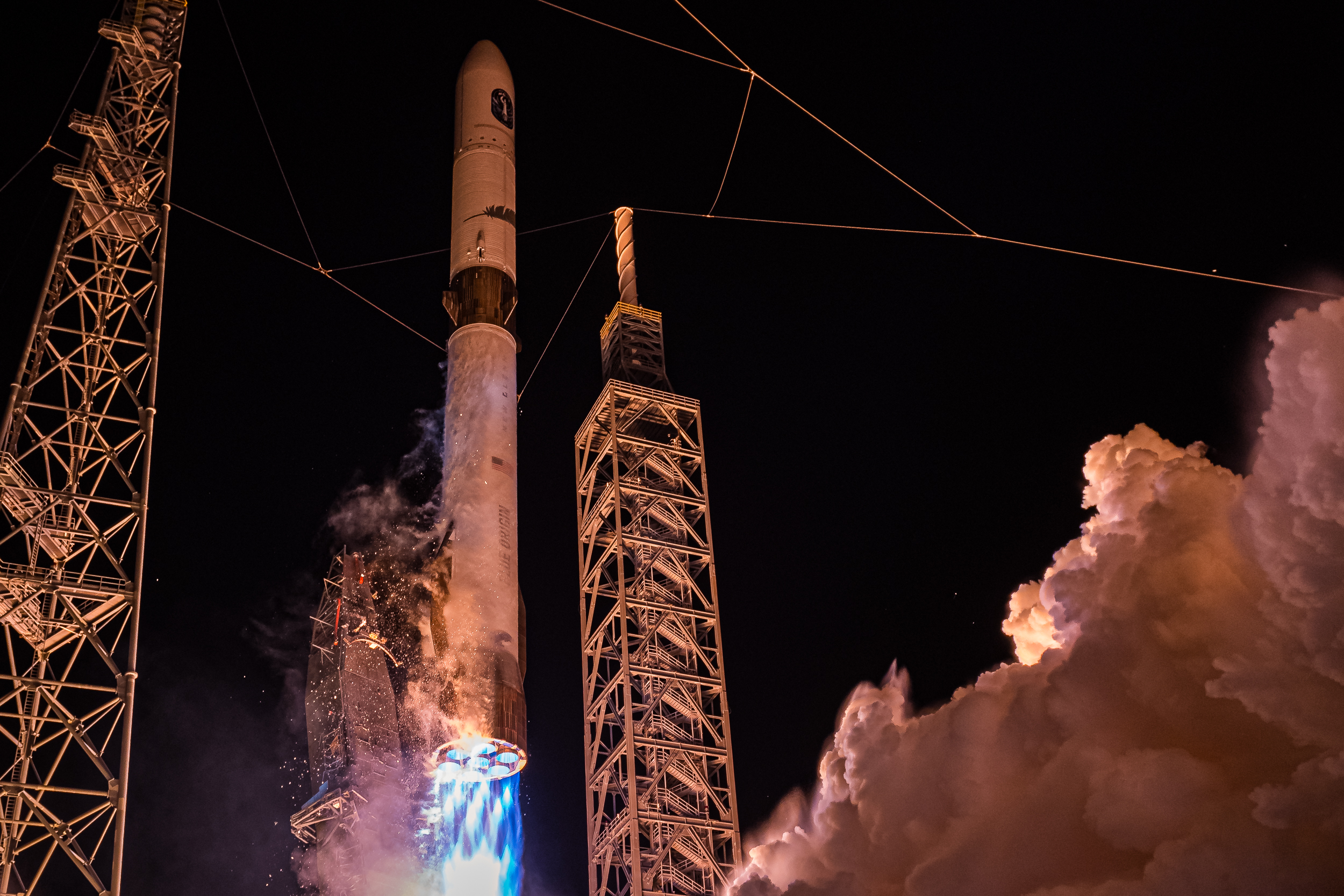
New Glenn lifts off on its debut flight. Credit: Blue Origin
"Winning 60% percent of the missions may sound generous, but the reality is that all SpaceX competitors combined cannot currently deliver the other 40%!," Elon Musk, SpaceX's founder and CEO, posted on X. "I hope they succeed, but they aren’t there yet."
This is true if you look at each company's flight rate. SpaceX has launched Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets 140 times over the last 365 days. These are the flight-proven rockets SpaceX will use for its share of Space Force missions.
ULA has logged four missions in the same period, but just one with the Vulcan rocket it will use for future Space Force launches. And Blue Origin, Jeff Bezos's space company, launched the heavy-lift New Glenn rocket on its first test flight in January.
"We are proud that we have launched 100 national security space missions and honored to continue serving the nation with our new Vulcan rocket," said Tory Bruno, ULA’s president and CEO, in a statement.
ULA used the Delta IV and Atlas V rockets for most of the missions it has launched for the Pentagon. The Delta IV rocket family is now retired, and ULA will end production of the Atlas V rocket later this year. Now, ULA's Vulcan rocket will take over as the company's sole launch vehicle to serve the Pentagon. ULA aims to eventually ramp up the Vulcan launch cadence to fly up to 25 times per year.
After two successful test flights, the Space Force formally certified the Vulcan rocket last week, clearing the way for ULA to start using it for military missions in the coming months. While SpaceX has a clear advantage in number of launches, schedule assurance, and pricing—and reliability comparable to ULA—Bruno has recently touted the Vulcan rocket's ability to maneuver over long periods in space as a differentiator.
"This award constitutes the most complex missions required for national security space," Bruno said in a ULA press release. "Vulcan continues to use the world’s highest energy upper stage: the Centaur V. Centaur V's unmatched flexibility and extreme endurance enables the most complex orbital insertions continuing to advance our nation’s capabilities in space."
Blue Origin's New Glenn must fly at least one more successful mission before the Space Force will certify it for Lane 2 missions. The selection of Blue Origin on Friday suggests military officials believe New Glenn is on track for certification by late 2026.
"Honored to serve additional national security missions in the coming years and contribute to our nation’s assured access to space," Dave Limp, Blue Origin's CEO, wrote on X. "This is a great endorsement of New Glenn's capabilities, and we are committed to meeting the heavy lift needs of our US DoD and intelligence agency customers."
Navigating NSSL
There's something you must understand about the way the military buys launch services. For this round of competition, the Space Force divided the NSSL program into two lanes.
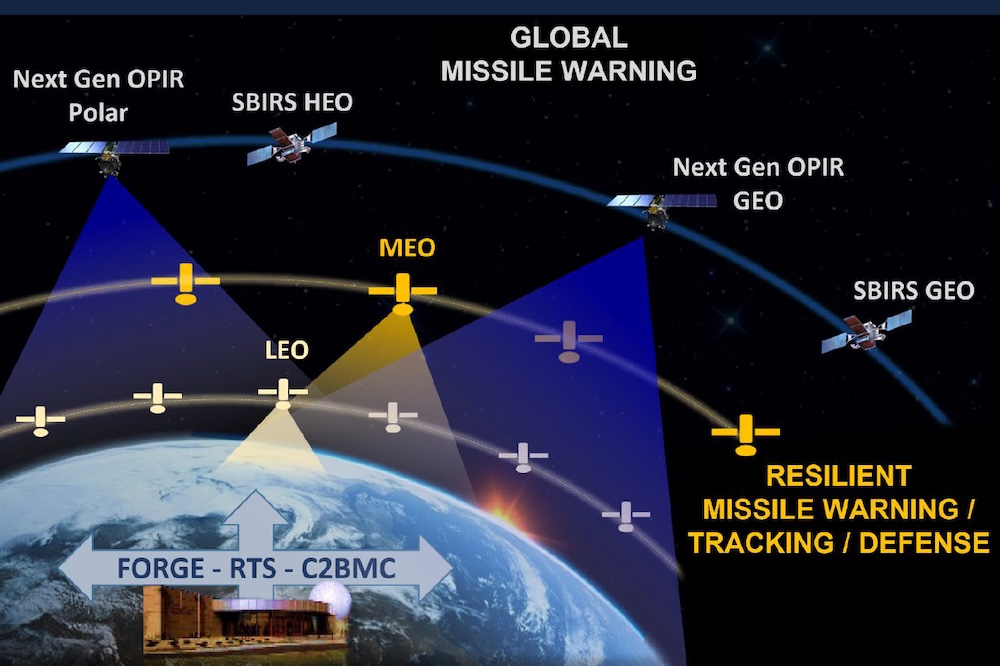
Friday's announcement covers Lane 2 for traditional military satellites that operate thousands of miles above the Earth. This bucket includes things like GPS navigation satellites, NRO surveillance and eavesdropping platforms, and strategic communications satellites built to survive a nuclear war. The Space Force has a low tolerance for failure with these missions. Therefore, the military requires rockets be certified before they can launch big-ticket satellites, each of which often cost hundreds of millions, and sometimes billions, of dollars.
The Space Force required all Lane 2 bidders to show their rockets could reach nine "reference orbits" with payloads of a specified mass. Some of the orbits are difficult to reach, requiring technology that only SpaceX and ULA have demonstrated in the United States. Blue Origin plans to do so on a future flight.
This image shows what the Space Force's fleet of missile warning and missile tracking satellites might look like in 2030, with a mix of platforms in geosynchronous orbit, medium-Earth orbit, and low-Earth orbit. The higher orbits will require launches by "Lane 2" providers. Credit: Space Systems Command
The military projects to order 54 launches in Lane 2 from this year through 2029, with announcements each October of exactly which missions will go to each launch provider. This year, it will be just SpaceX and ULA. The Space Force said Blue Origin won't be eligible for firm orders until next year. The missions would launch between 2027 and 2032.
"America leads the world in space launch, and through these NSSL Phase 3 Lane 2 contracts, we will ensure continued access to this vital domain," said Maj. Gen. Stephen Purdy, Acting Assistant Secretary of the Air Force for Space Acquisition and Integration. "These awards bolster our ability to launch critical defense satellites while strengthening our industrial base and enhancing operational readiness."
Lane 1 is primarily for missions to low-Earth orbit. These payloads include tech demos, experimental missions, and the military's mega-constellation of missile tracking and data relay satellites managed by the Space Development Agency. For Lane 1 missions, the Space Force won't levy the burdensome certification and oversight requirements it has long employed for national security launches. The Pentagon is willing to accept more risk with Lane 1, encompassing at least 30 missions through the end of the 2020s, in an effort to broaden the military's portfolio of launch providers and boost competition.
Last June, Space Systems Command chose SpaceX, ULA, and Blue Origin for eligibility to compete for Lane 1 missions. SpaceX won all nine of the first batch of Lane 1 missions put up for bids. The military recently added Rocket Lab's Neutron rocket and Stoke Space's Nova rocket to the Lane 1 mix. Neither of those rockets have flown, and they will need at least one successful launch before approval to fly military payloads.
The Space Force has separate contract mechanisms for the military's smallest satellites, which typically launch on SpaceX rideshare missions or dedicated launches with companies like Rocket Lab and Firefly Aerospace.
Military leaders like having all these options, and would like even more. If one launch provider or launch site is unavailable due to a technical problem—or, as some military officials now worry, an enemy attack—commanders want multiple backups in their toolkit. Market forces dictate that more competition should also lower prices.
"A robust and resilient space launch architecture is the foundation of both our economic prosperity and our national security," said US Space Force Chief of Space Operations Gen. Chance Saltzman. "National Security Space Launch isn't just a program; it's a strategic necessity that delivers the critical space capabilities our warfighters depend on to fight and win."
https://arstechnica.com/space/2025/04/with-new-contracts-spacex-will-become-the-us-militarys-top-launch-provider/ |
|
|
 Premier Premier
 Précédent
122 a 136 de 136
Suivant Précédent
122 a 136 de 136
Suivant
 Dernier
Dernier

|
 The flight will launch on a Falcon 9 rocket (
The flight will launch on a Falcon 9 rocket (