|
|
General: CHURCHILL S D-DAY DURING THE NORMANDY INVASION MADELEINE LETTER V
Choisir un autre rubrique de messages |
|
Réponse |
Message 1 de 12 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
 Premier
Premier
 Précédent
2 à 12 de 12
Suivant
Précédent
2 à 12 de 12
Suivant
 Dernier
Dernier

|
|
Réponse |
Message 2 de 12 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 3 de 12 de ce thème |
|
V For Victory – the sign which Churchill appropriated from the Belgians
 We have all seen photos of Winston Churchill giving his famous ‘V for Victory’ sign during the Second World War, but we actually have Belgian tennis star Victor de Laveleye to thank for this iconic sign. de Laveleye competed in the 1920 and 1924 Olympic Games for Belgium, but he was also a politician who served as Minister of Justice in 1937. As the Germans pushed west in 1940 de Laveleye fled to Britain where he was put in charge of the BBC’s broadcasts to occupied Belgium and soon became the symbol of free Belgians everywhere. On 14th January 1941 Laveleye asked all Belgians to use the letter ‘V’ as a symbol of resistance and a rallying cry to fight the invaders because, he said, ‘V is the first letter of Victoire (victory) in French and Vrijheid (freedom) in Flemish, like the Walloons and the Flemish who today walk hand in hand, two things that are consequences of each other, Victory will give you Freedom’. He went on to say that “the occupier, by seeing this sign, always the same, infinitely repeated, [will] understand that he is surrounded, encircled by an immense crowd of citizens eagerly awaiting his first moment of weakness, watching for his first failure.” The Belgian people willingly adopted the sign and the letter immediately began to appear daubed on walls in Belgium, the Netherlands, Northern France, and other parts of Europe, a symbolic act of defiance against the Nazis. We have all seen photos of Winston Churchill giving his famous ‘V for Victory’ sign during the Second World War, but we actually have Belgian tennis star Victor de Laveleye to thank for this iconic sign. de Laveleye competed in the 1920 and 1924 Olympic Games for Belgium, but he was also a politician who served as Minister of Justice in 1937. As the Germans pushed west in 1940 de Laveleye fled to Britain where he was put in charge of the BBC’s broadcasts to occupied Belgium and soon became the symbol of free Belgians everywhere. On 14th January 1941 Laveleye asked all Belgians to use the letter ‘V’ as a symbol of resistance and a rallying cry to fight the invaders because, he said, ‘V is the first letter of Victoire (victory) in French and Vrijheid (freedom) in Flemish, like the Walloons and the Flemish who today walk hand in hand, two things that are consequences of each other, Victory will give you Freedom’. He went on to say that “the occupier, by seeing this sign, always the same, infinitely repeated, [will] understand that he is surrounded, encircled by an immense crowd of citizens eagerly awaiting his first moment of weakness, watching for his first failure.” The Belgian people willingly adopted the sign and the letter immediately began to appear daubed on walls in Belgium, the Netherlands, Northern France, and other parts of Europe, a symbolic act of defiance against the Nazis.
 Resistance graffiti on a road in Norway the V sign cradeling the initials of King Haakon VII
 Winston Churchill realised how successful this symbol was in uniting people against Hitler’s regime and decided to use it during a speech in July 1941 when he said that ‘The V sign is the symbol of the unconquerable will of the occupied territories and a portent of the fate awaiting Nazi tyranny. So long as the people continue to refuse all collaboration with the invader it is sure that his cause will perish and that Europe will be liberated.” Churchill continued to use the sign as his ‘signature gesture’ for the remainder of the war. Winston Churchill realised how successful this symbol was in uniting people against Hitler’s regime and decided to use it during a speech in July 1941 when he said that ‘The V sign is the symbol of the unconquerable will of the occupied territories and a portent of the fate awaiting Nazi tyranny. So long as the people continue to refuse all collaboration with the invader it is sure that his cause will perish and that Europe will be liberated.” Churchill continued to use the sign as his ‘signature gesture’ for the remainder of the war.
Soon after Churchill’s broadcast Douglas Ritchie at the BBC noticed that the Morse code for V was three dots and a dash ( …_ ) which was the same as the rhythm for the opening of Beethoven’s Fifth Symphony, and the BBC used it in its foreign language programmes directed at occupied Europe for the rest of the war. It was not long before the rhythm was used as a symbol of defiance in Europe, one which people could tap out almost anywhere.
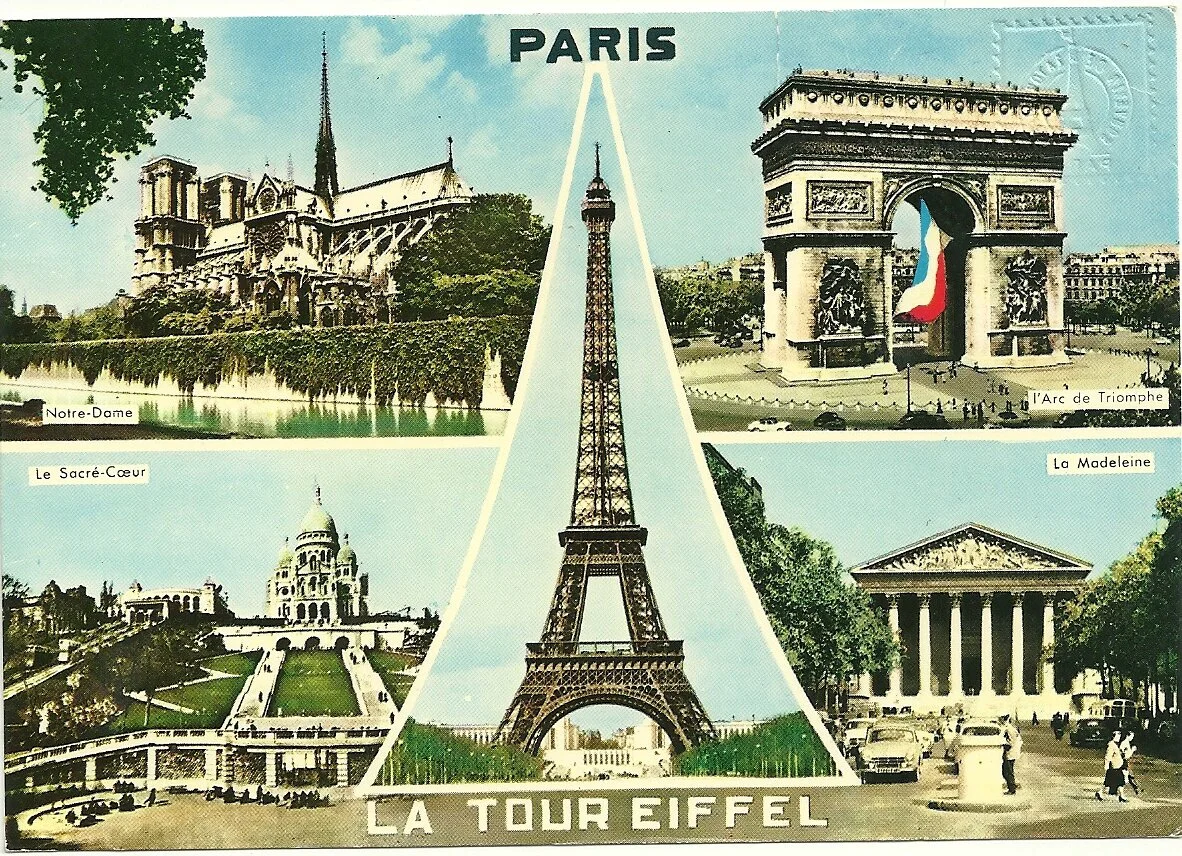
In Germany Goebbels, the Nazi Propaganda Minister, was infuriated by the ‘V campaign’, but there was nothing he could do to stop it. He tried to argue that because ‘V’ was the first letter of the German word ‘viktoria’ and the musical representation was from a symphony written by a German composer then it was really a symbol in support of the Nazi’s final victory and was a sign of the conquered population’s support of Hitler, but of course no one believed him. To try to bury the use of the symbol by the resistance the Germans started using the ‘V’ themselves, even the Eiffel tower had a ‘V’ with the slogan ‘Germany is Victorious on All Fronts’ underneath.
 TheEeiffel Tower during the German occupation of France TheEeiffel Tower during the German occupation of France

When Churchill first used the ‘V’ sign he sometimes did it with palm facing in until it was pointed out to him that this had a rather rude meaning for the working classes; from then on Churchill made a point of holding his hand palm outwards. Of course, the sign appealed to many people precisely because of its ‘double entendre’ meaning – with a simple movement of the wrist they could indicate a belief in victory and also tell Hitler where to go!

America also took the ‘V’ sign to heart and it appeared in numerous places, including on this poster from the War Production Board.
Four years after de Laveleye first urged the use of the ‘V’ sign the Allies finally achieved Victory in Europe, and months later came Victory against Japan, but by that time the iconic Second World War symbol of defiance had become so embedded in the minds of the people that it is still used today.
 The ground crew of a Lancaster bomber return the ‘V for Victory’ sign projected into the sky by a neighbouring searchlight crew on VE Day.
There are some interesting pictures of the use of the ’V’ sign during the Second World War in this video
https://dorindabalchin.com/2019/02/16/v-for-victory-the-sign-which-churchill-appropriated-from-the-belgians/ |
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 4 de 12 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 5 de 12 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 6 de 12 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 7 de 12 de ce thème |
|
| Enviado: 21/10/2024 10:30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 8 de 12 de ce thème |
|
Para otros usos de este término, véase Austerlitz.
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 9 de 12 de ce thème |
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 10 de 12 de ce thème |
|
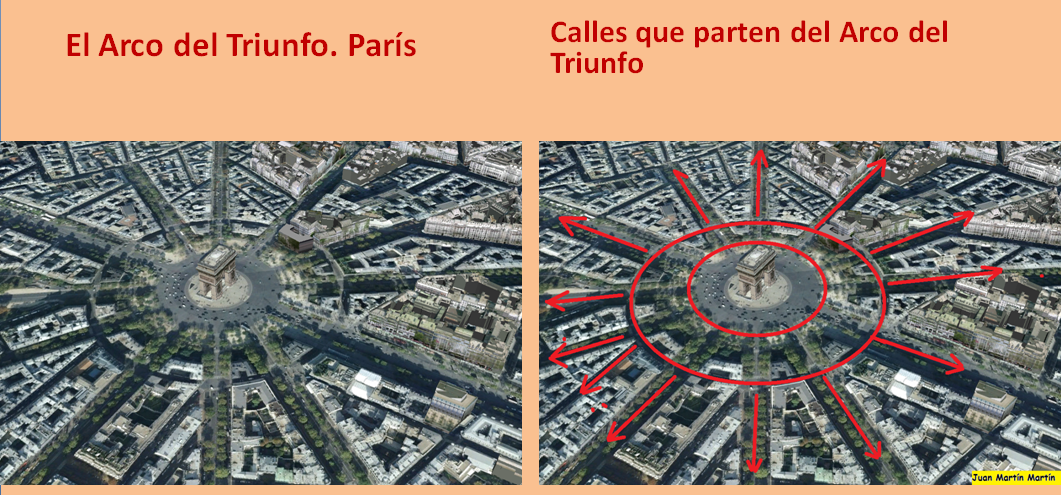
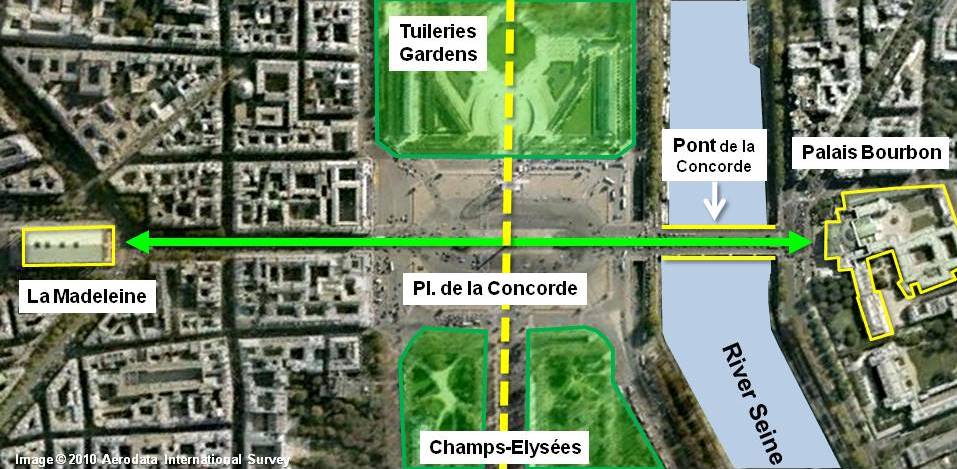
Llama de la Libertad (París)
 La Llama de la Libertad, ofrecida al pueblo francés por donantes de todo el mundo como símbolo de la amistad franco-americana, en la plaza Diana (París).
La Llama de la Libertad (en francés, Flamme de la Liberté) de París es una réplica del mismo tamaño de la nueva llama situada en el extremo de la antorcha que lleva en la mano la Estatua de la Libertad de Nueva York desde 1986.1 El monumento, que tiene aproximadamente 3,5 metros de longitud, es una escultura de una llama de cobre dorado, apoyada en un pedestal de mármol gris y negro. Está situado cerca del extremo norte del puente del Alma, en la plaza Diana, en el distrito 8 de París, Francia.2
Fue ofrecida a la ciudad de París en 1989 por el International Herald Tribune en nombre de los donantes, que habían contribuido aproximadamente 400 000 dólares para su realización. Representaba la culminación de las celebraciones de 1987 del periódico por su cien aniversario de la publicación de un periódico en inglés en París. Más importante, la Llama era una muestra de agradecimiento por la restauración de la Estatua de la Libertad realizada tres años antes por dos empresas francesas que hicieron el trabajo artesanal del proyecto: Métalliers Champenois, que hizo el trabajo del bronce, y Gohard Studios, que aplicó el pan de oro. Aunque el regalo a Francia fue motivado por el centenario del periódico, la Llama de la Libertad es un símbolo más general de la amistad que une los dos países, igual que la Estatua de la Libertad cuando fue regalada a los Estados Unidos por Francia.
Este proyecto fue supervisado por el director de la unión de artesanos franceses en aquel momento, Jacques Graindorge. Propuso la instalación de la Llama de la Libertad en una plaza pública llamada Place des États-Unis en el distrito 16, pero el alcalde de París, Jacques Chirac, se opuso a esto. Tras un prolongado período de negociaciones, se decidió que la alama se situaría en una zona abierta cerca de la intersección de la Avenue de New-York y la Place de l'Alma. El monumento fue inaugurado el 10 de mayo de 1989 por Chirac.
En la base del monumento hay una placa conmemorativa que relata la siguiente historia:
"La Llama de la Libertad. Una réplica exacta de la llama de la Estatua de la Libertad ofrecida al pueblo de Francia por donantes de todo el mundo como símbolo de la amistad franco-americana. Con ocasión del centenario del International Herald Tribune, París 1887-1987."
La llama se convirtió en un monumento no oficial de Diana de Gales después de su muerte en 1997 en el túnel bajo el Pont de l'Alma.3 La llama es una atracción para turistas y seguidores de Diana, quiens pegan pósteres y folletos con material conmemorativo en la base. El antropólogo Guy Lesoeurs dijo que "la mayoría de las personas que vienen aquí piensan que se construyó para ella."2 La plaza del monumento se llama desde entonces Plaza Diana (París).
El monumento está cerca de la estación del Metro de París llamada Alma-Marceau en la línea 9 y de la estación Pont de l’Alma Línea 'C' del RER, así como por los buses número 42, 63, 72, 80, 92, y los autobuses turísticos Balabus.
El 14 de junio de 2008 se inauguró una nueva Llama de la Libertad, una escultura de Jean Cardot, que también simboliza las relaciones cálidas y respetuosas entre Francia y los Estados Unidos. Fue instalada en los jardines de la Embajada de los Estados Unidos en Francia en la Place de la Concorde, y se inauguró en presencia del Presidente de la República Francesa, Nicolas Sarkozy, y el Presidente de los Estados Unidos, George W. Bush. Esta nueva llama es la realización de un impulso compartido por el empresario francés Marc Ladreit de Lacharrière, y el embajador estadounidense Craig Roberts Stapleton, y tiene dos inscripciones, una del francés Marqués de La Fayette y otra del estadista americano Benjamin Franklin.
|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 11 de 12 de ce thème |
|
Male and Female symbols

Male symbol, Mars, blade

Military patches
Female symbol, Venus, chalice

|
|
|
|
Réponse |
Message 12 de 12 de ce thème |
|


 
Pope Francis delivered a speech too progressive for Obama to give
Sep 24, 2015, 4:20 PM GMT-3
Pope Francis waves to the crowd from the Speakers Balcony at the US Capitol, September 24, 2015, in Washington, DC. Pool/Getty Images
If President Barack Obama had delivered the text of Pope Francis’s speech to Congress Thursday as a State of the Union address, he would have risked being denounced by Republicans as a socialist.
While most Republicans chose not to complain, and Democrats tried not to gloat, Francis’s speech to Congress was stunning in the breadth, depth, and conviction of its progressivism. That might not have been fully and immediately appreciated by everyone in the House chamber because the combination of Francis’s sotto voce delivery and his heavily accented English made it difficult, lawmakers said, to grasp everything he was saying.
But there was no mistaking his thrust. He made detailed arguments for openness to immigrants, addressing the human roots of climate change, closing the gap between the rich and the poor, and ending the death penalty — all of which invigorated the Democrats in the room.
“It was pretty progressive. He had a little right-to-life stuff in it,” Rep. James Clyburn, the third-ranking House Democrat, said as he cracked a smile thinking about how Republicans would receive the speech. “That’s enough for them.”
The pope isn’t going to change many hearts and minds in the badly divided Congress, lawmakers said, but the moment provided a brief respite from political warfare. Several presidential candidates, including Sens. Bernie Sanders, Lindsey Graham, Marco Rubio, and Ted Cruz, as well as Ben Carson, attended.
Rubio, a Roman Catholic, said in a brief interview that Francis “struck the right tone.” Sanders, a self-described socialist, seemed to like the content even more.
“Pope Francis is clearly one of the important religious and moral leaders not only in the world today but in modern history,” he said in a statement released after the speech. “He forces us to address some of the major issues facing humanity: war, income and wealth inequality, poverty, unemployment, greed, the death penalty and other issues that too many prefer to ignore.”
Democrats were eager enough to present Congress as united that they joined a Republican-led standing ovation when Francis told lawmakers of “our responsibility to protect and defend human life at every state of its development.” Several of them said it was out of respect for the pope. But there was another good reason: It strengthened the perception that the whole speech — most of which they liked — carried unifying themes.
Unity was good for Democrats because the speech favored their policies
Francis was interrupted a few times by whoops from the Democratic side of the chamber — by Steve Cohen, a Jewish Memphis Democrat who got excited about Francis’s mention of the Golden Rule; by New York’s Nydia Velázquez when he called for an end to the death penalty; and by Philadelphia Rep. Chaka Fattah when he mentioned his upcoming visit to that city. The Republicans in the room were a bit more staid. Cruz often appeared unmoved during moments when Rubio, who was sitting nearby, applauded. That was the case when Francis asked whether the greater opportunities sought by past generations of immigrants are “not what we want for our own children?”
It was a home crowd. Rep. Paul Gosar (R-AZ) had announced he would boycott the event over climate change, and there was a brief murmur when it became obvious that three conservative Catholic Supreme Court justices — Antonin Scalia, Samuel Alito, and Clarence Thomas — had not shown up. But it seemed that everyone in attendance just wanted to catch a glimpse of Francis and hear what he had to say.
Big-name guests filed into the public galleries above the House chamber long before the pope’s arrival: Former House Speaker Newt Gingrich, former Rep. Gabby Giffords, mega-donor Tom Steyer, and Carson. House members filled the seats in their chamber, followed by the Senate and four Supreme Court justices. At about a minute past 10 am, Francis strode down the center aisle of the House chamber, clad in his familiar white robe and skullcap.
Lawmakers, who had been admonished not to touch the pope, refrained from trying to shake his hand or pat his back. There was no rush to crowd him the way members of Congress try to get into pictures with the president during the annual State of the Union address. When he got to the end of the aisle, he quietly shook hands with Secretary of State John Kerry and then made his way to the rostrum.
Samantha Power, the US ambassador to the UN, pulled out a baby blue iPhone and began snapping pictures. Though she later took to Twitter to commemorate the moment, Power hadn’t posted any of her photos by midday.
For his part, Francis warmed up the audience by describing America as “the land of the free and the home of the brave.” He was slow to move into more politically charged territory but unimpeded when he did. There were 10 standing ovations after his initial greeting, and they were bipartisan.
Francis tackled tough issues at the heart of the US political debate and gently admonished lawmakers to build bridges
At times, Francis seemed to be speaking directly into the headlines and newscasts of the day.
Less than a week after Carson said that America shouldn’t elect a Muslim president, Francis warned that “a delicate balance is required to combat violence perpetrated in the name of a religion, an ideology or an economic system, while also safeguarding religious freedom, intellectual freedom and individual freedoms.”
As Republican presidential frontrunner Donald Trump promises to build a wall between Mexico and the US, and to prevent Syrian refugees from being admitted to America, Francis compared the current refugee crisis to the one that arose in World War II and said that “we the people of this continent are not fearful of foreigners, because most of us were once foreigners.” That drew a standing ovation. Rubio, who has shifted his emphasis on immigration reform over time, leaped to his feet.
And while Democrats continue to bask in this summer’s Supreme Court decision protecting same-sex marriage, the pope said he was concerned that “fundamental relationships are being called into question, as is the very basis of marriage and the family.” The issue that caused the biggest stir before the speech — climate change — factored prominently in Francis’s remarks. He spoke of the human roots of global warming and said, “I am convinced we can make a difference.”
But perhaps the most unexpected run in the speech was an admonishment as gentle as it was clear: Politics is about building bridges, not destroying them. Francis never mentioned the international nuclear nonproliferation deal with Iran by name or the gridlock in American politics, but he seemed to be speak to both matters.
“When countries which have been at odds resume the path of dialogue — a dialogue which may have been interrupted for the most legitimate of reasons — new opportunities open up for all,” he said. “A good political leader is one who, with the interests of all in mind, seizes the moment in a spirit of openness and pragmatism. A good political leader always opts to initiate processes rather than possessing spaces.”
Pennsylvania Republican Rep. Joe Pitts, speaking about the pope’s limited remarks on abortion and same-sex marriage, said he was displeased that Francis had been “unfortunately politically correct.”
For liberals, though, he was simply correct about politics.
https://www.vox.com/2015/9/24/9393731/pope-francis-speech-progressive-obama
|
|
|
 Premier
Premier
 Précédent
2 a 12 de 12
Suivant
Précédent
2 a 12 de 12
Suivant
 Dernier
Dernier

|
|
| |
|
|
©2025 - Gabitos - Tous droits réservés | |
|
|
 We have all seen photos of Winston Churchill giving his famous ‘V for Victory’ sign during the Second World War, but we actually have Belgian tennis star Victor de Laveleye to thank for this iconic sign. de Laveleye competed in the 1920 and 1924 Olympic Games for Belgium, but he was also a politician who served as Minister of Justice in 1937. As the Germans pushed west in 1940 de Laveleye fled to Britain where he was put in charge of the BBC’s broadcasts to occupied Belgium and soon became the symbol of free Belgians everywhere. On 14th January 1941 Laveleye asked all Belgians to use the letter ‘V’ as a symbol of resistance and a rallying cry to fight the invaders because, he said, ‘V is the first letter of Victoire (victory) in French and Vrijheid (freedom) in Flemish, like the Walloons and the Flemish who today walk hand in hand, two things that are consequences of each other, Victory will give you Freedom’. He went on to say that “the occupier, by seeing this sign, always the same, infinitely repeated, [will] understand that he is surrounded, encircled by an immense crowd of citizens eagerly awaiting his first moment of weakness, watching for his first failure.” The Belgian people willingly adopted the sign and the letter immediately began to appear daubed on walls in Belgium, the Netherlands, Northern France, and other parts of Europe, a symbolic act of defiance against the Nazis.
We have all seen photos of Winston Churchill giving his famous ‘V for Victory’ sign during the Second World War, but we actually have Belgian tennis star Victor de Laveleye to thank for this iconic sign. de Laveleye competed in the 1920 and 1924 Olympic Games for Belgium, but he was also a politician who served as Minister of Justice in 1937. As the Germans pushed west in 1940 de Laveleye fled to Britain where he was put in charge of the BBC’s broadcasts to occupied Belgium and soon became the symbol of free Belgians everywhere. On 14th January 1941 Laveleye asked all Belgians to use the letter ‘V’ as a symbol of resistance and a rallying cry to fight the invaders because, he said, ‘V is the first letter of Victoire (victory) in French and Vrijheid (freedom) in Flemish, like the Walloons and the Flemish who today walk hand in hand, two things that are consequences of each other, Victory will give you Freedom’. He went on to say that “the occupier, by seeing this sign, always the same, infinitely repeated, [will] understand that he is surrounded, encircled by an immense crowd of citizens eagerly awaiting his first moment of weakness, watching for his first failure.” The Belgian people willingly adopted the sign and the letter immediately began to appear daubed on walls in Belgium, the Netherlands, Northern France, and other parts of Europe, a symbolic act of defiance against the Nazis. Resistance graffiti on a road in Norway the V sign cradeling the initials of King Haakon VII
Resistance graffiti on a road in Norway the V sign cradeling the initials of King Haakon VII
 Winston Churchill realised how successful this symbol was in uniting people against Hitler’s regime and decided to use it during a speech in July 1941 when he said that ‘The V sign is the symbol of the unconquerable will of the occupied territories and a portent of the fate awaiting Nazi tyranny. So long as the people continue to refuse all collaboration with the invader it is sure that his cause will perish and that Europe will be liberated.” Churchill continued to use the sign as his ‘signature gesture’ for the remainder of the war.
Winston Churchill realised how successful this symbol was in uniting people against Hitler’s regime and decided to use it during a speech in July 1941 when he said that ‘The V sign is the symbol of the unconquerable will of the occupied territories and a portent of the fate awaiting Nazi tyranny. So long as the people continue to refuse all collaboration with the invader it is sure that his cause will perish and that Europe will be liberated.” Churchill continued to use the sign as his ‘signature gesture’ for the remainder of the war. TheEeiffel Tower during the German occupation of France
TheEeiffel Tower during the German occupation of France


 The ground crew of a Lancaster bomber return the ‘V for Victory’ sign projected into the sky by a neighbouring searchlight crew on VE Day.
The ground crew of a Lancaster bomber return the ‘V for Victory’ sign projected into the sky by a neighbouring searchlight crew on VE Day.









![Freemason Winston Churchill: A Life of Controversies and Leadership [5 Minute Recap] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/GtED39R74xs/hq720.jpg?sqp=-oaymwE7CK4FEIIDSFryq4qpAy0IARUAAAAAGAElAADIQj0AgKJD8AEB-AH-CYAC0AWKAgwIABABGGUgWShWMA8=&rs=AOn4CLBDKQVYdoGc3CAjTQFsabds6CkqCQ)