Start-up of 22nd Run at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC)
Physicists will try out innovative accelerator techniques and deliver high-energy polarized protons for explorations of protons' inner structure using new detector components at STAR
December 13, 2021
 enlarge
enlarge
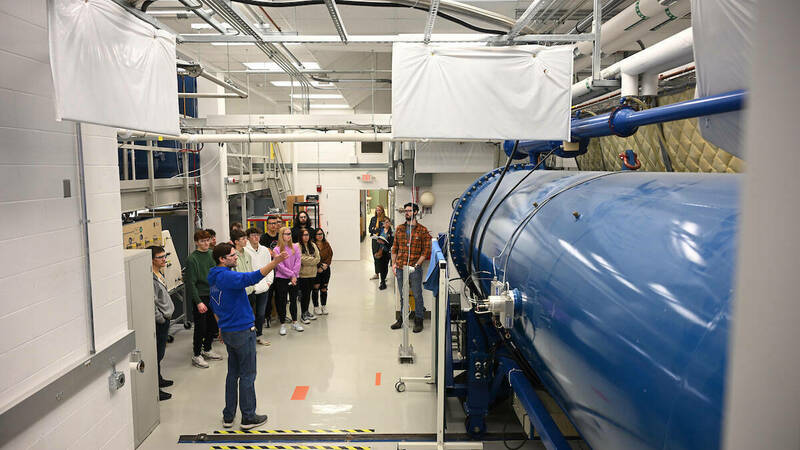
Run 22 at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) will feature collisions of polarized protons, new data collected by upgraded components of the STAR detector, and tests of innovative accelerator techniques.
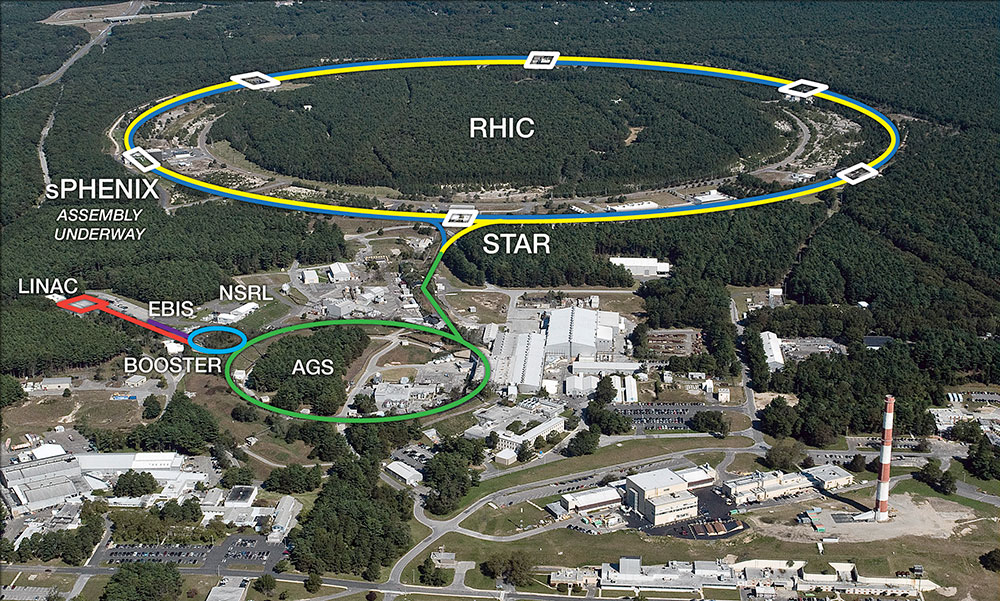
UPTON, NY—Particle smashups have begun for Run 22 at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC). RHIC, a 2.4-mile-circumference particle collider at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory, operates as a DOE Office of Science user facility, serving up data from particle collisions to nuclear physicists all around the world. On the menu this run: collisions between beams of polarized protons interspersed with tests of innovative accelerator techniques. During the run, RHIC’s recently upgraded STAR detector will track particles emerging from collisions at a wider range of angles than ever before.
The new data will add to earlier RHIC datasets exploring the fundamental building blocks of visible matter. In addition, the physics findings, accelerator tests, and detector technologies will play important roles in the Electron-Ion Collider (EIC)—DOE’s next planned nuclear physics facility, which will reuse key components of RHIC.
Discovering the universal properties of protons and how they emerge from the interactions of quarks and gluons, the building blocks within protons, is a central goal of both facilities. RHIC’s proton-proton collisions could reveal unprecedented details and a preview of how certain characteristics depend on the dynamic motions of the quarks and gluons.
 enlarge
enlarge
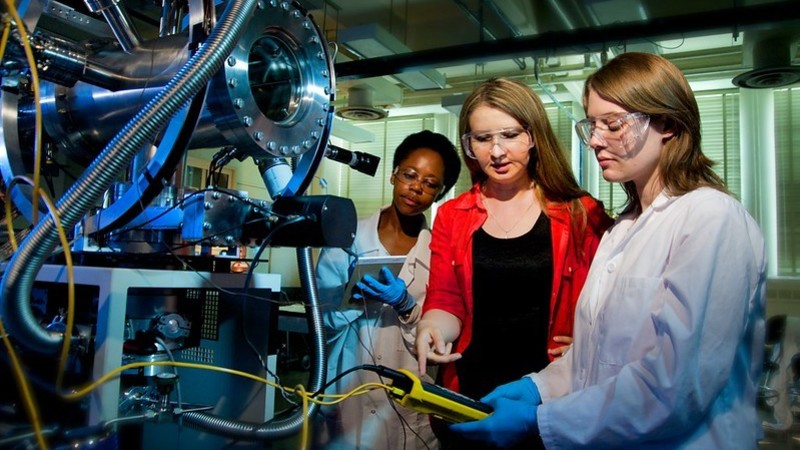
Brookhaven Lab physicist Elke Aschenauer, who led the STAR upgrade project, notes how the new detector components will enable measurements at RHIC that advance our understanding of nucleon structure and help to lay the foundations for future measurements at the Electron-Ion Collider.
“Our goal this run is basically doing EIC physics with proton-proton collisions,” said Brookhaven Lab physicist Elke-Caroline Aschenauer, a member of the STAR collaboration who is also involved in planning the experiments and scientific program at the EIC. “It’s important to do both [measurements at RHIC and the EIC] because you have to verify that what you measure in electron-proton collisions at the EIC and in proton-proton events at RHIC is universal—meaning it doesn’t depend on which probe you use to measure it,” she explained.
The measurements rely on RHIC’s ability to align the “spins” of protons in an upward pointing direction. This alignment, or polarization—a capability unique among colliders like RHIC—gives scientists a directional frame of reference for tracking how particles generated in the collisions move.
“We are using polarization as a vehicle to study proton structure, and particularly the 3D structure, including how the internal particles (quarks and gluons) are moving inside the proton,” Aschenauer said.
Delivering proton beams
The physicists in Brookhaven Lab’s Collider-Accelerator Department (C-AD), who steer the beams around RHIC, are determined to give STAR what it needs.
“For Run 22 we are going to focus on being as efficient as possible and racking up the collisions at the highest possible polarization,” said C-AD physicist Vincent Schoefer, this year’s run coordinator.
When we spoke with Schoefer, he was busy “waking up” equipment that hasn't been used since Run 17—the last time polarized protons were collided at RHIC. This equipment includes “helical dipole” magnets that help preserve the polarization of the protons as they make millions of turns around RHIC’s twin accelerator rings. This year’s run will take place at the highest collision energy: 500 billion electron volts (GeV) per colliding proton pair.
 enlarge
enlarge
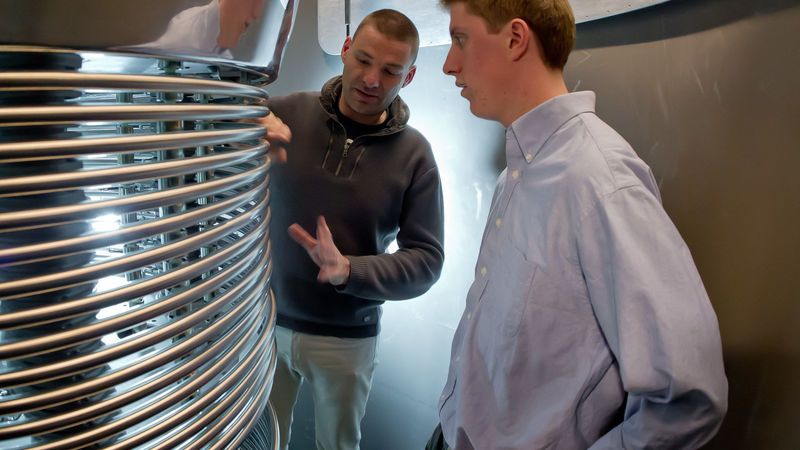
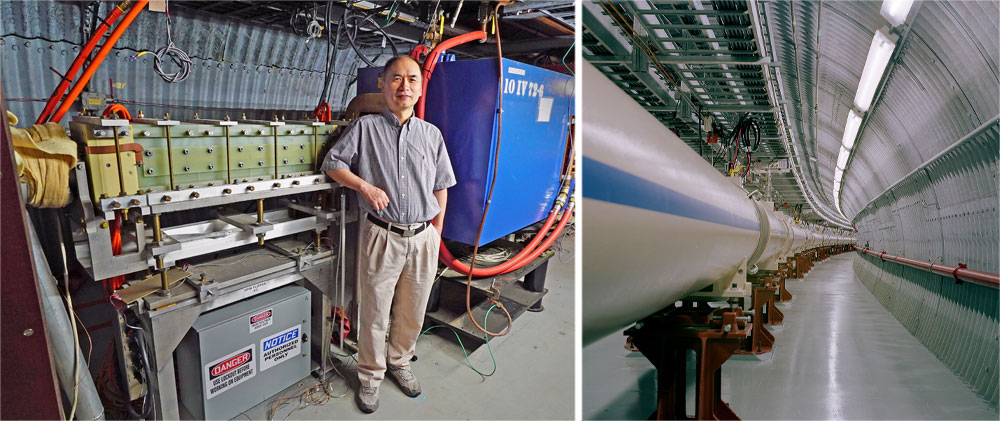
C-AD physicist Haixin Huang with some of the accelerator components that keep RHIC's proton beams aligned as they make their way around the 2.4-mile-circumference tunnel (right).
The C-AD team was also preparing “polarimeters” to measure just how aligned those proton spins are.
“It doesn't matter how highly polarized your beam is if you can't measure that. So, the polarimetry is really crucial,” Schoefer said.
Accelerator physicists in C-AD and experimental physicists involved in making measurements that rely on polarized beams collaborated on the design of RHICs polarimeters.
“This work is an example of the type of collaboration between groups that has been going on since the start of RHIC,” said C-AD physicist Haixin Huang.
Pumping up polarization
Keeping proton beams tightly packed helps preserve polarization. It also maximizes the likelihood that you get collisions when the beams cross. But keeping protons close together is a challenge.
“They're all positively charged particles, so they want to repel one another,” Schoefer explained. “The more tightly you pack them, the more they resist that packing.”
The repulsion is particularly strong in the early stages of acceleration—before protons have been ramped up to full collision energy. So, this run, the C-AD team will try a technique that’s worked when RHIC accelerates larger particles but has never been used with protons before.
“We are going to split each proton bunch into two when they’re still at low energy in the Booster, and accelerate those as two separate bunches,” Schoefer said. “That splitting will alleviate some of the stress during low energy, and then we can merge the bunches back together to put very dense bunches into RHIC.”
This merging maneuver is challenging, Schoefer said, because it takes “a really long time—where a really long time is one second! For the protons, that’s 300,000 turns around the Alternating Gradient Synchrotron (AGS).” (The AGS is the link in the accelerator chain after the Booster that feeds particle beams into RHIC.) “During those 300,000 turns, we have to handle the protons very gently, so we don’t ruin the nice beams we have prepared.”
The CA-D team will also calculate very careful trajectories for the particles’ paths through the collider. This step should help counteract the tendency of the accelerator’s magnetic fields (which physicists use to steer and focus the beams) to rotate the spins of protons away from ideal alignment.
“We're going to try different trajectories and see if we can learn something about what is making this misalignment happen,” Schoefer said.
The combination of techniques is now delivering highly polarized proton beams to collide inside STAR.
STAR upgrades
When they analyze results from these collisions, STAR physicists will be looking for differences in the numbers of certain particles emerging to the left and right of the polarized protons’ upward pointing direction.
For example, they want to test whether there’s a repulsive interaction between particles with like “color” charges that’s opposite to the attractive interaction observed between unlike color-charged particles. (Color charge is the type of charge through which quarks interact.) The opposite force should produce the opposite directional preference for certain particle decay products.
STAR first saw hints of this effect in data collected in 2011, published in 2016. A preliminary analysis of additional data collected in Run 17 indicates a small effect but with large uncertainties. Run 22 will help STAR reduce those uncertainties with larger data sets.
In addition, the recently installed STAR upgrades will give physicists the ability to track particles at previously inaccessible angles toward the front and rear of the detector.
“This is the region where we expect the left-right directional preference to be larger,” Aschenauer said.
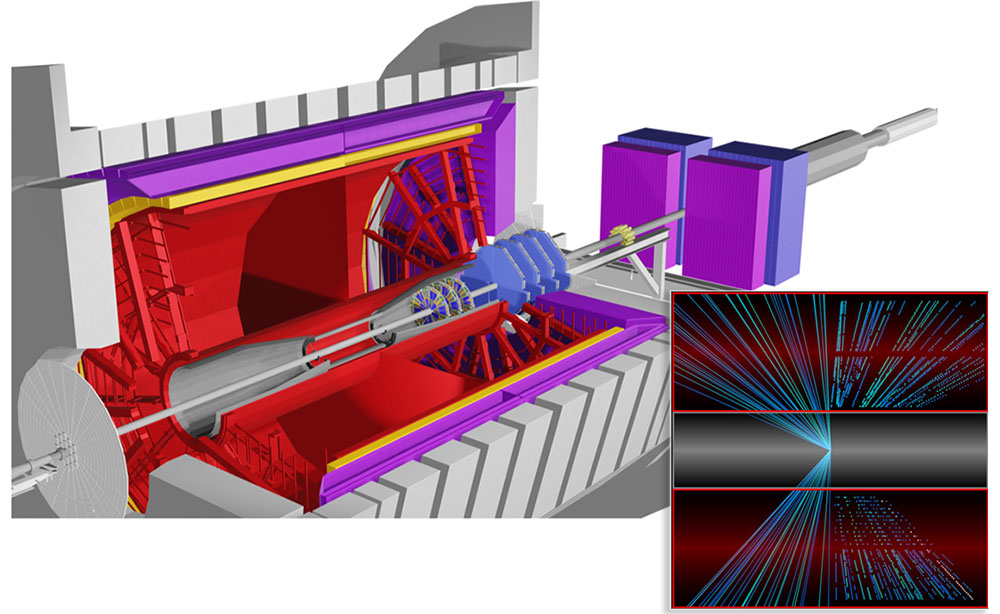 enlarge
enlarge
A side view of the STAR detector with an inset showing particle tracks (left) and particle detector "hits" (right) from a collision. The top part of the inset shows the coverage with the new iTPC sectors compared to the old sectors (bottom). Notice how the new sectors record more hits per track, especially close to the beamline, as well as tracks at more forward and rearward angles (more to the left and right in the inset view).
The upgrades include an inner Time Projection Chamber (iTPC), installed in 2019, which placed many more sensors in the inner sectors of the cylindrical STAR detector, close to the colliding particles. Then, earlier this year, the STAR team installed “forward” particle-tracking components outside one end of the detector.
To picture how these upgrades increase STAR’s particle tracking range, think of STAR as a barrel lying on its side with colliding particles entering at each end. Ever since RHIC’s first collisions in 2000, STAR has tracked particles emerging perpendicular to the colliding particles’ path all around the barrel. The classic end-on views of STAR particle tracks showcase this 360-degree detection capability. But looking from the side, the original STAR detector could only track particles emerging at angles up to 45 degrees off vertical in either the forward or rearward direction.
The upgrades “open wider the cone where the particles can go and be detected,” said Zhenyu Ye, a STAR collaborator from the University of Illinois, Chicago. Ye led the design and construction of the new silicon-based particle-tracking components installed at the forward end of STAR, working with scientists from National Cheng Kung University in Tainan and Shandong University in Qingdao.
These components give scientists the ability to detect particles emerging almost in line with the colliding beams, including jets of particles that reveal information about the colliding quarks’ energy, direction, and spin.
“This information is essential for mapping the 3D arrangement of the proton’s inner building blocks,” said Chi Yang from Shandong University. Yang worked with colleagues from the University of Science and Technology of China and Brookhaven Lab to build additional subdetector systems for the forward tracking detector.
“These upgrades cover exactly the angles where jets would go in the EIC,” said Brookhaven Lab physicist Prashanth Shanmuganathan. So, in addition to increasing the data set for exploring the color charge interactions, “Run 22 will help us learn about the detector technology and the behavior of nucleon structure so we can apply that knowledge to the EIC.”
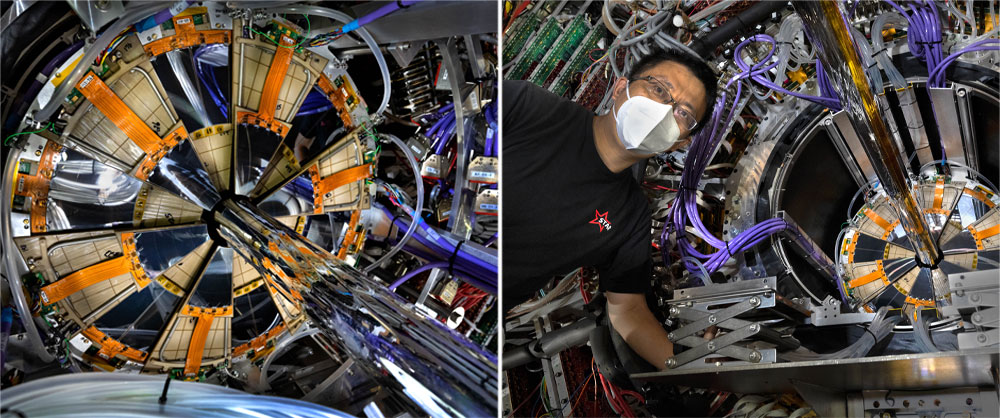 enlarge
enlarge
Left: One plane of three silicon tracker detector modules installed around the beampipe at one end of the STAR detector. The shiny mirrorlike wedges, arrayed in alternating "inner" and "outer" positions, form a ring around the beampipe, with each sector connected to readout electronics. Right: Zhenyu Ye inspects the silicon tracker after insertion into the STAR Time Projection Chamber (TPC), where it will operate closer to the point where particles collide. Violet tubes encase signal readout cables while clear tubes carry a cooling fluid to the detector.
Cooling protons
Interspersed with delivering proton-proton collisions for STAR’s Run 22 measurements, the C-AD team will also spend the equivalent of two weeks’ time testing a technique for keeping high-energy protons tightly packed.
You’ll recall that keeping particles packed is important for maximizing collision rates and maintaining polarization. But particle spreading, or heating up, is a problem for all accelerated ion beams—from protons to uranium nuclei (the heaviest ions that have been collided at RHIC).
“There’s no natural shrinking of these ion beams; they never get denser by accident,” Schoefer said.
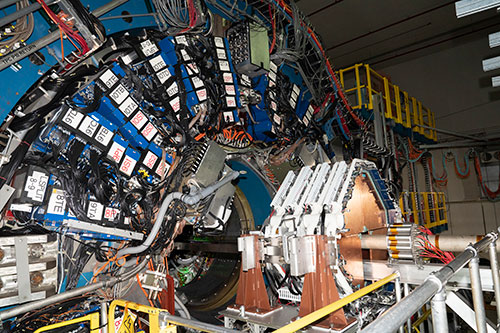 enlarge
enlarge
This view of STAR shows the endcap calorimeter electronics (blue with black cables) and four new planes of small-strip Thin Gap Chambers (copper colored with white at edges).
So RHIC accelerator physicists have developed a variety of successful techniques to keep ion beams “cool.” Some of these cooling methods involve delivering “kicks” to push particles closer together, while others literally use cool beams of other particles (electrons) to extract heat from circulating ions.
Realizing that different cooling techniques work best for different types of particles at different energies, physicists are exploring several strategies for possible use at the EIC. In Run 22 they’ll test something called “coherent electron cooling” (CeC) on high energy polarized protons.
Instead of just being cool in temperature, as described above, the negatively charged electrons in CeC play a more active role: They clump around each positively charged proton to create a “mold” of the proton beam.
“It's a little bit like getting braces when the orthodontist takes a mold of your teeth,” Schoefer said. “We take a mold of the proton beam and then we adjust the electron beam slightly to attract the protons closer to a central position. As the electrons move, their electrical attraction drags the protons with them.”
In 36-hour stints, the C-AD physicists will test and try to fine-tune the technique.
Measuring ion polarization
In addition, every two weeks during Run 22, the C-AD team will stop proton acceleration for 12- to 16-hour stretches of accelerator R&D experiments. For one of these projects, they’ll ramp up beams of Helium-3 ions to work on methods for measuring the polarization of particles other than protons.
“In RHIC, the only polarized species we’ve ever had is polarized protons. But EIC will do experiments with polarized ions such as Helium-3. That’s an entirely different beast,” Schoefer said.
 enlarge
enlarge
Felix Archampong, Robert Soja, William Struble, and Rahul Sharma of the STAR technical support group completed the mechanical design, construction, and installation of the small-strip Thin Gap Chambers—shown here in position for collecting data—with support from the STAR electronic support group.
The C-AD team worked in collaboration with members of the “Cold-QCD” group in the Physics Department to design ways to measure the polarization of these more complicated ions.
To measure polarization, physicists spray a gas through the beam to act as a target, and measure how the particles in the beam scatter.
“For a proton, that’s already a challenge, but at least the proton stays a proton. When Helium-3 scatters off a target, it may break up into two protons and a neutron, or a proton and a deuteron. To accurately measure the polarization, we have to identify when breakup occurs,” said William Schmidke, a scientist in the physics department who’s been developing polarimetry detectors to make the measurements.
During Run 22, physicists will test the components’ ability to accurately characterize scattering products using unpolarized beams of Helium-3.
“We can do these tests, without measuring polarization, to develop the methods so we’ll be able to measure polarization when we eventually have polarized beams at the EIC,” said Brookhaven physicist Oleg Eyser, another member of the Cold-QCD team.
“Many people made important contributions to the detector and accelerator components needed for Run 22 at RHIC. We are looking forward to the exciting opportunities for physics discoveries and for advancing the technologies and physics analysis methods we will need for the EIC,” said Haiyan Gao, Brookhaven’s Associate Laboratory Director for Nuclear and Particle Physics.
Brookhaven National Laboratory is supported by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit science.energy.gov.
https://www.bnl.gov/newsroom/news.php?a=119262 




 Flip
Flip