|
|
General: ASTERIX, OBELIX (FREEMASONRY, FRANCE, MADELEINE, LUXOR, PLACE DE LA CONCORDE)
Choose another message board |
|
Reply |
Message 1 of 6 on the subject |
|
Asterix
Asterix (French: Astérix or Astérix le Gaulois [asteʁiks lə ɡolwa], "Asterix the Gaul"; also known as Asterix and Obelix in some adaptations or The Adventures of Asterix) is a French comic album series about a Gaulish village which, thanks to a magic potion that enhances strength, resists the forces of Julius Caesar's Roman Republic Army in a nonhistorical telling of the time after the Gallic Wars. Many adventures take the titular hero Asterix and his friend Obelix to Rome and beyond.
The series first appeared in the Franco-Belgian comic magazine Pilote on 29 October 1959. It was written by René Goscinny and illustrated by Albert Uderzo until Goscinny's death in 1977. Uderzo then took over the writing until 2009, when he sold the rights to publishing company Hachette; he died in 2020. In 2013, a new team consisting of Jean-Yves Ferri (script) and Didier Conrad (artwork) took over. As of 2023, 40 volumes have been released; the most recent was penned by new writer Fabcaro and released on 26 October 2023.
By that year, the volumes in total had sold 393 million copies,[1] making them the best-selling European comic book series, and the second best-selling comic book series in history after One Piece.
 Some of the many characters in Asterix. In the front row are the regular characters, with Asterix himself in the centre, along with Obelix, Getafix, Vitalstatistix and others. Some of the many characters in Asterix. In the front row are the regular characters, with Asterix himself in the centre, along with Obelix, Getafix, Vitalstatistix and others.
Asterix comics usually start with the following introduction:
The year is 50 BC. Gaul is entirely occupied by the Romans. Well, not entirely... One small village of indomitable Gauls still holds out against the invaders. And life is not easy for the Roman legionaries who garrison the fortified camps of Totorum, Aquarium, Laudanum and Compendium...[2][3]
The series follows the adventures of a village of Gauls as they resist Roman occupation in 50 BC. They do so using a magic potion, brewed by their druid Getafix (Panoramix in the French version), which temporarily gives the recipient superhuman strength. The protagonists, the title character Asterix and his friend Obelix, have various adventures. The "-ix" ending of both names (as well as all the other pseudo-Gaulish "-ix" names in the series) alludes to the "-rix" suffix (meaning "king", like "-rex" in Latin) present in the names of many real Gaulish chieftains such as Vercingetorix, Orgetorix, and Dumnorix.
In some of the stories, they travel to foreign countries, whilst other tales are set in and around their village. For much of the history of the series (volumes 4 through 29), settings in Gaul and abroad alternate, with even-numbered volumes set abroad and odd-numbered volumes set in Gaul, mostly in the village.
The Asterix series is one of the most popular Franco-Belgian comics in the world, with the series being translated into 111 languages and dialects as of 2009.[4]
The success of the series has led to the adaptation of its books into 15 films: ten animated, and five live action (two of which, Asterix & Obelix: Mission Cleopatra and Asterix and Obelix vs. Caesar, were major box office successes in France). There have also been a number of games based on the characters, and a theme park near Paris, Parc Astérix. The very first French satellite, Astérix, launched in 1965, was named after the character, whose name is close to Greek ἀστήρ and Latin astrum, meaning a "star". As of 20 April 2022, 385 million copies of Asterix books had been sold worldwide and translated in 111 languages making it the world's most widely translated comic book series,[5] with co-creators René Goscinny and Albert Uderzo being France's best-selling authors abroad.[6][7]
In April 2022, Albert and René's general director, Céleste Surugue, hosted a 45-minute talk entitled 'The Next Incarnation of a Heritage Franchise: Asterix' and spoke about the success of the Asterix franchise, of which he noted "The idea was to find a subject with a strong connection with French culture and, while looking at the country's history, they ended up choosing its first defeat, namely the Gaul's Roman colonisation". He also went on to say how, since 1989, Parc Asterix has attracted an average of 2.3 million visitors per year. Other notable mentions were how the franchise includes 10 animated movies, which recorded over 53 million viewers worldwide. The inception of Studios Idéfix in 1974 and the opening of Studio 58 in 2016 were among the necessary steps to make Asterix a "100% Gaulish production", considered the best solution to keep the creative process under control from start to finish and to employ French manpower. He also noted how a new album is now published every two years, with print figures of 5 million and an estimated readership of 20 million.[5]
|
|
|
 First
First
 Previous
2 to 6 of 6
Next
Previous
2 to 6 of 6
Next
 Last
Last

|
|
Reply |
Message 2 of 6 on the subject |
|
Publication history
[edit]
 Évariste Vital Luminais' (1821–1896) paintings of Goths had been rather popular in France and are a possible model for the Asterix series.[8] Évariste Vital Luminais' (1821–1896) paintings of Goths had been rather popular in France and are a possible model for the Asterix series.[8]
Prior to creating the Asterix series, Goscinny and Uderzo had had success with their series Oumpah-pah, which was published in Tintin magazine.[9] Astérix was originally serialised in Pilote magazine, debuting in the first issue on 29 October 1959.[10] In 1961, the first book was put together, titled Asterix the Gaul. From then on, books were released generally on a yearly basis. Their success was exponential; the first book sold 6,000 copies in its year of publication; a year later, the second sold 20,000. In 1963, the third sold 40,000; the fourth, released in 1964, sold 150,000. A year later, the fifth sold 300,000; 1966's Asterix and the Big Fight sold 400,000 upon initial publication. The ninth Asterix volume, when first released in 1967, sold 1.2 million copies in two days.
Uderzo's first preliminary sketches portrayed Asterix as a huge and strong traditional Gaulish warrior. But Goscinny had a different picture in his mind, visualizing Asterix as a shrewd, compact warrior who would possess intelligence and wit more than raw strength. However, Uderzo felt that the downsized hero needed a strong but dim companion, to which Goscinny agreed. Hence, Obelix was born.[11] Despite the growing popularity of Asterix with the readers, the financial backing for the publication Pilote ceased. Pilote was taken over by Georges Dargaud.[11]
When Goscinny died in 1977, Uderzo continued the series by popular demand of the readers, who implored him to continue. He continued to issue new volumes of the series, but on a less frequent basis. Many critics and fans of the series prefer the earlier collaborations with Goscinny.[12] Uderzo created his own publishing company, Éditions Albert René, which published every album drawn and written by Uderzo alone since then.[11] However, Dargaud, the initial publisher of the series, kept the publishing rights on the 24 first albums made by both Uderzo and Goscinny. In 1990, the Uderzo and Goscinny families decided to sue Dargaud to take over the rights. In 1998, after a long trial, Dargaud lost the rights to publish and sell the albums. Uderzo decided to sell these rights to Hachette instead of Albert-René, but the publishing rights on new albums were still owned by Albert Uderzo (40%), Sylvie Uderzo (20%) and Anne Goscinny (40%).[citation needed]
In December 2008, Uderzo sold his stake to Hachette, which took over the company.[13] In a letter published in the French newspaper Le Monde in 2009, Uderzo's daughter, Sylvie, attacked her father's decision to sell the family publishing firm and the rights to produce new Astérix adventures after his death. She said:
... the co-creator of Astérix, France's comic strip hero, has betrayed the Gaulish warrior to the modern-day Romans – the men of industry and finance.[14][15]
However, René Goscinny's daughter, Anne, also gave her agreement to the continuation of the series and sold her rights at the same time. She is reported to have said that "Asterix has already had two lives: one during my father's lifetime and one after it. Why not a third?".[16] A few months later, Uderzo appointed three illustrators, who had been his assistants for many years, to continue the series.[12] In 2011, Uderzo announced that a new Asterix album was due out in 2013, with Jean-Yves Ferri writing the story and Frédéric Mébarki drawing it.[17] A year later, in 2012, the publisher Albert-René announced that Frédéric Mébarki had withdrawn from drawing the new album, due to the pressure he felt in following in the steps of Uderzo. Comic artist Didier Conrad was officially announced to take over drawing duties from Mébarki, with the due date of the new album in 2013 unchanged.[18][19]
In January 2015, after the murders of seven cartoonists at the satirical Paris weekly Charlie Hebdo, Astérix creator Albert Uderzo came out of retirement to draw two Astérix pictures honouring the memories of the victims.[20]
Numbers 1–24, 32 and 34 are by Goscinny and Uderzo. Numbers 25–31 and 33 are by Uderzo alone. Numbers 35–39 are by Jean-Yves Ferri and Didier Conrad. Years stated are for their initial album release.[21]
Asterix Conquers Rome is a comics adaptation of the animated film The Twelve Tasks of Asterix. It was released in 1976 and was the 23rd volume to be published, but it has been rarely reprinted and is not considered to be canonical to the series. The only English translations ever to be published were in the Asterix Annual 1980 and never an English standalone volume. A picture-book version of the same story was published in English translation as The Twelve Tasks of Asterix by Hodder & Stoughton in 1978.
In 1996, a tribute album in honour of Albert Uderzo was released titled Uderzo Croqué par ses Amis, a volume containing 21 short stories with Uderzo in Ancient Gaul. This volume was published by Soleil Productions and has not been translated into English.
In 2007, Éditions Albert René released a tribute volume titled Astérix et ses Amis, a 60-page volume of one-to-four-page short stories. It was a tribute to Albert Uderzo on his 80th birthday by 34 European cartoonists. The volume was translated into nine languages. As of 2016, it has not been translated into English.[65]
In 2016, the French publisher Hachette, along with Anne Goscinny and Albert Uderzo decided to make the special issue album The XII Tasks of Asterix for the 40th anniversary of the film The Twelve Tasks of Asterix. There was no English edition.
|
|
|
|
Reply |
Message 3 of 6 on the subject |
|
|
|
|
Reply |
Message 4 of 6 on the subject |
|

Post by shipstamps » Tue Nov 18, 2008 4:27 pm
 Not much is know about the caravel, where and when built unknown. Tonnage 200 ton, dim. 85 x 25 x 14ft. (draught) Four masts, fore and main mast square rigged, mizzen and Bonaventura mast lateen rigged. She was the flagship of Don Pedro de Mendoza (1487-1537) expedition to the River Plata. Mendoza held a post in the court of Charles V, when he in 1534 made an offer to Emperor Charles V to make an expedition on his own account for the discovery and conquest of Paraguay and the countries on the Rio La Plata. 24 August 1534 Mendoza on board the MAGDALENA and 13 other vessels, with 3000 men set sail from San Lucar, Spain. Receive from the Emperor before sailing 2.000 ducats, with the condition, when he transported to the new founded colonies 1000 colonists and 100 horses, build a road to the Pacific Ocean, erect three forts within two years he would receive 2.000 ducats more. Also he had to take 8 monks, a physician, a surgeon, and an apothecary, but he was forbidden to introduce a lawyer in the colony. He was to have half the treasure of the chiefs killed and nine-tenths of the ransom. Mendoza was made before sailing military governor of all the territory between the Rio de la Plata and the Strait of Magellan. The office of the Governor was also made hereditary. Off the coast of Brazil the fleet was scattered in a heavy storm, and Medoza lieutenant Osario, was assassinated, according to some authorities by the orders of Mendoza himself because of suspected disloyalty. 1535 Mendoza sailed up the Rio de la Plata, and founded Buenos Aires on 02 February 1536. He erected two forts there to defend the place. Pestilence broke out and the natives became unfriendly after ill treatment by the Spaniards. His brother Don Diego led a force against the hostile tribes, but was killed with three-fourths of his men. A general conspiracy of the natives was formed, and Buenos Aires was captured and burned by the natives. Mendoza retired to the forth Sanctus-Spiritus, from where he dispatched Juan de Ayolas to explore the upper part of the river. Another brother, Gonzalo arrived with reinforcements and founded the city of Ascención in Paraguay in 1536. Mendoza, disappointed and with a broken health, embarked on board the MAGDALENA for Spain in 1537, leaving Juan de Ayolas in charge. During the long voyage to Spain he died maniac on board the MAGDALENA on 23 June 1537. The fate of the MAGDALENA is not known. Argentine 1979 400p + 400p sg 1646 Source: mostly copied from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pedro_de_Mendoza http://famousamericans.net/pedrodemendoza
https://shipstamps.co.uk/forum/viewtopic.php?t=6731
|
|
|
|
Reply |
Message 5 of 6 on the subject |
|
Reyes españoles y los colores de la bandera

Carlos IV de Borbón (Portici, Nápoles, 11 de noviembre de 1748 – Roma, 20 de enero de 1819) fue Rey de España desde el 14 de diciembre de 1788 hasta el 19 de marzo de 1808. Hijo y sucesor de Carlos III y de María Amalia de Sajonia.

Fernando VII de Borbón (San Lorenzo de El Escorial, 14 de octubre de 1784 - Madrid, 29 de septiembre de 1833), llamado el Deseado o el Rey Felón, fue rey de España entre marzo y mayo de 1808 y, tras la expulsión del rey intruso José Bonaparte, nuevamente desde diciembre de 1813 hasta su muerte, exceptuando un breve intervalo en 1823, en que fue destituido por el Consejo de Regencia.

Alfonso XII de Borbón, el Pacificador (Madrid, 28 de noviembre de 1857 – El Pardo, 25 de noviembre de 1885), fue rey de España entre 1874 y 1885; era hijo de la reina Isabel II de España y su marido, Francisco de Asís de Borbón. Nacido Alfonso Francisco Fernando Pío Juan de María de la Concepción Gregorio Pelayo de Borbón y Borbón. Reinó tras la Restauración borbónica, hasta su muerte prematura a los 27 años, víctima de la tuberculosis. Fue sucedido en el trono por su hijo póstumo, Alfonso XIII de España, cuya minoría estuvo encabezada por la regencia de su viuda, María Cristina de Austria.

https://histeducarg.wordpress.com/extras/reyes-espanoles-y-los-colores-de-la-bandera/ |
|
|
|
Reply |
Message 6 of 6 on the subject |
|
Por Ing. Sergio A. Luñansky
|
 |
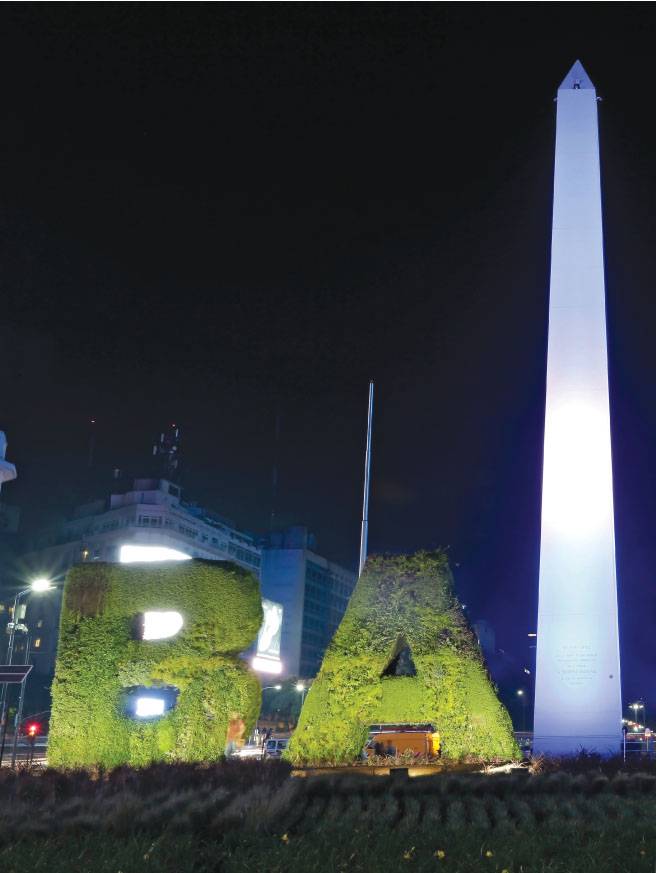
 
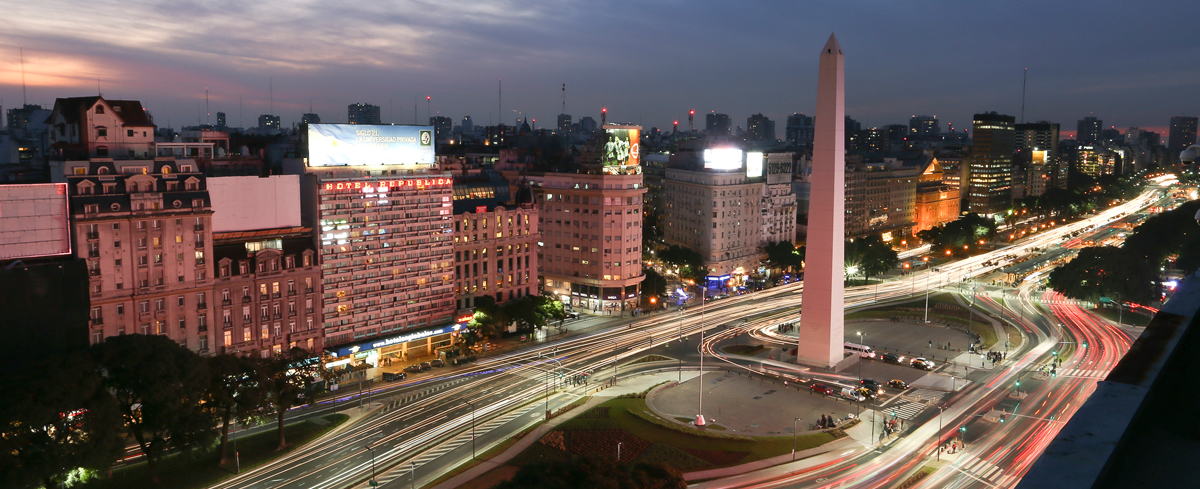
Miles de personas se congregan en su entorno para festejar o manifestarse. El Obelisco es el mayor símbolo de la ciudad de Buenos Aires y fue erigido el 1936 para conmemorar los cuatrocientos años de su primera fundación. El monumento está ubicado estratégicamente en la intersección de dos de sus avenidas más importantes: 9 de Julio, una de las más anchas del mundo, y Corrientes, con intensa vida cultural y nocturna.
Su construcción demoró solo 31 días. Más de 150 obreros lo levantaron con 680 metros cúbicos de cemento y 1.300 metros de piedra calcárea, de acuerdo al proyecto del arquitecto argentino Alberto Prebisch. El monumento tiene una altura total de 67,5 metros y una base cuadrada de 6,8 metros de lado.
Se trata de una estructura hueca de hormigón armado que posee una escalera interna con 206 peldaños que conducen hasta la cima. Allí hay una habitación de tres por tres metros con cuatro ventanas.
La estética racionalista del Obelisco despertó quejas entre los ciudadanos, y los más radicales hasta propusieron demolerlo a pocos años de construido. Hoy, los rasgos de identidad de Buenos Aires se ven fielmente representados en sus líneas rectas y en las superficies de piedra blanca iluminadas con tecnología led.
La iluminación del Obelisco
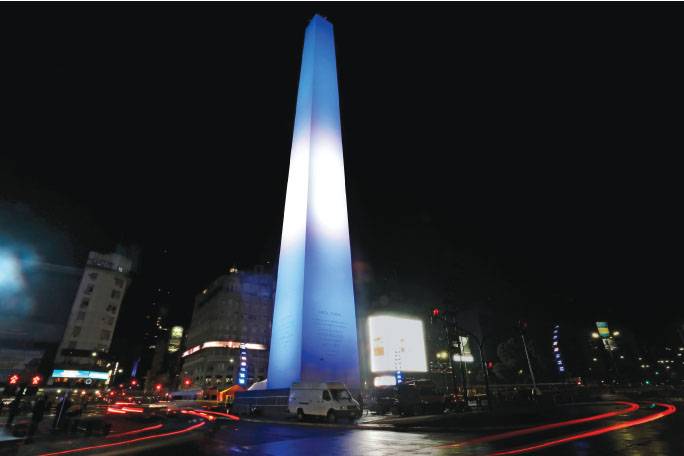  Philips Lighting fue convocada por el Gobierno de la Ciudad de Buenos Aires para colaborar en la puesta en valor del monumento. Con el fin de embellecer y destacar la estructura en el escenario urbano nocturno, se realizó un proyecto de iluminación con tecnología led, adecuada para crear una amplia variedad de efectos de luz garantizando la máxima vida útil de la fuente con mínimo consumo de energía. La iluminación instalada permite que todo el sistema pueda ser controlado de manera remota por una computadora y así programar los distintos encendidos para todo el año, según fechas patrias o eventos especiales. Philips Lighting fue convocada por el Gobierno de la Ciudad de Buenos Aires para colaborar en la puesta en valor del monumento. Con el fin de embellecer y destacar la estructura en el escenario urbano nocturno, se realizó un proyecto de iluminación con tecnología led, adecuada para crear una amplia variedad de efectos de luz garantizando la máxima vida útil de la fuente con mínimo consumo de energía. La iluminación instalada permite que todo el sistema pueda ser controlado de manera remota por una computadora y así programar los distintos encendidos para todo el año, según fechas patrias o eventos especiales.
En las plazoletas que rodean al monumento se instalaron seis columnas de iluminación con ocho proyectores led cada una. Las luminarias ColorReach Compact Powercore Gen2 aptas para uso en exterior ofrecen un cambio dinámico de color y largo alcance, lo que las hace adecuadas para la iluminación de edificios, puentes y estructuras icónicas.
Además, ofrecen una gama de accesorios que permiten personalizar el haz para la iluminación de acento, el destaque de texturas o el bañado de pared.
La polución lumínica de las pantallas publicitarias cercanas al monumento planteó uno de los mayores desafíos para el proyecto de iluminación. En ese sentido, las luminarias instaladas optimizan la mezcla de colores proporcionando mayor fuerza y calidad, permitiendo proyectar la luz exactamente donde se desee.
  Todas las luminarias están comandadas por un controlador iPlayer 3, encargado de darle animación al diseño lumínico. Este dispositivo ofrece sofisticación y flexibilidad para diseñar las instalaciones de iluminación al tiempo que no requiere de conocimientos técnicos específicos de programación. Todas las luminarias están comandadas por un controlador iPlayer 3, encargado de darle animación al diseño lumínico. Este dispositivo ofrece sofisticación y flexibilidad para diseñar las instalaciones de iluminación al tiempo que no requiere de conocimientos técnicos específicos de programación.
Cada noche, el Obelisco se enciende con luz propia. El sistema de iluminación diseñado por la empresa fabricante lo convierte en un protagonista urbano de aniversarios, conmemoraciones y eventos especiales en la ciudad, transformando el espacio público.
La intervención sobre el monumento se complementa con un ambicioso plan de modernización de las luminarias de toda la ciudad de Buenos Aires al cual se incorpora el eje de la Avenida 9 de Julio. La reconversión de luminarias y farolas convencionales a luminarias led interconectadas con el sistema City Touch le permitirá a Buenos Aires reducir en un cincuenta por ciento el consumo de electricidad para la iluminación.
Philips también se enorgullece de iluminar otros lugares emblemáticos de Buenos Aires como el Teatro Colón, el Monumento a los Españoles y la Catedral Metropolitana.
|
 |
https://www.editores.com.ar/revistas/lu/136/philips_bs_as_obelisco |
|
|
 First
First
 Previous
2 a 6 de 6
Next
Previous
2 a 6 de 6
Next
 Last
Last

|
|
| |
|
|
©2025 - Gabitos - All rights reserved | |
|
|




























