|
|
General: INDIA 15 OF AUGUST INDEPENDENCE DAY NAPOLEON S BORN APOLLO GATE DA VINCI CODE
Triar un altre plafó de missatges |
|
|
THE SWASTIKA
The swastika, hackenkreuz, gamma cross, gammadion, St. Brigid's cross, or fylfot cross is a symbol found around the world. It not universally drawn either clockwise or counterclockwise, and it occurs in both curved and squared forms.
This postcard, copyright 1907 by E. Phillips, a U.S. card publisher, speaks for the universally high regard in which the swastika was held as a good luck token before use by the Nazis corrupted its meaning.

The text on the card back reads:
GOOD LUCK EMBLEM
"The Swastika" is the oldest cross and emblem in the world. It forms a combination of four "L's" standing for Luck, Light, Love and Life. It has been found in ancient Rome, excavations in Grecian cities, on Buddhist idols, on Chinese coins dated 315 B.C., and our own Southwest Indians use it as an amulet.
It is claimed that the Mound Builders and Cliff Dwellers of Mexico, Central America consider "The Swastika" a charm to drive away evil and bring good luck, long life and prosperity to the possessor.
It should be noted that this text is not entirely accurate: The Mound Builders inhabited the Ohio River Valley and the Cliff Dwellers lived in the Southwestern United States; however, both did use the swastika, as did the Mayas of Mexico. Furthermore, although the swastika may look like four "L's" to one who uses the Roman alphabet, in Greek it forms four Gammas ("G's"), in Hebrew it can be seen as four Daleths ("D's"), and among the non-literate people of North America, it corresponded to no letters at all. Thus the ascription of Luck, Light, Love, and Life to the amulet is simply an English mnemonic, although it is prettily reinforced on this card by images of a horseshoe (luck), the rising Sun (light), twin hearts (love), and Earth (life). Finally, not mentioned in the text is the swastika's use as the specific emblem of Ganesha, the Hindu god of good luck, who is also represented as an elephant.

At left is a very nice American-made beaded item from the 1920s that bears the initials J.B.Y. and a black swastika on a white background. It is a simple strap-woven seed-bead piece of the type often made for a merit badge by Girl and Boy Scouts, or, as in this case, woven on a "while you wait" basis by American Indians for tourists at places like the Fred Harvey hotel chain in Arizona and New Mexico. It was found in an estate collection of Native American bead-work that had been put away and wrapped in 1929-dated newspapers. The twisted cotton threads terminate in a brass pin for hanging.
The use of the swastika in domestic ornament was fairly common in the 19th century. I have seen a beautiful white wedding dress, circa 1900, covered all over with embroidered swastikas. It came from the trousseau of a Polish-German immigrant woman, a "mail-order-bride" who was married in the U.S.
The swastika or hackencreuz was not a Nazi symbol originally, but was adopted by them as a "lucky" logo. (Imagine a political party of butchering madmen adopting the four-leaf clover as their symbol!) Some people believe that the swastika has been permanently co-opted or ruined by its brief appropriation by the Nazis -- who stood it up diagonally and placed it in a circle rather than running it four-square, and gave it their brand-logo colour scheme of black, white, and red, thus making THEIR swastika a national seal, unlike the non-Nazi swastikas of varied colour and form one finds all around the world.
It is a common misconception, almost an urban legend of sorts, to impute directional or positional preference or meaning to the swastika, and to claim that the Nazis "reversed the swastika" or "rotated it backwards" and therefore rendered it "evil." But this idea that directionality is important in the history of swastika usage is demonstrably untrue: counter-balancing (bilaterally symmetrical) arrays of clockwise and counterclockwise swastikas are common in both ancient and modern Indian art.
I believe that these considerations concerning the left- and right-turning swastika arose after the Nazis adopted the device -- and were part of a failed attempt to salvage at least a part of its former meaning by establishing a "good swastika versus bad swastika" dichotomy. Unfortunately, this swastika purity restoration attempt failed because ancient monuments and steles do not bear the theory out: The swastika appears in both left- and right-turned models in virtually all past cultures with no "deosil" and "widdershins" thought behind the direction, nor with "good" or "evil" concepts attached. The Nazis tipped the swastika up on end (diagonally), but it is even found that way in some old historical artifacts as well, such as this lovely example of the lucky swastika -- an embossed and airbrushed American postcard of the 1905 - 1910 era, bearing the legend "To Darling Baby," accompanied by a lavender swastika and a bunch of Lily-of-the-Valley flowers.

Some people believe that the display of any sort of swastika should be forbidden because it is offensive to Jews. From first-hand experience, i can assure you that dozens of elderly German Jews i personally know who lived through or escaped the holocaust, were and are well aware that the swastika pre-dated the Nazis and do not consider it a Nazi symbol. One thing most of them have learned -- and have taught to me -- is that RELIGIOUS TOLERANCE is a key to preventing future holocausts. Therefore they honour and respect the religious iconography of others. including the Jains and the Hindus, who revere the swastika as a symbol of a symbol of long life, good health, and good luck, and the special symbol of the Hindu elephant headed god Ganesh. My own mother, a Jew raised in Germany in the early 20th century, tells me that her family's sun-porch had an inlaid tile design of swastikas on the floor -- and her mother once told her it was "wrong" of Hitler to use the symbol as a political emblem. The swastikas were still there on the floor when she and her family fled Germany to escape.
For more information on the swastika, see Will's Cigarette Card #24: The Swastika. For more images of good luck swastikas see:
swastikas on good luck coins
swastika on Lucky Mon-Gol Curio Number XI
|
|
|
|
|

 
  ![Stargate Special Edition [Reino Unido] [DVD]: Amazon.es: Kurt Russell: Películas y TV](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/51Gr2lgt03L.jpg)
LA SANGRE DEL CORDERO EN EL DINTEL, EN CONTEXTO AL EXODO PASCUAL, ES UN TIPO DEL GRIAL
1. Éxodo 12:7: Y tomarán de la sangre, y la pondrán en los dos postes y en el DINTEL de las casas en que lo han de comer.
2. Éxodo 12:22: Y tomad un manojo de hisopo, y mojadlo en la sangre que estará en un lebrillo, y untad el DINTEL y los dos postes con la sangre que estará en el lebrillo; y ninguno de vosotros salga de las puertas de su casa hasta la mañana.
3. Éxodo 12:23: Porque Jehová pasará hiriendo a los egipcios; y cuando vea la sangre en el DINTEL y en los dos postes, pasará Jehová aquella puerta, y no dejará entrar al heridor en vuestras casas para herir.
Dintel
De Wikipedia, la enciclopedia libre

Esquema de estructura adintelada.
Un dintel es un elemento estructural horizontal que salva un espacio libre entre dos apoyos. Es el elemento superior que permite abrir huecos en los muros para conformar puertas, ventanas o pórticos. Por extensión, el tipo de arquitectura, o construcción, que utiliza el uso de dinteles para cubrir los espacios en los edificios se llama arquitectura adintelada, o construcción adintelada. La que utiliza arcos o bóvedas se denomina arquitectura abovedada.
Los mejores exponentes de arquitectura adintelada en piedra son los edificios monumentales del Antiguo Egipto y la Grecia clásica. La palabra dintel proviene de la palabra latina: limitellus, que deriva etimológicamente de limen y limes. En latín la palabra limen significa umbral, puerta, entrada o comienzo, y limes se refiere a un sendero entre dos campos, límite o muralla.
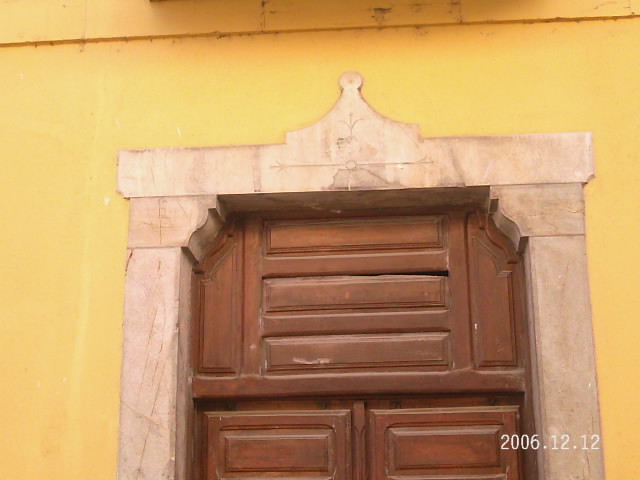

Comparen las dos figuras anteriores y noten que la LUZ SOLAR PENETRA, en este caso EN LA PUERTA DE TIWANAKU (BOLIVIA) en los equinoccios, osea el 20/21 de marzo y los 21/22 de septiembre. CONCRETAMENTE LA FIESTA DE LOS TABERNACULOS ES PRIMA HERMANA DE LA FIESTA PASCUAL. EN ESTE MARCO, INSISTO, EL SOL, SI USTED COMPARA CON LA FIGURA SUPERIOR, EN LOS MISMOS EQUINOCCIOS LA LUZ SOLAR CHOCA CON LA PIRAMIDE VATICANA E INCLUSO INGRESA O PENETRA ADENTRO DEL TEMPLO DE SAN PEDRO. PREGUNTO: ¿SI LA PLAZA DE MARIA DE LA VICTORIA ESTA UBICADA EN LA MISMA LINEA EQUINOCCIAL, QUIEN ES EN ESTE MARCO LA MISMA, EN EL CONTEXTO QUE LA PASCUA TAMBIEN TIENE ESA REFERENCIA? CUALQUIER PERSONA QUE TIENE TRES DEDOS DE FRENTE SE DA CUENTA QUE ES MARIA LA MAGDALENA. SI NO ES ASI PREGUNTO:
¿PORQUE CRISTO SE PRESENTO SIENDO VENCEDOR EL 17 DE NISSAN, OSEA EN EL EQUINOCCIO FRENTE A MARIA MAGDALENA?
CONCLUYO:
MARIA LA VICTORIA ES MARIA MAGDALENA
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
La Crucifixión La Crucifixión con María, Juan, María Magdalena, San Longino y el centurión convertido
(The Crucifixion The Crucifixion with Mary, John, Mary Magdalene, St Longinus and the Converted Centurion)
|
|
|
|
|
|
I don’t know if it’s a right answer but I think it’s because the numerical system used was/is decimal
Known in the west as arabic number (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9) but originated from India it’s a decimal system (ten symbols)
and the vast majority of human numerical system is decimal.
I guess that’s why.
But yes the base 12 system would have been interesting (not only for measurment but priorly for mathematics)
divider in decimal system 2 and 5
divider in 12 system 3, 2 and 2 again
https://www.quora.com/In-1793-decimal-time-was-tried-in-the-French-Revolution-10-hr-day-x-100-min-hr-x-100-sec-min-instead-of-24-x-60-x-60-Why-was-decimal-time-unsuccessful-after-1795 |
|
|
|
|
While the original sculpture at Troyes has largely disappeared, the cathedral still has a large number of its original stained glass windows, installed from the 13th to 16th century, along with some windows incorporating sections of medieval glass, for a total of 1,600 square meters of stained glass. The windows illustrate vividly the evolution of stained glass in France, from the 13th-century windows, with their deeply-colored, thicker pieces of glass assembled like mosaics, to the 15th- and 16th-century windows, using silver stain and enamel painting to create the effects of shading and perspective similar to those of Renaissance painting.
-
The Apostles - Lower windows of the nave, (south side Bay 51) (14th century)
-
Saint Peter (south side-Bay 47) (14th century)
-
The Annunciation (south side Bay 47) (14th century)
-
Apostles - Upper windows of nave (Bay 51)
-
Sainte Catherine of Alexandria and Saint Maurice of Agaune (16th c.)
-
The Mystical Wine Press - Bay 49 (1625)
The nave has glass from a wide variety of periods and styles – sometimes in the same bay. Some of the oldest windows, from the end of the 13th and beginning of the 14th century, are in the lateral chapels. Most of these underwent considerable restoration in the 19th century.
Other bays were given new windows in the 16th and 17th centuries. Of these, some were designed by Linard Gontier, a prominent Troyes artist of the Renaissance. His most famous window in the cathedral is the "Mystical Wine Press", inspired by the prominence of the champagne from the region. It depicts Christ with grapevines sprouting from this chest, and a variety of scenes associating grapes and wine with the apostles.
Choir and ambulatory
[edit]
-
Windows of the axis chapel of the apse, dedicated to the Virgin Mary (13th–19th c.)
-
The Flight to Egypt and Adoration of the Magi (13th century)
-
Musician in the Tree of Jesse window, 13th c. Chapel of Joan of Arc, (Bay 31)
-
Detail of 15th-century window (Bay 38)
-
King Philip II of France (Choir, Bay 52)
-
Powers of the Ecclesiastical hierarchy (Bishops and Kings) (Bay 52)
-
Upper windows of the choir (Bay 208); Parable of the Wise and Foolish Virgins
The choir and the ambulatory, to the east of the cathedral, still have much of their original stained glass. The oldest windows are in the radiating chapels on the east, some dating to 1200–1230. The higher windows and those of the triforium date to about 1235–40. Some of these windows are more recent, but include portions of the older original glass, which had not yet been installed at the time of the hurricane of 1228. While many of the lower windows were considerably modified, the upper windows of the choir are mostly in their original state.
The transept windows have a mixture of styles. The windows on the west are from the 14th century, while those on the east were replaced in the 16th century with windows with tracery of the Flamboyant Gothic style. The triforium windows on the west were made in the 19th century, while the triforium windows on the east include vestiges of restored 13th-century glass.
-
The west rose window (partly hidden by organ)
-
Rose window of the north transept
-
Detail of the north rose window
The rose window at the west end of the nave, from 1239, was made by the artist Jean Soudain on the theme of the celestial court. The view of this window from the ground floor is largely obscured by the organ.
The rose window in the north transept, ten meters in diameter, was installed in the 15th century to replace the earlier window, which fell in 1340. It is in the Rayonnant Gothic style, with its tracery radiating outward from the center. The rose window on the south transept is a copy of the north window.
The grand organ is located on a tribune over the portal on the reverse side of the west front. It was originally built in 1730 for Clairvaux Abbey in Burgundy. When the abbey was closed in 1793 during the Revolution, the organ was nationalised and sold at auction. It was purchased by the overseers of Troyes Cathedral, but was not put into place until 1808. It replaced the original Troyes organ, built in the 15th century and placed next to the choir. That organ had been destroyed in 1792. The installation of the new organ was controversial because it largely blocked the view of the west rose window from the nave and choir.[24]
The organ has fifty-five jeux or sounds, played with four keyboards and a set of pedals. The instrument was classified as an historical monument in 1963, and the case in 1974.[25] The organ is decorated with statues of angels and atlantes.
The cathedral has a second, smaller organ, which is located in the choir. This instrument was built in 1865 and was restored in 1987. It has thirteen jeux, played with two keyboards and a set of pedals.
Troyes Cathedral has four bourdons, heavy bells which made a deep note, for tolling on solemn occasions. Each has a name, and all were made in the early 19th century, replacing the early bells taken out and melted down during the French Revolution.
- Petrus Carolus - (4500 kilos, made in 1827)
- Paulus Ana - (3,269 kilos, made in 1813)
- Savinianus - (2,437 kilos, made in 1813)
- Marie - (2000 kilos, made in 1827)
-
The Coffret of Troyes (Ivory, 11th century)
-
The Stuart Cross, made of crystal
-
Reliquary of Saint Bernard of Clairvaux, with silver, copper and enamel (12th century)
The treasury of the cathedral was constructed at the beginning of the 13th century within the choir, next to the apse. It was particularly designed to display the collection of sacred relics which the Bishop Garnier de Traînel had brought back to France from the Fourth Crusade. Some of the relics and other valuable objects were used as ransom for the captive King Francois I in 1525, and others were lost during the Revolution, but the collection was gradually rebuilt. It has a particularly large collection of medieval enamel art, made by local craftsmen in the 12th century, as well as vestments, reliquaries and other medieval liturgical objects. Notable objects include the coffret of Troyes, an ivory chest of Byzantine craftsmanship from the 11th century.
Possible Indian connection
[edit]
Among the stained-glass windows is one which appears to have a representation of the famous Indo-Parthian king Gondophares who was ruling in ancient Taxila from 20 to 41 CE, in what is now north-western Pakistan.[27]
According to the legends and traditions contained in the Acts of Thomas, and preserved by the Indian Christians of St. Thomas, the Apostle Thomas fled to the East after the crucifixion. He stayed for some time at Gondophares' court where Thomas is said to have built a palace for him before heading on to southern India where he was, according to the legend, martyred near modern Chennai (Madras) [28]
|
|
|
 Primer Primer
 Anterior
3 a 17 de 17
Següent Anterior
3 a 17 de 17
Següent
 Darrer
Darrer

|
|
| |
|
|
©2025 - Gabitos - Tots els drets reservats | |
|
|

